TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: The recent massive earthquake in Taiwan highlights the vulnerability of regions along the Pacific “Ring of Fire” to seismic activity.
EXPLANATION:
- This geological phenomenon, characterized by a string of volcanoes and earthquake-prone sites, plays a significant role in shaping the Earth’s landscape and poses risks to human populations in affected areas.
Defining the Ring of Fire:
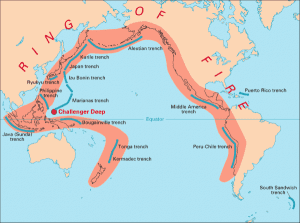
- The Ring of Fire is essentially a string of hundreds of volcanoes and earthquake-sites which runs along the Pacific Ocean.
- It is a semicircle or horse shoe in shape and stretches nearly 40,250 kilometres.
- The Ring of Fire traces the meeting points of numerous tectonic plates, including the Eurasian, North American, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Caribbean, Nazca, Antarctic, Indian, Australian, Philippine, and other smaller plates, which all encircle the large Pacific Plate, according to a report by National Geographic.
- It runs through 15 more countries including the USA, Indonesia, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Chile, Peru, and the Philippines.
Geological Significance:
- The Ring of Fire serves as a hotspot for tectonic plate interactions, making it one of the most seismically active regions on Earth.
- The convergence, divergence, and subduction of tectonic plates generate immense geological pressure, leading to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- This constant movement and interaction of plates create a dynamic and volatile environment along the Ring of Fire.
Causes of Earthquakes in the Ring of Fire:
- The high frequency of earthquakes along the Ring of Fire is primarily attributed to the movement of tectonic plates.
- As these plates slide past, collide with, or move beneath one another, they create friction and stress along their boundaries.
- When the accumulated stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, it results in sudden movements known as earthquakes.
- The rugged edges of tectonic plates often become locked together, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves when they eventually slip or rupture.
Impact on Taiwan:
- Taiwan, situated along the western edge of the Pacific Ring of Fire, experiences frequent seismic activity due to its location between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate.
- The collision and subduction of these plates contribute to the formation of earthquakes, posing significant risks to the island’s population and infrastructure.
- The recent earthquake in Taiwan underscores the ongoing threat posed by geological hazards in the region.
Role of Volcanoes in the Ring of Fire:
- The presence of numerous volcanoes along the Ring of Fire is closely linked to the process of subduction, where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another.
- Subduction zones, prevalent in the Ring of Fire, create conditions conducive to volcanic activity by melting crustal rocks and generating magma.
- The magma, rising to the surface, forms volcanic eruptions, contributing to the formation of new landforms and geological features.

