Art and Culture
Tribal Village Vision 2030 Declaration:
-
- India declared 15 Nov 2024 to 15 Nov 2025 as Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh, celebrating tribal heritage.
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs launched Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan, the world’s largest tribal grassroots leadership program, reaching 11 crore people in 1 lakh tribal villages across 30 states/UTs.
- Key highlights of Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan
i) 20 Lakh Trained Change-Makers – officials, SHG women & youth
ii) 1 Lakh Villages, 1 Vision – formal adoption of Tribal Village Vision 2030
iii) 1 Lakh Adi Sewa Kendras – single-window citizen service centres with weekly Adi Sewa Hour
iv) Village-led Grievance Redressal – timely resolution of issues and scheme coverage
-
- On 2 October 2025, 1 lakh tribal villages will hold Special Gram Sabhas to adopt the Tribal Village Vision 2030 Declaration, promoting participatory governance and local leadership.
- Each village will establish an Adi Sewa Kendra as a single-window citizen service center for voluntary service and connectivity via the AI-enabled Adi Vaani App for communication with government officers.
- Since July 2025, 20 lakh officials, women SHG members, and tribal youth have been trained as Adi Karmayogis for grassroots leadership and governance.
- The initiative aims to empower tribal communities as co-creators of development, strengthening accountability and contributing to the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047.
(PIB)
Economy
Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses:
-
- Union Cabinet approved the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses, aiming for self-sufficiency in pulses with a financial outlay of ₹11,440 crore over 2025–26 to 2030–31.
- The mission targets increasing pulses production to 350 lakh tonnes and expanding cultivation to 310 lakh hectares by 2030–31.
- Strategies include research on high-yield, pest-resistant, and climate-resilient varieties, large-scale certified seed distribution, and expansion into rice fallow and diversifiable areas.
- Around 126 lakh quintals of certified seeds and 88 lakh free seed kits will be distributed, and 1000 processing units will be set up with subsidies available for infrastructure development.
- A major feature of the Mission will be assured maximum procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masoor under Price Support Scheme (PSS) of PM-AASHA. NAFED and NCCF will undertake 100% procurement in participating states for the next four years from farmers who register with these agencies and enter into agreements.
- Environmental benefits include promotion of climate-resilient agriculture, improved soil health, and enhanced use of fallow crop areas.
(PIB)
Geography & Environment
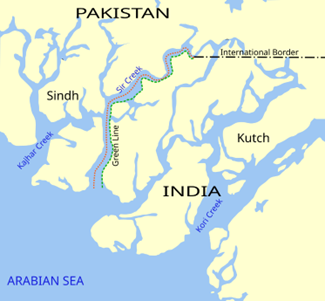
Sir Creek:
-
- Sir Creek is a 96-kilometer tidal estuary located in the marshlands of the Rann of Kutch, forming the boundary between India’s Gujarat state and Pakistan’s Sindh province.
- The area is largely uninhabited and marshy, with significant tidal changes affecting its geography.
- The Sir Creek dispute between India and Pakistan arises from differing interpretations of the maritime boundary, with implications for maritime rights, Exclusive Economic Zones, and access to natural resources like oil and gas.
- Pakistan claims the entire creek based on a 1914 resolution placing the boundary on the eastern bank, while India claims the boundary lies along the mid-channel according to a 1925 map and the internationally recognized Thalweg principle.
- The dispute remains unresolved despite multiple talks since the 1968 Tribunal Award that settled other parts of the Rann of Kutch boundary.
- Control over Sir Creek impacts strategic military positioning, fishing rights, and economic zones in the Arabian Sea.
(TH)
Defence News
UNTCC Chiefs’ Conclave 2025 hosted by the Indian Army in New Delhi:
-
- The Indian Army will host the United Nations Troop Contributing Countries’ (UNTCC) Chiefs Conclave from 14–16 October 2025 in New Delhi, with over 30 major troop-contributing nations participating.
- The event provides a high-level platform for sharing best practices, fostering cooperation, and planning future approaches in UN peacekeeping.
- India reaffirms its status as one of the largest and most consistent contributors to UN missions, emphasizing operational experience, innovations, and commitment to global stability.
- Discussions will aim to enhance collective preparedness and partnerships to meet contemporary peacekeeping challenges.
- The Conclave reflects India’s ethos of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (“the world is one family”) and its proactive approach to shaping international peacekeeping.
(PIB)
INS SUTLEJ:
-
- INS Sutlej arrived at Port Louis for the 18th Joint Hydrographic Survey Mission with Mauritius on 29 September 2025.
- The mission, under a bilateral MoU, will survey about 35,000 square nautical miles.
- Mauritian officials will receive hands-on training in hydrographic data collection and processing as part of capacity-building.
- The deployment highlights advanced scientific collaboration, deep maritime cooperation, and shared commitment to navigational safety and sustainable ocean resource management in the Indian Ocean Region.
- INS Sutlej (J17) is a hydrographic survey ship in the Indian Navy, under the Southern Naval Command. Like other ships of the Sandhayak class, the ship is equipped with an Operating Theater and necessary equipment to attend to medical emergencies at sea.

(PIB)
INDIAN NAVY DEMONSTRATES GLOBAL SUBMARINE RESCUE CAPABILITY AT EXERCISE PACIFIC REACH (XPR-25):
-
- The Indian Navy’s Submarine Rescue Unit (East), on INS Nistar, participated in Exercise XPR-25 hosted by the Republic of Singapore Navy, along with over 40 nations, from 15–25 September 2025.
- The unit successfully conducted three matings with international submarines, marking the first-ever Indian Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV) operation outside the Indian Ocean Region, including rescue with ROK Navy and Singapore Navy submarine.
- The sea phase saw a historic first—an R3 (three-asset) multinational coordinated submarine rescue led by INS Nistar, highlighting rapid and successful international collaboration.
- India presented its DSRV system philosophy and post-rescue medical capabilities during the shore phase, reinforcing its growing role in global submarine rescue operations.
- The exercise showcased India’s operational proficiency, international interoperability, and commitment to submarine safety.
(PIB)
Government Schemes/Initiatives
Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0:
-
- The Anganwadi Services [earlier known as Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) launched in 1975] has now been revised and subsumed under ‘Mission Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0 (Mission Poshan 2.0)’.
- It is an integrated nutrition support program combating malnutrition among children (0-6 years), adolescent girls (14-18 years), pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- The scheme merges Anganwadi Services, Poshan Abhiyan, and the Scheme for Adolescent Girls under a comprehensive framework running from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Focus is on improving nutrition content and delivery through upgraded Anganwadi centers called Saksham Anganwadis, fostering a convergent ecosystem promoting health, wellness, and immunity.
- Key components include supplementary nutrition with fortified food, early childhood care and education, capacity building, and ICT-based real-time monitoring via the Poshan Tracker.
- Poshan 2.0 prioritizes maternal nutrition, infant and young child feeding guidelines, treatment of moderate and severe acute malnutrition, and wellness practices including AYUSH interventions.
- The mission aims to reduce malnutrition indicators such as stunting, wasting, underweight, and anemia, promoting healthier growth and development outcomes across the country.
(TH)
Captions and Quotations
-
- “Non-violence is the greatest force at the disposal of mankind. It is mightier than the mightiest weapon of destruction devised by the ingenuity of man,” – Mahatma Gandhi.
Facts and Data
1. NCRB Report ‘Crime in India for 2023’ –
-
- Crime against children: A total of 1,77,335 cases of crime against children were registered across the country in 2023, showing an increase of 9.2% as compared to the previous year.
- In percentage terms, major crime heads in 2023 were kidnapping and abduction of children (79,884 cases or 45%) and Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act (67,694 cases or 38.2%).
2. Crimes against Scheduled Tribes (STs): Crimes against STs increased 28.8% in 2023, with 12,960 cases registered.
-
- Manipur, which has been grappling with ethnic violence between the Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities since May 2023, emerged as the worst-affected state. “Madhya Pradesh reported the second-highest number of crimes against STs with 2,858 cases, next was Rajasthan with 2,453 cases in 2023,” the report said.
3. Crime against Scheduled Castes (SCs): There were 57,789 cases registered in 2023 for crimes against SCs, with Uttar Pradesh accounting for the highest share at 15,130 cases. Rajasthan recorded the second-highest number at 8,449, followed by Madhya Pradesh (8,232) and Bihar (7,064).
4. Cybercrime: Cybercrime in India saw a sharp surge in 2023, with fraud, extortion and sexual exploitation accounting for the majority of cases. The crime rate, which is the number of crimes per lakh population, increased from 4.8 in 2022 to 6.2 in 2023.
-
- “Defrauding gullible victims was a primary motive of the cyber criminals, with 68.9% of them driven by the desire to scam their victims in 59,526 such cases”, the report said.
- The rise in cases under the cybercrime category has been steady — from 27,248 in 2018, 44,735 in 2019, 50,035 cases in 2020, 52,974 in 2021 and 65,893 in 2022. Karnataka, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh saw the most cases.
5. Crime against women: A total of 4,48,211 cases of crime against women were registered, marking an increase of 0.7%. The national crime rate stood at 66.2 incidents per lakh female population.
6. E-waste: India generated 2.2 million tonnes (MT) of e-waste in 2025, making it the third-largest e-waste generator globally, after China and the United States.
-
- This figure represents a 150% surge from the 0.71 million tonnes recorded in 2017–18. At current growth rates, India’s e-waste volume is expected to nearly double by 2030.
- Urban India is the epicentre of this explosion. More than 60% of e-waste originates from just 65 cities, with key hotspots including Seelampur and Mustafabad (Delhi), Moradabad (Uttar Pradesh), and Bhiwandi (Maharashtra).
- Despite the existence of 322 registered formal recycling units with a combined capacity to treat over 2.2 million metric tonnes annually, more than half of the country’s e-waste is still processed informally or not at all.
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Consider the following statements regarding the Sir Creek dispute between India and Pakistan:
1. The dispute arises due to different interpretations of the boundary alignment in the Rann of Kutch region, with implications for Exclusive Economic Zones in the Arabian Sea.
2. Pakistan bases its claim on the internationally recognized Thalweg principle, whereas India asserts that the boundary lies along the eastern bank of Sir Creek.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer A
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct: The Sir Creek dispute indeed concerns boundary interpretation, which affects EEZ claims, resource rights, and maritime control.
Statement 2 is incorrect: India invokes the Thalweg principle (boundary lies mid-channel), while Pakistan claims the boundary should lie along the eastern bank based on a 1914 resolution.
Q2. With reference to the Tribal Village Vision 2030 Declaration, consider the following statements:
1. It was organised by the Ministry of Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
2. Under this 1 lakh tribal villages will establish an Adi Sewa Kendra as a single-window citizen service center for voluntary service and connectivity.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: It was organised by the Ministry of Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Statement 2 is correct: Under this 1 lakh tribal villages will establish an Adi Sewa Kendra as a single-window citizen service center for voluntary service and connectivity.
Q3. Consider the following statements about Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses:
1. It will be implemented for period of over 2025–26 to 2030–31.
2. It guarantees 100% procurement of tur, urad, masoor at MSP in all states of India.
3. The assured procurement will be done under Price Support Scheme (PSS) of PM-AASHA
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Union Cabinet approved the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses, aiming for self-sufficiency in pulses with a financial outlay of ₹11,440 crore over 2025–26 to 2030–31. The mission targets increasing pulses production to 350 lakh tonnes and expanding cultivation to 310 lakh hectares by 2030–31. Strategies include research on high-yield, pest-resistant, and climate-resilient varieties, large-scale certified seed distribution, and expansion into rice fallow and diversifiable areas.
Statement 2 is incorrect & statement 3 is correct: A major feature of the Mission will be assured maximum procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masoor under Price Support Scheme (PSS) of PM-AASHA. NAFED and NCCF will undertake 100% procurement in participating states for the next four years from farmers who register with these agencies and enter into agreements.
Q4. Consider the following government schemes:
1. Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
2. POSHAN
3. Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG)
How many of the above schemes have been subsumed under umbrella program of Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) All three
d) None
Answer: C
Explanation: ‘Mission Poshan 2.0’ subsumes the Anganwadi Services (AWS), along with two other schemes namely POSHAN (Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment) Abhiyaan and Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG), and provides nutritional support for children below 6 years of age, Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers (PW&LM), Adolescent Girls (14-18 years); in aspirational districts and all districts of north east region, while also emphasizing on Early Childhood Care and Education (3-6 years); and Anganwadi infrastructure including modern and upgraded Saksham Anganwadi.
Spread the Word



