Topic- 1: National Conference on “Good Governance Practices”
GS- 2: Good Governance
The context:
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG), in partnership with the Government of Odisha, is hosting a two-day National Conference focused on “Good Governance Practices” in Bhubaneswar on July 17-18, 2025.
The Key Highlights: National Conference on “Good Governance Practices”:
-
- It is organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) in collaboration with the Government of Odisha.
- The conference features 5 plenary sessions covering themes like:
- Prime Minister’s Awarded Initiatives 2024 for Holistic Development of Districts.
- Aspirational Block Programme.
- Innovations in governance.
- The event aims to promote experience-sharing on innovations in public administration, digital governance, and good governance to improve quality of life.
- It provides a platform for national and state public administration bodies to present and replicate successful governance models.
Focus Areas:
-
- Highlighting and celebrating initiatives recognized with Prime Minister’s Excellence Awards
- Showcasing award-winning best governance practices from districts and states
- Sharing innovations in public administration, digital governance, and improving quality of life
Objective:
-
- Facilitate exchange of ideas and experiences on best governance practices
- Promote replication of successful governance models across states and districts
- Foster collaboration between national and state-level public administration bodies for future-ready governance solutions
Source: PIB
Topic- 2: Solar Blasts that Lit up Ladakh Skies Uncoded: Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
GS- 3: Science & Technology
The context:
A team of Indian astronomers led by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) has decoded the complex sequence of six successive Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) from the Sun that caused rare and vivid northern lights over Ladakh in May 2024. These massive solar eruptions triggered a powerful geomagnetic storm, the most intense seen in two decades, with significant implications for Earth’s space weather.
What are CMEs?
-
- CMEs are massive ejections of magnetized plasma from the Sun’s corona, capable of disturbing Earth’s magnetosphere, affecting satellites, communication systems, and power grids.
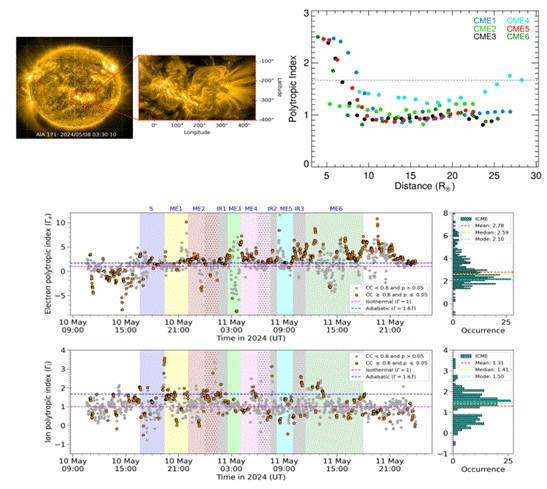
Findings:
-
- Tracked six interacting CMEs from the Sun to Earth using a model called the Flux Rope Internal State (FRIS).
- Discovered CMEs initially release heat but then switch to absorbing and holding heat as they travel.
- The final storm reaching Earth contained “double flux ropes,” complex intertwined magnetic structures with varying heating and cooling patterns.
- Electrons were mostly in heat-releasing states, while ions showed mixed heating/cooling.
Thermodynamic Behavior:
-
- Initially, CMEs release heat but then switch to a heat-absorbing state as they expand.
- At Earth’s orbit, the final CME cloud had two intertwined magnetic structures (double flux ropes) causing complex heating and cooling patterns between electrons and ions.
- Electrons were mostly heat-releasing, while ions exhibited mixed behavior with heating dominant.
Significance:
-
- First study in India and internationally capturing continuous thermal evolution of multiple interacting CMEs across the heliosphere.
- Enhances understanding of how solar storms disrupt Earth’s space environment.
- Could improve forecasting of intense geomagnetic disturbances by using thermal properties as predictive markers.
Future Prospects:
-
- Integration of data from India’s Aditya-L1 mission and its instruments like Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) and Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) for comprehensive Sun-to-Earth CME studies.
Importance for Space Weather and Technology:
-
- Improved prediction of geomagnetic storms safeguards satellites, communication, navigation, and power infrastructure.
- Understanding CME interactions aids in developing early warning systems against solar storms impacting Earth.
Source: PIB
Topic- 3: Robust Urban River Management Plan Launched to Rejuvenate Yamuna: National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
GS- 2 and 3: Governance and Science & Technology
The context:
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in partnership with the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and the Government of NCT of Delhi, formally launched the Urban River Management Plan (URMP) for Delhi through an Inception Stakeholder Workshop held at Bharat Mandapam.
Key Highlights:
-
- The URMP aims to be a dynamic, science-driven framework incorporating risk assessments and active stakeholder participation, embedding river-sensitive urban planning to ensure sustainable development.
- Delhi Chief Secretary emphasized that “Yamuna improves, Delhi improves,” urging for practical and visible actions including sewage infrastructure upgrades and restoring the city’s relationship with the river.
- Ministry of Jal Shakti, Ms. Debashree Mukherjee called for a collective and sustained movement involving government, media, partners, and citizens to achieve a healthy Yamuna and resilient urban future.
- International collaboration was spotlighted by the Dutch Ambassador Ms. Marisa Gerards, highlighting the upcoming Centre of Excellence on Urban Water Resilience, a joint initiative between India and the Netherlands, which will support URMP development.
- The World Bank and IIT Delhi representatives shared valuable insights on stakeholder engagement and flood risk management, respectively.
- The URMP will address pollution control, wetland and encroachment management, and promote water reuse through coordinated multi-agency efforts.
- Progress will be tracked using a new Urban River Management Index covering ten key domains.
- The initiative includes public engagement activities recognizing the crucial role of citizens in river restoration.
Vision & Approach:
-
- URMP is not just a document but a dynamic planning and action tool.
- Emphasizes scientific risk assessment, river-sensitive urban planning, pollution control, wetland management, encroachment removal, and water reuse.
- Framework integrates global best practices, including Dutch concepts like “Water as Leverage,” and nature-based solutions.
Significance:
-
- Marks a shift from fragmented efforts to a unified, science-driven, and inclusive framework for urban river management.
- Aims to restore Yamuna as a healthy, resilient urban ecosystem integral to Delhi’s identity and sustainable development.
- Exemplifies international collaboration and multi-agency coordination in addressing complex urban environmental challenges.
Source: PIB
Topic- 4: Union Cabinet Approves Investment Exemption for NLCIL to Boost Renewable Energy Expansion
GS- 3: Economy and Science & Technology
The context:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved a special exemption allowing NLC India Limited (NLCIL) to invest ₹7,000 crore in its subsidiary, NLC India Renewables Limited (NIRL), without prior approvals and beyond the usual 30% net worth limit for CPSEs.
-
- This strategic move accelerates NLCIL’s renewable energy ambitions, targeting 10.11 GW capacity by 2030 and 32 GW by 2047.
The Key Highlights:
-
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by the Prime Minister, approved a special exemption for NLC India Limited (NLCIL) from the existing investment guidelines for Navratna CPSEs.
-
Exemption Details:
- NLCIL can invest up to Rs. 7,000 Crore in its wholly owned subsidiary, NLC India Renewables Limited (NIRL), without prior approval requirements under current delegation of powers.
- This investment is exempted from the 30% net worth ceiling for investments in joint ventures and subsidiaries set by the Department of Public Enterprises (DPE).
- These relaxations provide greater operational and financial flexibility to NLCIL and NIRL.
-
Strategic Objectives:
- Support NLCIL’s ambitious target to develop 10.11 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030, expanding to 32 GW by 2047.
- Align with India’s international climate commitments, including:
- Achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity by 2030 (Panchamrit goals).
- Net Zero carbon emissions target by 2070.
-
Current Status:
- NLCIL currently operates seven renewable energy assets totaling 2 GW capacity, either operational or nearing commercial operation.
- These assets will be transferred to NIRL, which will be the flagship platform for NLCIL’s green energy initiatives.
- NIRL is exploring new opportunities including participation in competitive renewable energy project bidding.
-
Significance:
- Reinforces India’s leadership in green energy transition by reducing fossil fuel dependence and coal imports.
- Enhances the reliability of 24×7 power supply across the country.
- Expected to generate significant employment opportunities during project construction and operation, supporting local economies and inclusive growth.
Source: PIB
Topic- 5: Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana to Boost Agriculture in 100 Districts
GS- 3: Economy and Science & Technology
The context:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, a six-year initiative starting from 2025-26 aimed at accelerating agricultural development in 100 selected districts across India. Inspired by NITI Aayog’s Aspirational District Programme, this scheme exclusively focuses on agriculture and allied sectors.
About the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana:
-
- The Union Cabinet approved the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, a six-year program (2025-26 onwards) targeting 100 districts across India to fast-track agricultural and allied sector development.
-
Objectives:
- Enhance agricultural productivity and promote crop diversification.
- Encourage sustainable agricultural practices and natural/organic farming.
- Improve post-harvest storage facilities at panchayat and block levels.
- Upgrade irrigation infrastructure.
- Facilitate access to long-term and short-term credit.
-
Implementation Strategy:
- The scheme will be implemented through the convergence of 36 existing schemes from 11 Central Departments, state schemes, and partnerships with the private sector.
- Districts are selected based on low productivity, low cropping intensity, and lower credit disbursement. Each state will have at least one district chosen based on its net cropped area and operational holdings.
- District, State, and National committees will oversee planning, execution, and monitoring.
- A District Agriculture and Allied Activities Plan will be prepared by the District Dhan Dhaanya Samiti including progressive farmers.
- The plan aligns with national goals: crop diversification, water and soil conservation, self-sufficiency, and natural farming expansion.
-
Monitoring & Evaluation:
- Progress tracked using 117 key performance indicators on a monthly dashboard.
- NITI Aayog and Central Nodal Officers will regularly review district plans and progress.
-
Expected Outcomes:
- Improved agricultural productivity and value addition.
- Creation of local livelihoods and enhancement of domestic agricultural production.
- Contribution to India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat by advancing self-reliance in agriculture.
- Incremental improvement in national agricultural indicators through focused district-level interventions.
Significance:
-
- The scheme aims to address regional disparities in agriculture by prioritizing underperforming districts.
- Promotes holistic and integrated agricultural development linking productivity, sustainability, infrastructure, and credit access.
- Represents a major step towards modernizing India’s agricultural sector through coordinated multi-departmental efforts.
Source: PIB
Spread the Word



