TAG: GS: 2- INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATION
CONTEXT: Recently, the UN panel has formed a panel specifically focused on critical energy transition minerals. These critical minerals are generally found in the underdeveloped nations, such as African nations. The heavy demand for these minerals is leading to emerging concerns of resource nationalism and environmental destruction.
EXPLANATION:
About the UN Panel:
- The Panel of External Auditors of the United Nations, the Specialized Agencies and the International Atomic Energy Agency was established by the General Assembly Resolution 1438 (XIV) of 5 December 1959.
The Key Facts About the UN Panel on Critical Energy Transition Minerals:
- The panel will address issues relating to equity, transparency, investment, sustainability, and human rights in the context of critical minerals for renewable energy technologies.
- Developing countries see critical minerals as an opportunity to create jobs, diversify economies, and boost revenues, but proper management is essential to avoid trampling over the poor.
- The panel’s objective is aligned with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the United Nations Framework Agreement on Climate Change, and its Paris Agreement to harness the potential of critical minerals for shared prosperity and leaving no one behind.
- The panel utilises past UN efforts, especially the Working Group on Sustainable Extractive Industries and its ‘Harnessing Critical Energy Transition Minerals for Sustainable Development’ initiative.
- It will help to develop principles to ensure a fair and transparent approach globally and for local communities in the entire value chain upholding the highest sustainability and human development standards.
- The goal of combating climate change and limiting global warming to 1.5°C hinges on a secure and accessible supply of critical energy transition minerals.
The global shift towards renewable energy to mitigate carbon emissions has increased the demand for critical minerals. Recent projections have suggested a threefold increase by 2030.
What are Critical Minerals?
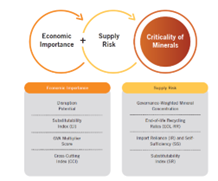
- Critical Minerals:
- These are those minerals that are essential for economic development and national security, the lack of availability of these minerals or concentration of extraction or processing in a few geographical locations may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and even disruption of supplies.
-
- These minerals, such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements, are essential components of clean energy technologies like wind turbines, solar panels, electric vehicles, and battery storage, which are crucial for powering a sustainable future.
Critical Minerals for India:
-
- Expert Committee under Ministry of Mines has identified a set of 30 critical minerals for India.
- These are Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, Rare Earth Elements (REEs), Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
- The creation of Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals (CECM) in the Ministry of Mines is also recommended by the Committee.
- CECM will periodically update the list of critical mineralsfor India and notify the critical mineral strategy from time to time.
Source:
Spread the Word
