Polity
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
-
- The constitutional basis of ADR in India is enshrined in Article 39A, which mandates the state to provide equal justice and free legal aid.
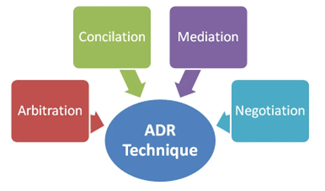
- Various ADR processes, such as arbitration, conciliation, mediation, and judicial settlement (Lok Adalat), are recognised under Section 89 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- An ADR mechanism is a method of resolving conflicts outside of a formal court trial.
- Common types include:
i) Mediation: A neutral third party (a mediator) helps the parties communicate, understand each other’s perspectives, and work towards a mutually acceptable, voluntary agreement.
ii) Arbitration: An independent third party (an arbitrator) hears evidence and arguments from both sides and decides (an arbitral award) that is typically binding and final.
iii) Conciliation: A third party (a conciliator) actively works with the parties to find common ground and a mutually agreeable solution, much like mediation but with a more proactive role in proposing terms.
iv) Negotiation: The parties themselves directly communicate and negotiate to resolve their differences without the assistance of a third party.
-
- ADR is generally less formal, faster, and less expensive than litigation, offering a less stressful path to resolution.
(TH)
Lok Adalats:
-
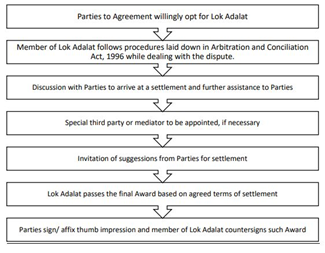
- Lok Adalats are governed by the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, inspired by Article 39A.
- Apart from Permanent Lok Adalat (Section 22-B of the Act), provisions of the National Lok Adalat and e-Lok Adalat are directly helpful in strengthening the justice system.
- The first Lok Adalat in India was organised in Gujarat in 1999.
- Their decisions shall be final and there is no possibility of appeal.
- Lok Adalats handle various disputes, such as family disputes, matrimonial cases, and criminal compoundable offenses, resolving them through mutual consent.
- Unlike regular Lok Adalats, Permanent Lok Adalats have the power to decide a dispute if the parties fail to reach a settlement, and their award is binding and final.
(TH)
Habeas corpus:
-
- Context: A habeas corpus petition filed by climate activist Sonam Wangchuk’s wife in SC.
- Habeas Corpus is a Latin term meaning “you shall have the body,” and it is a legal writ used to challenge the legality of a person’s detention or imprisonment by requiring the detaining authority to bring the detainee before a court to examine if the detention is lawful.
- It acts as a crucial safeguard against arbitrary and unlawful detention by the government or other authorities, ensuring individuals have the right to personal liberty and protection from illegal confinement.
- It is a fundamental legal remedy. It is a guaranteed right that can only be suspended under exceptional conditions like war, rebellion, or invasion.
- Supreme Court and High Courts have the authority to issue habeas corpus petitions under Article 32 and Article 226 respectively, allowing courts to order the release of a person unlawfully detained.
- Habeas Corpus proceedings do not determine guilt or innocence but only examine whether the detention has legal justification.
- It can be filed by the detained person, relatives, friends, or any public-spirited individual or organization on behalf of the detainee, against police authorities, government officials, or even private individuals in cases of unlawful confinement.
(TH)
International Day of Older Persons:
-
- Department of Social Justice & Empowerment is celebrating the International Day of Older Persons 2025 on October 6, 2025, at Manas Bhavan, Jabalpur in collaboration with the Cantonment Board (Ministry of Defence) and Madhya Pradesh State Government.
- The event represents a partnership between Central and State governments to showcase efforts toward building an inclusive society for senior citizens.
- The celebration demonstrates the government’s commitment to promoting the welfare and dignity of older persons in India.
(PIB)
Defence News
Exercise KONKAN-25:
-
- It is an annual bilateral maritime exercise conducted between the Indian Navy and the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom, aimed at strengthening interoperability, joint maritime operations, and mutual understanding between the two navies.
- The exercise in 2025 commenced on October 5 and will be conducted in two phases until October 12, off the western coast of India.
- This exercise exemplifies the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership under India-UK Vision 2035, reaffirming the shared commitment to secure, open, and free seas and enhancing regional maritime stability.
- It marks the first time both navies have deployed full carrier strike groups together, highlighting the growth in scale, complexity, and strategic importance of the exercise over the past two decades.
- Major assets deployed include the UK Carrier Strike Group led by HMS Prince of Wales (along with Norway and Japan), and the Indian carrier battle group led by INS Vikrant.

(TH)
10th Edition of NATPOLREX and 27th NOSDCP Meeting:
-
- The Indian Coast Guard is conducting the 10th National Level Pollution Response Exercise (NATPOLREX-X) along with the 27th National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP) meeting off the coast of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- Over 100 national delegates and more than 40 foreign observers from 32 countries are participating, reflecting the exercise’s growing international significance in marine pollution response.
- The two-day event will see active participation from central ministries, coastal state governments, major ports, oil handling agencies, and maritime organizations.
- It aims to evaluate and enhance India’s preparedness for marine oil spill incidents and test inter-agency coordination under the NOSDCP framework.
- The Coast Guard is deploying ships, aircraft, and pollution control assets to demonstrate its multi-tiered response and showcase operational capabilities.
- The exercise reaffirms India’s commitment to marine environmental protection, inter-agency collaboration, best practices in pollution response, and sustainable development.
(PIB)
Commissioning of Androth:
-
- The Indian Navy is set to commission ‘Androth,’ the second Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC), at Visakhapatnam on 6 October 2025, further boosting its ASW capabilities.
- Androth, built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, features over 80% indigenous content and represents India’s strides toward maritime self-reliance and technological innovation.
- The ship will enhance security in littoral waters and is part of a recent wave of state-of-the-art indigenous warship inductions, including Arnala, Nistar, Udaygiri, and Nilgiri.
- This commissioning embodies the Navy’s focus on indigenisation, capability enhancement, and its commitment to the Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision.
(TH)
Science & Technology
Ram air turbine (RAT):
-
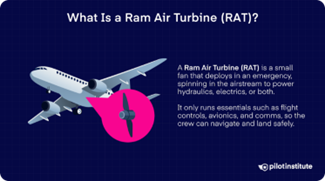
- Context: Recently, the operating crew of Air India’s Amritsar-Birmingham flight reported that the Boeing 787’s ram air turbine (RAT) unexpectedly deployed during the final approach, but the aircraft landed safely.
- RAT deploys automatically in the eventuality of a dual engine failure or total electronic or hydraulic failure.
- It uses wind speed to generate emergency power.
- It operates by deploying into the airstream, where the flow of air spins the turbine blades, generating energy either for vital flight controls, avionics, or other critical systems needed for safe aircraft operation and landing.
- Deploying a RAT increases aerodynamic drag and shortens the aircraft’s glide range, so it supplies power only to vital systems and not to nonessential amenities.
(TH)
Small modular reactors (SMRs):
-
- Context: The Indian government has eased nuclear power sector restrictions to encourage private participation in building small modular reactors (SMRs).
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with an output of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, designed to be physically much smaller than conventional nuclear reactors and to enable factory fabrication and modular installation at power sites.
- SMRs use nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity, and their modular nature allows for scalable power generation by adding multiple reactor units as needed.
- SMRs use nuclear fission to generate low-carbon electricity and often feature advanced passive safety systems that minimize risk and core damage frequency.
(IE)
Geography & Environment
Torsa river:
-
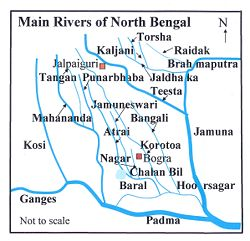
- Context: Incessant rainfall triggered by a low-pressure system over the Bay of Bengal caused the Torsa river to overflow, inundating vast areas across West Bengal and Bhutan.
- It originates from the Chumbi Valley in Tibet, where it is known as Machu or Kambu Maqu. It flows through Bhutan (where it is called Amo Chu), India, and Bangladesh before joining the Brahmaputra River.
- In India, it flows through the northern part of West Bengal, passing important towns like Jaigaon, Hasimara, and Cooch Behar, and through the Jaldapara National Park region known for its wildlife.
- It has several tributaries and distributaries like the Ghargharia River and Buri Torsa, and eventually it merges with the Brahmaputra River in Bangladesh under the name
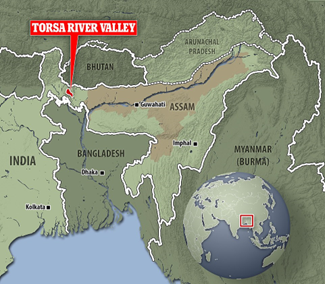
(TH)
Coral Triangle:
-
- The Coral Triangle is a marine region in Southeast Asia and the western Pacific, encompassing the waters of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste, and the Solomon Islands, and sometimes including Singapore and Brunei.
- It covers an estimated area of 7 to 6 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest and most biologically diverse marine areas globally, often described as the “Amazon of the seas”.
- It contains over 600 species of reef-building corals (about three-quarters of global coral species), more than 2,200 species of coral reef fish, six of seven species of marine turtles, vast mangrove forests, and is a major nursery for tuna and other commercially important marine life.
- The region supports the food security and livelihoods of more than 120 million people.
- Its fisheries and tourism industries generate billions of dollars annually.
- It is recognized as a global hotspot for marine biodiversity and a high-priority conservation area, but it faces significant threats from climate change, coral bleaching, pollution, destructive fishing practices, and habitat loss.
- Conservation efforts such as the Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI) promote regional cooperation and sustainable management to protect habitat and biodiversity, support local communities, and mitigate environmental threats.
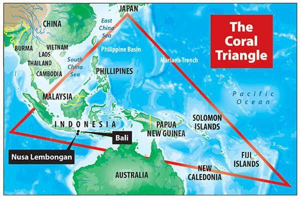
(TH)
Coral larvae cryobank:
-
- A coral larvae cryobank is a facility that preserves coral larvae at ultra-low temperatures (typically -196°C in liquid nitrogen) to safeguard genetic diversity and support future reef restoration efforts beyond the brief annual spawning window.
- The process involves using cryoprotectants and advanced techniques like vitrification and laser warming to prevent ice crystal formation, which can damage the lipid-rich cells of coral larvae during freezing and thawing.
- In 2022, researchers successfully froze and reanimated Great Barrier Reef coral larvae for the first time.
- Philippines is establishing the Coral Triangle’s first regional coral larvae cryobank network in collaboration with Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, focusing initially on fast-growing pocilloporid corals to accelerate reef recovery despite climate stress.
- These cryobanks are part of larger global initiatives like the Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program (RRAP) and Coral Research & Development Accelerator Platform (CORDAP).
- RRAP is an initiative launched by the Australian Government.
- CORDAP is an initiative launched byG20 nations.
(TH)
First Commercial Coal Mine in Arunachal Pradesh:
-
- Arunachal Pradesh launched its first commercial coal mine at the Namchik-Namphuk coal block on 6 October 2025.
- The coal block has reserves of 1.5 crore tonnes and is expected to generate over ₹100 crore annually for the state, creating local jobs, prosperity, and supporting Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Mining operations emphasize transparency, accountability, and ecological responsibility, including a commitment to land reclamation and sustainable development under Mission Green Coal Regions.
- Critical minerals are being unlocked for the first time for technology and security, and enhanced worker benefits and safety packages are introduced as part of welfare measures.
- The initiative aligns with over ₹6 lakh crore investment in the Northeast since 2014, with a focus on connectivity, economic transformation, sustainable development, and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
(PIB)
Terms in the News
Xenobiology:
-
- Xenobiology (XB) is a subfield of synthetic biology focused on creating and studying biological systems that differ fundamentally from natural life, often using non-natural biochemical components such as xeno nucleic acids (XNA) instead of DNA or RNA.
- The term “xenobiology” comes from the Greek xenos, meaning “stranger” or “alien,” reflecting its goal of creating life forms that are biochemically “alien” to Earth’s natural biosphere.
- It aims to engineer organisms with expanded or altered genetic codes, including the use of unnatural base pairs and non-canonical amino acids, to build life forms with novel functions and properties not found in nature.
- A major application of xenobiology is biocontainment, designing synthetic organisms that cannot exchange genetic material with natural life, thus preventing genetic pollution and enhancing biosafety.
- It holds potential for industrial biotechnology, medicine, and origin-of-life research.
(TH)
Xeno nucleic acids (XNAs):
-
- Xeno nucleic acids (XNAs) are synthetic, artificial nucleic acids with chemically altered sugar-phosphate backbones, making them different from natural DNA and RNA.
(TH)
Captions and Quotations
Economy:
-
- Employment generation is critical for equity and inclusion.
(TH)
Facts and Data
Polity:
-
- According to the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG), the total number of pending cases in India is 4,57,96,239. In the Supreme Court, the number of pending cases is 81,768, and in the High Courts, it is approximately 62.9 lakh.
(TH)
Government Schemes
PM-SETU:
-
- PM felicitated All India ITI toppers and presided over the 4th National Skill Convocation at Vigyan Bhawan, highlighting the significance of skill development for youth empowerment.
- PM-SETU (Pradhan Mantri Skilling and Employability Transformation through Upgraded ITIs) was launched. It is a ₹60,000 crore scheme to modernize 1,000 Government ITIs using a hub-and-spoke model.
- It is aiming to build model skill ecosystems with advanced infrastructure, innovation, incubation, and industry-led training.
- PM also inaugurated 1,200 Vocational Skill Labs in Navodaya Vidyalayas and Eklavya Model Residential Schools nationwide to provide early, hands-on industry-oriented training to school students in 12 sectors.
- These initiatives are aligned with NEP 2020 to build a future-ready talent pool, and reaffirm the Government’s commitment to transforming India into a skill-based, globally competitive economy, contributing to Viksit Bharat @2047.
- PM said, “ITIs are not only premier institutions of industrial education, they are also the workshops of an Atmanirbhar Bharat.”
(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Consider the following statements about Xenobiology (XB):
1. It involves the use of xeno nucleic acids (XNA) to create biological systems with biochemical properties distinct from natural life.
2. Its primary aim is to design organisms that can freely exchange genetic material with natural ecosystems.
3. It has potential applications in biocontainment, preventing genetic pollution by limiting horizontal gene transfer.
4. Xenobiology focuses exclusively on studying extraterrestrial life forms discovered in outer space.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Xenobiology involves engineering biological systems using non-natural components like xeno nucleic acids (XNA), which differ from DNA/RNA.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Because xenobiology aims to prevent, not enable, genetic exchange with natural organisms.
Statement 3 is correct: A key goal is biocontainment, ensuring synthetic organisms cannot genetically interact with natural life, thus enhancing biosafety.
Statement 4 is incorrect: While the term may evoke ideas of alien life, xenobiology in practice refers to synthetically created life forms on Earth, not the study of extraterrestrial life.
Q2. Consider the following statements about the Coral Triangle:
1. It hosts over 75% of the world’s coral species and more than half of the global coral reef fish species.
2. The Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI) is a multilateral partnership among six countries—Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste, and the Solomon Islands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Because while the Coral Triangle hosts over 75% of the world’s coral species (approximately 76%, or 605 out of 798 species), it does not contain more than half of the world’s coral reef fish species. It has 37% (about 2,228 species) of the world’s coral reef fish, not over 50%. However, it is indeed a major spawning and nursery area for tuna, which is accurate.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI) is a multilateral partnership launched in 2009 by the six aforementioned countries to promote regional cooperation in marine conservation, sustainable use of marine resources, and climate resilience.
Q3. Consider the following statements about the Torsa River:
1. It originates in the Chumbi Valley of Tibet, and flows through Bhutan, India, and Bangladesh before merging with the Brahmaputra River.
2. In India, the river flows through the state of Assam and is a major tributary of the Barak River, which later joins the Meghna in Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: The Torsa River originates in the Chumbi Valley in Tibet, where it is known as Machu or Kambu Maqu. It flows through Bhutan (as Amo Chu), enters India through West Bengal (not Assam), and continues into Bangladesh, where it eventually merges with the Brahmaputra River (known as the Jamuna there) under the name Kaljani.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Torsa River does not flow through Assam nor is it a tributary of the Barak River. It flows through West Bengal, passing towns like Jaigaon, Hasimara, and Cooch Behar, and through the Jaldapara National Park region. The Barak River is a separate system that flows through Manipur, Nagaland, and Assam, and is unrelated to the Torsa.
Q4. Consider the following statements about coral larvae cryobanks and associated initiatives:
1. Coral larvae cryobanks use techniques like vitrification and laser warming to preserve larvae.
2. Philippines, Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, is establishing the Coral Triangle’s first regional coral larvae cryobank network.
3. The Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program (RRAP) is supported by Australia.
4. CORDAP is a global initiative launched by the G20 nations to accelerate coral reef research.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: D
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: Coral larvae cryobanks preserve larvae at ultra-low temperatures using cryoprotectants, vitrification, and laser warming to prevent ice crystal damage, especially in lipid-rich cells, allowing year-round use for reef restoration.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Philippines, through UP MSI, is setting up the first regional coral larvae cryobank network in the Coral Triangle with partners including Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, supported by CORDAP.
- Statement 3 is correct: RRAP is an Australian Government-supported program that includes coral cryopreservation as a core strategy for large-scale reef restoration.
- Statement 4 is correct: CORDAP was launched by the G20 nations to promote global collaboration in coral research and development, particularly for climate adaptation.
Q5. Consider the following statements regarding the Ram Air Turbine (RAT) in aircraft:
1. The RAT is an emergency power source that automatically deploys during dual engine failure.
2. The RAT generates power using wind flow due to the aircraft’s forward motion, and it can operate even without battery or engine power, as it is mechanically driven by ram air.
3. Once deployed, the RAT can be retracted in flight if primary power is restored, allowing the aircraft to resume normal operations without landing.
4. Deployment of the RAT increases aerodynamic drag, which reduces the aircraft’s glide range and performance.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 1, 2 and 4 only
c) 2, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: The RAT is designed to deploy automatically (or manually) during catastrophic failures such as dual engine shutdown or loss of primary electrical/hydraulic systems. It powers critical systems like flight controls and essential instruments to enable safe landing.
- Statement 2 is correct: The RAT operates purely on ram air—the airflow generated by the aircraft’s speed. It does not require external power to deploy or function and drives a hydraulic pump or generator mechanically.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Once deployed in flight, the RAT cannot be retracted mid-air in most modern aircraft. It remains extended until the aircraft lands and maintenance personnel stow it on the ground. This makes uncommanded deployment a serious incident, as it increases drag unnecessarily.
- Statement 4 is correct: RAT deployment creates significant aerodynamic drag, reducing glide efficiency and fuel efficiency. Hence, it powers only essential systems like flight controls and core avionics, not non-critical amenities.
Q6. Consider the following statements regarding Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) and Lok Adalats in India:
1. Article 39A of the Indian Constitution provides the constitutional foundation for ADR by mandating the State to ensure equal justice and free legal aid.
2. Section 89 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, empowers courts to refer pending disputes to arbitration, mediation, conciliation, or Lok Adalat.
3. Awards passed by Lok Adalats are final and binding, and no appeal lies against them.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
Explanation:
-
- Statement 1 is correct: Article 39A of the Constitution, a Directive Principle of State Policy, directs the State to ensure equal access to justice and provide free legal aid to prevent the denial of justice due to economic or other disabilities. This provision forms the constitutional basis for promoting ADR mechanisms as tools for inclusive and accessible justice.
- Statement 2 is correct: Section 89 of the CPC, introduced by the 1999 amendment, enables courts to refer disputes to ADR methods like arbitration, conciliation, mediation, or judicial settlement (including Lok Adalat) once the issues are framed, thereby formalizing and encouraging settlement outside adversarial litigation.
- Statement 3 is correct: Lok Adalat awards are deemed to be civil court decrees under Section 21 of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, and are final and non-appealable. However, if a party is dissatisfied and no settlement is reached, they may initiate a fresh suit in the appropriate court, as the compromise is based on mutual consent.
Q7. Consider the following statements regarding the habeas corpus:
1. It is a legal writ used to challenge the legality of a person’s detention, requiring the detainee to be presented before the court.
2. The Supreme Court can issue Habeas Corpus under Article 32 of the Constitution, and High Courts under Article 226.
3. Habeas Corpus proceedings determine the guilt or innocence of the detained person.
4. Habeas Corpus is suspended only under exceptional circumstances such as war, rebellion, or invasion.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 1, 2 and 4 only
c) 2, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
Habeas Corpus ensures protection against unlawful detention and can be issued by the Supreme Court (Article 32) or High Courts (Article 226). It does not determine guilt or innocence but only examines the legality of detention. The remedy can be suspended only in exceptional circumstances, such as a proclamation of emergency.




