Topic- 1: Outcomes of the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to Brazil
GS-2: International Relation (IR)
The context:
Agreements were signed during the Indian Prime Minister’s state visit to Brazil.
-
- Indian PM was also conferred with Brazil’s highest civilian award, the Grand Collar of the National Order of the Southern Cross.
Memoranda of Understanding / Agreements Signed:
-
- Agreement on Cooperation in Combating International Terrorism and Transnational Organized Crime.
- MoU on Cooperation for the Sharing of Successful Large-scale Digital Solutions for Digital Transformation.
- MoU on Cooperation in Renewable Energy.
- MoU on Agricultural Research between EMBRAPA (Brazil) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Agreement on the Exchange and Mutual Protection of Classified Information.
- MoU on Cooperation in the Field of Intellectual Property between DPIIT (India) and the Secretariat of Competitiveness and Regulatory Policy, MDIC (Brazil).
Major Announcements:
-
- Formation of a ministerial-level mechanism to monitor bilateral trade, commerce & investment.
- Brazil aims to triple India‑Brazil trade, currently around USD 12 billion, with targets set at USD 20 billion over the next 5 years.
Broader Strategic Cooperation:
-
- Defense & Security: The terrorism agreement includes Brazil’s Federal Police opening an attaché office in New Delhi, underscoring heightened intelligence collaboration.
- Clean Energy & Climate: Cooperation in renewable energy is aligned with shared commitments toward COP30 and the Global Biofuels Alliance. Brazil invited India to collaborate on its Tropical Forest Forever Facility.
- Agriculture & Livestock: EMBRAPA–ICAR partnership builds on 60 years of genetic collaboration, including Brazilian Zebu cattle derived from India.
- Digital Infrastructure & Innovation: India offers to help set up a “center of excellence” in digital public infrastructure in Brazil, leveraging India’s experience in open models and UPI.
- Space & Technology: Discussions included space cooperation, vaccine development, AI, supercomputers, and leveraging EMBRAER aircraft for India’s UDAN regional connectivity.
Diplomatic & Symbolic Highlights:
-
- PM Modi received Brazil’s highest civilian honour, the Grand Collar of the National Order of the Southern Cross.
- He became the first Indian Prime Minister in 57 years to make a full state visit to Brazil.
Strategic Significance:
-
- This visit consolidates the India–Brazil Strategic Partnership across defense, digital, energy, agriculture, health, and space.
- It reinforces a South-South alliance amplifying voices of emerging economies in global forums like COP, BRICS, and the Global South.
About India-Brazil Relations
-
- Global Cooperation: Strategic Partnership from 2006.
- Work closely at plurilateral fora such as BRICS, BASIC, G-20, G-4, IBSA, and larger multilateral bodies such as the UN, WTO, UNESCO, and WIPO
- Trade: In 2024-25, bilateral trade reached USD 12.20 billion with India in trade surplus.
- Defence Cooperation: A defence cooperation agreement was ratified in 2006, which created a Joint Defence Committee (JDC) as an institutional mechanism.
- Renewable Energy: Brazil became the co-founder member of Global Biofuel Alliance.
- Brazil ratified the International Solar Alliance (ISA) Agreement in 2022.
Source: PIB
Topic- 2: Prime Minister Conferred with Namibia’s Highest Civilian Award
GS-2: IR
The context:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi was honored with Namibia’s highest civilian award — The Order of the Most Ancient Welwitschia Mirabilis — by H.E. President Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah. Prime Minister Modi is the first Indian leader to receive this prestigious award.
The Key Highlights:
-
- The award was presented by the President of Namibia, H.E. Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, during the Prime Minister’s State Visit to the country.
- This marks the first time an Indian leader has received Namibia’s highest civilian honor.
- Prime Minister Modi dedicated the award to the 1.4 billion people of India and the historic ties between India and Namibia.
- He expressed deep gratitude to President Nandi-Ndaitwah and the Namibian people for the recognition.
- The honor reflects the growing strategic and diplomatic closeness between India and Namibia.
- The conferment signifies a milestone in the bilateral relations between the two nations.
- It is seen as an inspiration for future generations in both countries to strengthen their partnership.
- The award underscores Namibia’s appreciation of India’s role in promoting South-South cooperation.
- The recognition highlights India’s growing global stature and its impactful relations with African nations.
About Namibia:
-
- Location: Namibia lies in southwestern Africa, offering access to the Atlantic Ocean and serving as a strategic gateway to the African interior.
- Capital: Windhoek.
- Neighbours: Angola, Zambia, Botswana, South Africa, Atlantic Ocean.
-
- Geological Features
- Major Rivers: Kunene, Okavango, Zambezi, and Orange are the main rivers, flowing along borders and vital for irrigation and regional cooperation.
- Namib Desert: Located along the west coast, it is hyper-arid, famous for the Skeleton Coast and rich in minerals like diamonds and uranium.
- Kalahari Desert: A semi-arid sandy region in the east, it merges into savanna grasslands, supporting scattered pastoral activity.
- Mountains: Brandberg, at 2,573 m, is Namibia’s highest peak and part of the western escarpment, known for rock art and
- Central Plateau: This elevated zone is Namibia’s agricultural heartland, housing the Fish River Canyon and saline Etosha Pan.
- Soils: Fertile soils are found in Otavi Highlands and Caprivi Strip, while other areas have infertile sandy or rocky terrain.
- Climate: Characterized by arid to semi-arid conditions, rainfall is <50 mm on the coast and exceeds 600 mm in the Caprivi Strip, with frequent droughts inland.
- Geological Features
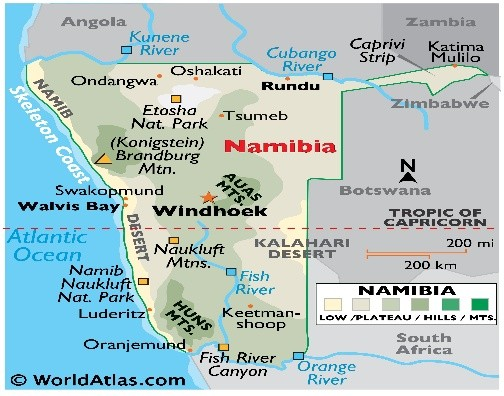
-
- Importance of Namibia to India:
-
-
- Strategic Mineral Partnership:
- Namibia holds vast reserves of uranium, rare earths, oil, and copper.
- India is exploring energy and critical mineral cooperationfor clean energy transition and strategic security.
- Strategic Mineral Partnership:
-
-
- Defence and Security Cooperation:
-
- Bilateral discussions now include security, defence manufacturing, and potential partnerships in maritime domain awareness.
- Namibia joined Indian-led platforms like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
-
- Digital and Technological Collaboration: India is supporting UPI-based fintech adoption in Namibia through a technology licensing agreement.
- Health and Human Development: MoUs signed on healthcare, medicine, and entrepreneurship development.
- Conservation and Symbolism: Namibia played a key role in Project Cheetah, aiding India in the transcontinental translocation of cheetahs to Kuno National Park
- Defence and Security Cooperation:
Source: PIB
Topic- 3: Delivery of First Indigenous Diving Support Vessel – ‘Nistar’
GS-3: Science & Technology
The context:
On 8 July 2025, Hindustan Shipyard Limited delivered ‘Nistar’, the first indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Vessel, to the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam.
The Key Highlights:
-
- ‘Nistar’ has been designed and built as per classification rules of the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS).
- The ship is highly specialised and can undertake Deep Sea Diving and Rescue Operations– a capability with select Navies across the globe.
- The ship’s name, ‘Nistar’, originates from Sanskrit and means liberation, rescue or salvation.The ship, measuring 118 m with a tonnage of nearly 10,000 tons, is installed with state-of-the-art Diving Equipment and has the capability to undertake Deep Sea Saturation Diving up to 300 m depth. The ship also has a Side Diving Stage for undertaking Diving Operations up to 75 m depth.
- The ship will also serve as the ‘Mother Ship’for the Deep Submergence Rescue Vessel (DSRV), to rescue and evacuate personnel, in case of an emergency in a submarine underwater.
- The ship is equipped with a combination of Remotely Operated Vehicles to undertake Diver Monitoring and Salvage Operations up to a depth of 1000 m.
- The delivery of Nistar, with nearly 75% indigenous content, is yet another milestone in the Indian Navy’s quest for indigenous construction and is in line with the GoI’s vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharatand the Make in India
Significance:
-
- The vessel’s name ‘Nistar’ means liberation, rescue, or salvation in Sanskrit, symbolizing its core mission of saving lives underwater.
- Represents a major milestone in India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative and Make in India campaign, highlighting the Indian Navy’s push for indigenous shipbuilding and self-reliance.
- Enhances the Indian Navy’s capacity for underwater rescue, salvage, and deep-sea diving operations, crucial for submarine safety and underwater emergencies.
Source: PIB
Topic- 4: ‘Aspirational DMF Programme’ to Boost Inclusive Grassroots Development
GS-3: Economy
The context:
Union Minister of Coal and Mines, on 9th July 2025 launched the operational guidelines for the ‘Aspirational DMF Programme’, aimed at converging District Mineral Foundation (DMF) initiatives with the Aspirational District Programme (ADP) and Aspirational Block Programmes (ABP). The programme focuses on aligning DMF planning and implementation with socio-economic priorities in India’s most underserved mining-affected regions.
The Key Highlights:
-
- Key Focus Areas: Health, education, nutrition, infrastructure, livelihood, and skill development in mining districts.
- Transparency and Accountability: Presentations on DMF transparency, audit practices by CAG, and innovative implementation strategies.
- Coffee Table Book 2.0: Launched to showcase transformative DMF projects across India.
- State Felicitations: Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Odisha, Gujarat, and others honored for adopting PMKKKY 2024 guidelines and audit compliance.
- DMF Exhibition at Handloom Haat: Showcased products by Self-Help Groups from mining-affected areas, promoting local enterprise and livelihoods.
About the Aspirational DMF Programme:
-
- Its objective is to converge District Mineral Foundation (DMF) initiatives with the Aspirational District Programme (ADP) and Aspirational Block Programmes (ABP)
- Its goal to align DMF planning and implementation with development priorities in underserved mining-affected regions
- Focus Areas: Socio-economic indicators like health, education, nutrition, infrastructure, livelihood, and skilling
Significance:
-
- DMFs have transformed mining-affected communities over the past decade by funding crucial sectors
- DMFs exemplify cooperative federalism and a whole-of-government approach inspired by PM Modi
- Urged District Collectors, State Governments to treat DMF as a mission for impactful, community-centered development
- Emphasized 100% saturation of available funds to maximize impact
- Highlighted alignment with PM’s vision of a Viksit (Developed) and Atmanirbhar Bharat
- DMF is more than a fund; it’s a powerful tool for inclusive development reaching the last mile
- Underlined DMF’s role in catalyzing healthcare, education, livelihood, and skill development in mining districts
Source: PIB
Topic- 5: India Highlights Maritime Safety and Gender Inclusivity at the 134th Session of IMO Council
GS-3: Economy and environment & Ecology
The context:
The Indian delegation, led by Shri T.K. Ramachandran, IAS, Secretary, Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, participated actively in the 134th session of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Council held in London.
The Key Highlights:
-
- India raised serious safety concerns over recent maritime incidents involving foreign-flagged container vessels in Indian waters due to undeclared hazardous cargo and structural issues.
- India called for a comprehensive IMO-led investigation and global review of such incidents to strengthen safety protocols for container shipping worldwide.
- The Indian delegation highlighted the proactive role of the Indian Navy and Coast Guard in ensuring maritime safety and urged enhancements in international regulations.
- India emphasized the need to reinforce protocols on packaging, declaration, stowage, and monitoring of lithium-ion batteries and IMDG cargo.
- India proposed that IMO-led investigations help build global best practices and improve standardization and operational norms for container ship safety.
- India actively contributed to the IMO’s agenda on gender equality, aligning with its Gender Inclusion Strategy.
- The delegation showcased India’s national initiative ‘Sagar Mein Samman,’ aimed at fostering a safe and inclusive maritime ecosystem empowering women at all levels.
- India reported a 650% increase in Indian women seafarers, reflecting strong commitment towards gender inclusivity in the maritime sector.
- The Indian delegation reaffirmed support for IMO’s goals on maritime safety, environmental protection, and inclusive development of the global maritime community.
About the International Maritime Organization (IMO):
-
- The International Maritime Organisation (IMO) is a specialised agency of the United Nations (UN), responsible for the safety and security of international shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships.
- It contributes directly to UN Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14, which focuses on the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources.
- The IMO formulates regulations on shipping safety, maritime security, and environmental protection, but does not enforce them. Once a member state adopts a regulation, it becomes part of that country’s domestic law.
- The organisation also deals with legal matters such as liability, compensation, and facilitation of maritime traffic.
- It was initially established as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organisation (IMCO) in 1948, became a UN specialised agency in 1959, and was renamed IMO in 1982.
- The IMO has 174 member statesand is headquartered in London.
- Organisational Structure of IMO
- The Assembly is the supreme governing body, comprising all member states. It meets every two years to approve the work programme, budget, and elect members to the Council.
- The Council acts as the Executive Organ, overseeing IMO’s work in between Assembly sessions.
- The IMO has five major Committees, which are responsible for policy development and regulation formulation, including the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC).
- Funding is sourced through mandatory contributions by member states, and also from voluntary donations and commercial revenue.
Source: PIB
Spread the Word



