Constitutionalism is the bedrock of a healthy democracy. It revolves around the concept of a limited government, bound by the rule of law. This ensures no individual or branch of government operates above the law.
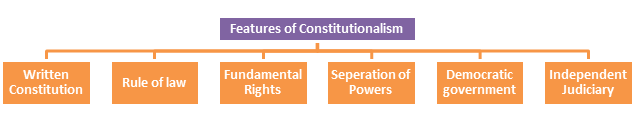
Difference between Constitution and Constitutionalism
| Constitution | Constitutionalism |
|---|---|
| • A legal document which deals with system of polity. • It is static in nature as it is an adopted document. • It can be liberal or socialist. | • A process based on the idea of limited government. • It is dynamic as it represents working of the Constitution. • It is a liberal idea. |
-
- Though written Constitution is a feature of Constitutionalism but there are exceptions like in UK which has unwritten Constitution but has constitutionalism.
Working of Constitutionalism
| Positive developments | Negative developments |
|---|---|
| • Basic structure doctrine (Keshavananda Bharati Case 1973) • Due process of law • Socio-economic justice (Laws, schemes and policies) - MGNREGA, PDS etc. • Free and fair elections- India has emerged has the largest democracy. • Right to Information | • 42nd Amendment Act • Invoking emergency and misuse of Article 356 • Criminalization of Politics (~46% MPs with criminal background in 18th LS) • Misuse of ordinances • Arbitrary application of draconian laws like UAPA/ NSA/ ED/ CBI. • Human rights violations- NHRC registered more than126 deaths in police custody, 1,673 deaths in judicial custody, and 55 alleged extrajudicial killings in 2023. |
Thus, it can be concluded that Constitution alone cannot ensure constitutionalism if people lack constitutional morality. Constitutionalism is essential for ensuring constitutional democracy. It strengthens trust of people in democracy and people enjoy the ideals of democracy, including liberty and prosperity.
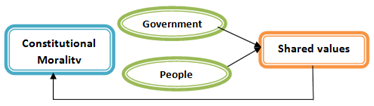
Constitutional morality
-
- It is about the shared values of people in the context of relationship between government and governed. The ideals which govern their relationship are considered constitutional morality.
-
- According to George Grote, constitutional morality is implied obligations for both the citizens as well as the authority which have been given powers to govern.
- Ambedkar defined constitutional morality as harmonious interaction between governing and governed including peaceful settlement of descent faced from the latter and conflict of interest arising between them without indulging in any major confrontation of resorting to violent revolutions. For him values of constitutional morality along with constitutionalism are core ideals of Constitution and establishment of a society which enjoyed political, social and economic democracy.
Difference between Constitutionalism and Constitutional Morality
| Constitutionalism | Constitutional Morality |
|---|---|
| • It is an idea of limited government. • It imposes restraint on the government actions. • It is a process and phenomenon. • It is more concerned about authority of government which should not be absolute. | • It is about an implied obligation between government and governed. • It is related to morality of both government and governed and imposes restraint on both. • It is the values. • It is broad in outlook as it is related to relationship between government-governed. |
Constitutional Morality and Judiciary – case laws
-
- Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973):Basic structure to preserve core constitutional values.
- Naz Foundation v. Govt of NCT Delhi (2009): constitutionalmorality should prevail over public morality.
- Manoj Narula v. Union of India (2014): constitutional morality as adherenceto constitutional principles and values.
- Government of NCT Delhi v. Union of India (2018):Constitutional morality to‘second basic structure doctrine’.
- Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India (2018):Constitutional morality must prevail over social morality
- Indian Young Lawyers Association v. State of Kerala (2018): In the Sabarimala case, constitutional morality prioritized over religious customs
- Joseph Shine v. Union of India (2018):constitutional morality requires laws to be in accordance with individual dignity.
Constitutional Morality versus Social Morality
| Constitutional Morality | Social Morality |
|---|---|
| It represents modern liberal values based on rationality and scientific temper imbibing ideals of modern liberal democracy like liberty, equality, freedom, justice and fraternity. | It is based on the traditional socio-cultural norms of society, which guides lives of people like different cultures have their own cultural values. For example concept of piousness or celibacy. |
Though there are differences but these are complementary as social morality can become basis for constitutional morality and they influence each other. But when social morality becomes discriminatory and it comes into conflict with constitutional morality, it is the later which prevails like in Sabarimala case.For a progressive society, constitutional morality should work as a guiding force.
Spread the Word