Topic- 1: Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 Awards
GS- 2 &3: Governance and Economy
The context:
Hon’ble President of India conferred Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 Awards at Vigyan Bhagwan, New Delhi hosted by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
-
- Swachh Survekshan is an annual cleanliness survey initiated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission (Clean India Mission).
- It ranks cities based on their sanitation and cleanliness performance, motivating cities to improve their urban hygiene standards through a competitive framework.
- This year’s edition (2024-25) introduced a revamped methodology to include 10 new parameters and distinct population categories, allowing smaller cities to compete fairly with metropolitan areas. The initiative also focuses on sustainability via the 3R approach and circular economy principles, emphasizing waste management innovations and social empowerment.
- The launch of the Swachh City Partnership aims to scale up impact through peer mentoring, while the Accelerated Dumpsite Remediation program is designed to tackle long-standing waste disposal challenges, unlocking urban spaces and improving environmental health.

-
Top Cities & Awards:
-
- Super Swachh League Cities: Indore, Surat, and Navi Mumbai entered the premier league.
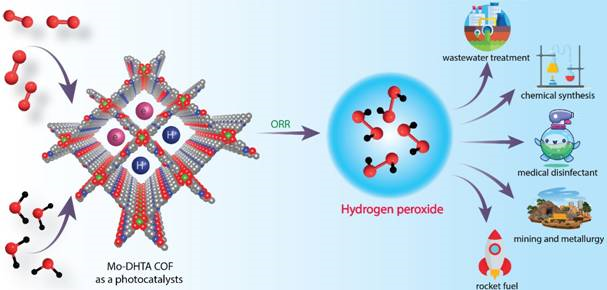
- New Clean Cities: Ahmedabad, Bhopal, and Lucknow emerged as India’s new top clean cities.
- Special Awards: Prayagraj was awarded Best Ganga Town; Secunderabad Cantonment recognized as Best Cantonment Board.
- Sanitation Worker Safety: GVMC Visakhapatnam, Jabalpur, and Gorakhpur honored for safety and dignity of sanitation workers.
- Special Recognition: For exemplary urban waste management during the Mahakumbh festival in Prayagraj, which had a footfall of around 66 crore people.
-
Promising Clean Cities:
-
-
- 34 cities across States/UTs recognized as Promising Swachh Shehars under ‘One City, One Award’ principle.
- Smaller cities encouraged through simplified framework to compete equally with larger cities.
-
Swachh City Partnership Initiative:
-
-
- Launched by Union Minister Shri Manohar Lal.
- Top 78 cities to mentor 78 underperforming cities from their respective States.
- Aim: Peer learning, ‘Each One Clean One’ mantra to uplift low-performing cities.
-
Accelerated Dumpsite Remediation Program:
-
-
- One-year program starting 15 August 2025.
- Focus on legacy waste remediation, urban space unlocking, and scientific waste processing capacity expansion.
-
President’s Remarks:
-
- Praised Ministry’s promotion of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3R) approach.
- Emphasized ‘Waste is best’ mantra supporting circular economy, youth empowerment, green jobs, SHGs, and entrepreneurship.
- Commended swachhata standards in cities with population below 1 lakh.
- Highlighted role of school interventions, source segregation, zero waste colonies.
- Affirmed that Viksit Bharat 2047 will set a global example.
Additional Highlights:
-
-
- ‘Waste to wealth’ sarangi presented to the President symbolizing sustainability and craftsmanship.
- Digital launch of Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 Results Dashboard for interactive data viewing.
- Audio-visual presentations highlighted the achievements of the Super Swachh League Cities.
-
Source: PIB
Topic- 2: Successful Trial of Akash Prime at High Altitude
GS- 3: Science & Technology
The context:
On July 16, 2025, India successfully tested the Akash Prime missile system by destroying two high-speed aerial unmanned targets at high-altitude in Ladakh (above 4,500 meters).
About Akash Prime:
-
- It is an upgraded variant of the Akash Weapon System, tailored for high-altitude operations with improvements such as an indigenously developed Radio Frequency seeker. The upgrades were made based on operational feedback to enhance effectiveness.
-
- The system was validated through joint efforts of the Indian Army Air Defence, DRDO, and Defence PSUs like Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), along with industry partners.
Key Features of Akash Prime:
-
- Customized to operate efficiently above 4,500 meters altitude.
- Equipped with an indigenously developed Radio Frequency seeker.
- Incorporates multiple upgrades based on operational feedback to improve effectiveness.
Collaborating Organizations:
-
- Indian Army Air Defence
- DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation)
- Defence PSUs: Bharat Dynamics Limited, Bharat Electronics Limited
- Other Industry Partners
Significance:
-
- The trial is part of the First of Production Model firing trials and aims to facilitate timely induction into the armed forces.
- It boosts India’s air defence capabilities in challenging high-altitude border regions.
- This success builds on the exemplary performance of indigenous air defence systems in Operation Sindoor.
- It reflects India’s growing prowess in missile development, gaining global recognition.
Source: PIB
Topic- 3: Automotive Mission Plan 2047
GS- 3: Economy and Science & Technology
The context:
India’s automotive sector is a vital part of its industrial landscape, contributing significantly to GDP, employment, and exports. Previous Automotive Mission Plans helped accelerate the sector’s growth, innovation, and manufacturing capabilities.
What is Automotive Mission Plan 2047 (AMP 2047)?
-
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries has launched Automotive Mission Plan 2047 (AMP 2047), a strategic roadmap aligned with India’s long-term vision of ‘Viksit Bharat @2047’ to position India as a global leader in the automotive sector by the year 2047.
-
-
Objectives:
- Enhance innovation and sustainability in the automotive industry.
- Increase India’s share in global automotive trade.
- Promote global competitiveness and industry advancement.
- Build a self-reliant and sustainable automotive ecosystem.
- The inaugural meeting of seven Sub-Committees was held to define objectives and frameworks. These Sub-Committees include experts from government ministries, industry bodies, academia, and testing agencies.
-
Stakeholder Involvement:
- Collaborative effort involving multiple ministries:
- Ministry of Power
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
- Ministry of Commerce
- Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
- DPIIT
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- Industry bodies: SIAM (Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers), ACMA (Automotive Component Manufacturers Association), CII (Confederation of Indian Industry), FICCI.
- Academia, research think tanks, and testing agencies also engaged.
- Collaborative effort involving multiple ministries:
- The plan will have targets set for 2030, 2037, and 2047, guiding technological advancement (including charging infrastructure for EVs) and policy measures.
- The Apex Committee is chaired by Ministry of Heavy Industries.
-
Significance:
-
- Builds on earlier Automotive Mission Plans that fueled sector growth.
- Not just aspirational, but a strategic roadmap with concrete targets.
- Aims for innovation-driven quality and competitiveness on a global scale.
Source: PIB
Topic- 4: Greenhouse Gas Dynamics in the Central Himalayas
GS- 3: Economy and Environment
The context:
For the first time, Indian scientists have conducted detailed, continuous measurements of key greenhouse gases—carbon dioxide, methane, and carbon monoxide—in the Central Himalayas, a sensitive and under-studied ecosystem.
-
- The Central Himalayas play a critical role in regional and global climate systems, but their greenhouse gas dynamics have been poorly understood due to the lack of long-term, high-resolution data. The Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), under India’s Department of Science & Technology, conducted a five-year study at a high-altitude research station in Nainital.
- The study revealed complex interactions between natural processes like photosynthesis and meteorological patterns, and human activities such as biomass burning and agriculture, shaping the region’s greenhouse gas levels.
The Key Highlights: Complex Greenhouse Gas Dynamics in the Central Himalayas
-
- Indian scientists, for the first time, have captured detailed, continuous measurements of key greenhouse gases—carbon dioxide, methane, and carbon monoxide—in the Central Himalayas.
- This study was conducted by ARIES, a research institute under India’s Department of Science & Technology, at a high-altitude site in Nainital over five years.
- The research shows that both natural processes (like photosynthesis) and human activities (such as biomass burning and agriculture) influence greenhouse gas levels in this sensitive Himalayan ecosystem.
- Greenhouse gas concentrations here are higher than at other remote sites but lower than urban areas, indicating effects from both local and distant pollution sources.
Findings on Emissions & Influences:
-
-
- GHG concentrations higher than other remote background sites but lower than urban/semi-urban areas.
- Both natural processes (biospheric uptake, meteorological patterns) and human activities (biomass burning, agriculture) influence GHG levels.
- Diurnal cycle:
- CO₂ lowest during daylight due to photosynthesis.
- CH₄ and CO peak during daytime from mountain wind transport of pollutants from lower altitudes.
- Seasonal variations:
- CO₂ peaks in spring due to biomass burning and low vegetation.
- CH₄ peaks in autumn, linked to agriculture (e.g., rice cultivation).
- CO peaks in late spring, indicating regional pollution transport.
-
-
- Daily and seasonal patterns were observed: carbon dioxide is lowest during the day due to plants absorbing it, methane peaks in autumn linked to agriculture, and carbon monoxide peaks in late spring due to regional pollution.
- Long-term trends indicate carbon dioxide and methane levels are rising steadily, faster than at Mauna Loa (a global background monitoring site), highlighting growing human impact.
- Carbon monoxide levels, however, are gradually declining, possibly due to cleaner combustion and changing emission sources.
- Environmental factors like sunlight, temperature, and how high pollution can rise in the atmosphere affect greenhouse gas patterns just as much as human activities.
- This data fills a critical gap in ground-based monitoring for South Asia’s mountainous regions and helps improve satellite data, emissions inventories, and climate models.
- The findings provide valuable, localized information to policymakers and scientists, aiding climate mitigation strategies and policy decisions in South Asia’s changing climate scenario.
Long-Term Trends (2014-2018):
-
-
- CO₂ increasing at 2.66 ppm/year.
- CH₄ increasing at 9.53 ppb/year.
- Increases exceed those at Mauna Loa (a global baseline site), reflecting rising anthropogenic emissions.
- CO decreasing at 3.15 ppb/year, possibly due to improved combustion or changing emission sources.
-
Source: PIB
Topic- 5: Photocatalytic Breakthrough Enables Green Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
GS- 3: Science & Technology
The context:
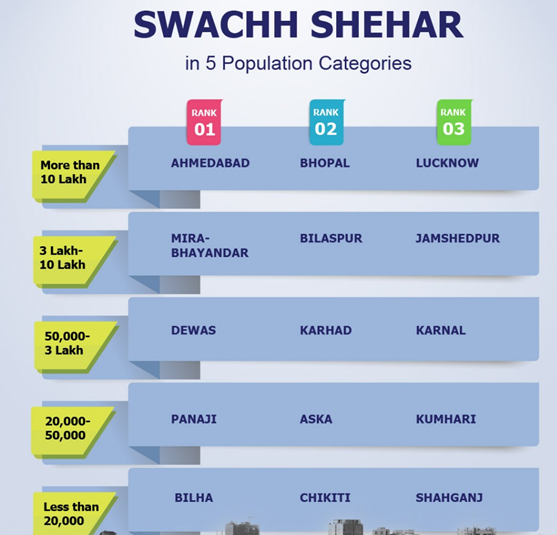
Scientists at the S. N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), have developed a pioneering method to produce hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) directly from sunlight and water using an advanced photocatalyst called Mo-DHTA COF—a dimolybdenum-embedded covalent organic framework.
About the Hydrogen peroxide:
-
- It is a vital disinfectant and oxidizing agent with broad uses in healthcare, water purification, fuel cells, and chemical manufacturing. Conventional production methods are energy-intensive, costly, and environmentally harmful. This novel approach offers a clean, energy-efficient, and sustainable alternative by harnessing solar energy under mild conditions.
About Mo-DHTA COF:
-
-
- Integrates dimolybdenum units with α-hydroquinone linkers forming a stable, high-performance framework.
- Under visible light, it generates excitons that drive oxygen reduction to produce hydrogen peroxide.
- Demonstrates high photocatalytic efficiency even in pure water and organic solvents.
- Exhibits excellent structural stability and recyclability.
-
Advantages over Traditional Photocatalysts:
-
-
- Traditional catalysts (metal oxides, polymers, MOFs) have wide band gaps, low stability, and fewer active sites.
- Mo-DHTA COF improves catalytic activity, charge separation, and electron mobility by embedding metal centers into COFs (M-COFs).
-
Potential Applications:
-
-
- Pharmaceuticals & healthcare: cost-effective and sustainable H₂O₂ production.
- Environmental remediation: green sterilization and pollutant treatment methods.
- Materials & energy science: water splitting, CO₂ reduction, and synthesis of value-added chemicals.
-
Future Directions:
-
-
- Optimization and scaling for industrial use.
- Exploring other metal-embedded COFs to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
-
Significance:
-
-
- Marks a pivotal step toward cleaner, low-cost, greener chemical synthesis.
- Potential to revolutionize the industrial production of hydrogen peroxide and other green chemicals by harnessing solar energy and water.
-
Source: PIB
Spread the Word