| Article 15 | Article 16 | |
|---|---|---|
| Explanation | State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. It prohibits discrimination both by the State and private individuals | No citizen can be discriminated against or be ineligible for any employment or office under the State on grounds of only religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth or residence. |
| Exceptions | • Special provision for women and children(Article-15(3)) • Special provision for advancement of socially and educationally backward classes or SC/STs(Article-15(4)) • Special provision regarding their admission to educational institutions(Article-15(5)) • Special provision for advancement of economically weaker sections of citizens (Article-15(6)) | • Parliament can prescribe residence as a condition for certain employment(Article-16(3)) • State can provide for reservation of post for backward class(Article-16(4)) • Special rules for office post in religious or denominational institutions (Article-16(5)) • State can provide 10% reservation to economically weaker sections in appointments (Article-16(6)) |
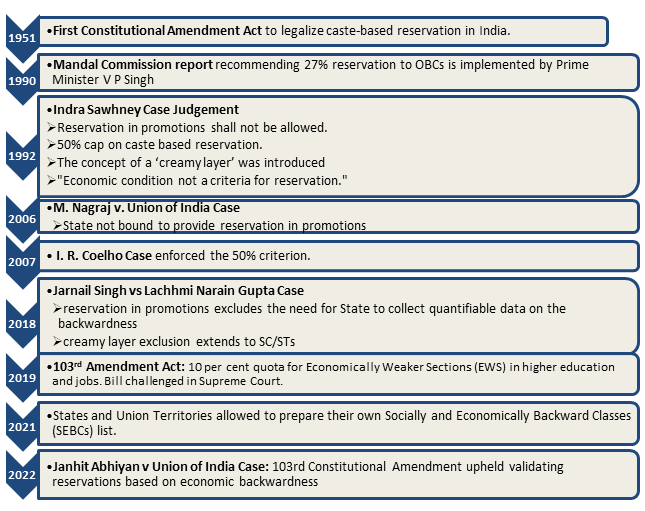
Evolution of reservation in India
Indira Sawhney Case
-
- Meaning of social and economic backwardness
Criterias:
-
-
-
- Social disadvantages
- Primitive style of living
- Cultural backwardness and living conditions
- Historical injustice
-
-
Backwardness is social not necessarily educational. Social backwardness leads to educational and economic backwardness. Thus, caste can be called backward.
-
- 50% ceiling
- To maintain a balance between equity & equality and merit & justice.
- Parent Optimality- breach would affect equality and merit.
- Breached by some states like Tamil Nadu which provides for 68% reservation.
- R. Balaji v. State of Mysore (1962)- Supreme Court established a 50% cap on reservations in educational institutions.
- 50% ceiling
EWS reservation (103rd CAA)
About:
-
- 10% reservation for Economically Weaker Sections (EWS)in educational institutions and government jobs.
- Added Article 15(6)&16(6).
- Criterias:
- annual income should be less than ₹8 lakh.
- not own more than 5 acresof agricultural land.
- residential flat of less than 1,000 sq. feet or house of less than 100 sq. yards in a notified municipality.
Purpose:
-
- Make reservations more progressive by including economic criteria,as even general category has 18% poverty rates.
- A balancing act due to increasing demands from general category like Jats, Patels, Marathas.
- Minimizing the level of divisiveness in society.
- Economic parameters have been considered by the Mandal Commission while defining socio educational backwardness.
Janhit Abhiyan vs Union of India case in 2022
-
- SC upheld the constitutional validity of 103rd amendment act by 3:1.
- Supporting view: Treating different groups equally is unjust.Just as equals cannot be treated unequally, unequals cannot be treated equally.
- Dissenting view: It violates the basic structureof Constitution and breaches the 50% reservation limit set in Indra Sawhney judgment.
Transformative Constitutionalism
-
- It means bringing about change in the society by infusion of equality, liberty, fraternity and dignity in social order.
- It aims at fulfilling the basic purpose of the Constitution which is meant to transform society for the better.
- In Indian context it can be seen in form of PIL, Navtej Singh Johar case on LGBTQ rights, Sabarimala case, Triple Talaq case and Janhit case etc.
Justification for reservation:
-
- Underrepresentation of reserved category: The representation of SC and ST officers at Secretary and Joint Secretary-level officers stood at 4% and 4.9%, respectively.
- Inclusive merit: Reservation does not dilute the meritocratic nature of the process as even UPSC follows 13-point roster system by providing different cut-offs for different categories to provide a level playing field and still known for recruiting some of the best minds of the country.
- In K. Pavitra v Union of India (2019), the Supreme Court of India introduced a new definition of administrative efficiency, which balances merit with ensuring adequate representation.
- Social justice:It is an affirmative action to uphold the principles of equity and justice enshrined in the Constitution.
- Even USA undertakes affirmative actions to improve employment, educational, and other opportunities for members of groups that have been subjected to discrimination.
- Inclusive governance: Policies are more likely to be sensitive to the needs of marginalized groups if these groups have a voice in their formulation and implementation.
- Public trust and confidence:Enhance the legitimacy of policy in the eyes of the public and help mitigate perceptions of elitist bureaucracy.
Article 335 (Claims of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes to services and posts)
It provides relaxation in qualifying marks in any examination or lowering the standards of evaluation, for reservation in matters or promotion to any class or classes of services or posts in connection with the affairs of the Union or of a State.
Should there be creamy layer for SC/ST?
| Yes | No |
|---|---|
| It can be introduced for those who have received first/ second generation reservation benefits. | Already poorly represented in various public institutions |
Jarnail Singh vs Lachhmi Narain Gupta case (2018)
-
- Upheld the Nagaraj judgment (2006)
- requirement for the State to demonstrate the current backwardness of SCsand STs.
- The creamy layer exclusion principleextended to SC/STs.
- Quantifiable data requirement for inadequate representation
This judgment struck a balance between enabling reservations for the truly disadvantaged within SC/ST groups and ensuring fairness and equality in public employment.
Vikas KishanraoGawali vs The State of Maharashtra (2021)
(Triple test before giving reservation to OBCs in local bodies)
-
- A dedicated commission to conduct an inquiry into the nature and implications of backwardness in local bodies.
- Specify the proportion of reservation required in local body based on the recommendations of the Commission.
- Total reservation for SCs/STs/OBCs shall not exceed 50 %.