Topic- 1: RECLAIM
GS-2: Governance
The context:
The Ministry of Coal is set to launch RECLAIM—a Community Engagement and Development Framework—on 4th July 2025, under the leadership of Union Minister of Coal and Mines.
About RECLAIM Framework
-
- It is a community engagement and development framework designed specifically for mine closures.
- The Coal Controller Organisation, under the Ministry of Coal, in partnership with the Heartfulness Institute, has developed this comprehensive Community Development Framework.
- It recognizes that mine closures significantly impact both landscapes and local livelihoods; this framework is a key step toward ensuring a just and sustainable transition for communities that have developed alongside mining operations over decades.
Features of the RECLAIM Framework
-
- The framework—referred to as the RECLAIM—serves as a structured guide for inclusive community engagement and development throughout the mine closure and post-closure phases.
- It offers a practical, step-by-step approach to institutionalizing community participation in the transition process.
- It is supported by a suite of actionable tools, templates, and field-tested methodologies tailored to the Indian context. Special emphasis is placed on gender inclusivity, the representation of vulnerable groups, and alignment with Panchayati Raj Institutions, ensuring that the transition is equitable and locally relevant.
- Ultimately, the RECLAIM Framework aspires to facilitate a seamless and resilient transition for mining communities—grounded in trust, ecological restoration, and long-term socio- economic well-being.
Source: PIB
Topic- 2: Financial Fraud Risk Indicator
GS-3: Internal Security
The context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued an advisory (30 June 2025) urging all Scheduled Commercial Banks, Small Finance Banks, Payments Banks, and Co-operative Banks to integrate the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) developed by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
The Key Highlights of the guidelines:
-
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has advised all banks to integrate the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) developed by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) into their systems.
- The FRI is a risk-based metric launched in May 2025 by DoT’s Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU) to classify mobile numbers as Medium, High, or Very High risk for financial fraud.
- It uses inputs from the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), Chakshu platform, and intelligence from banks and financial institutions.
- The system enables real-time alerts and responses through API-based integration between banks and DoT’s Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP).
- Banks can use FRI to prevent cyber fraud by declining or delaying suspicious transactions and issuing alerts for high-risk numbers.
- The Mobile Number Revocation List (MNRL) shared by DIU includes numbers disconnected due to cybercrime links or misuse.
- Major institutions like PhonePe, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Punjab National Bank, and Paytm are already using the FRI system.
- This integration is expected to significantly reduce UPI-based and other digital transaction frauds in India.
- The move is part of a broader push to improve digital trust and security under the Digital India initiative.
- As more financial entities adopt FRI, it is set to become a national standard for combating cyber-enabled financial fraud.
About Financial Fraud Risk Indicator:
-
- It was launched by DoT’s Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU).
- It is a risk-based metric that classifies a mobile number to have been associated with Medium, High, or Very High risk of financial fraud.
- This classification is an outcome of inputs obtained from various stakeholders including reporting on Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C’s) National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), DoT’s Chakshu platform, and Intelligence shared by banks and financial institutions.
- It empowers stakeholders-especially banks, NBFCs, and UPI service providers- to prioritize enforcement and take additional customer protection measures in case a mobile number have high risk.
- The Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU) of DoT regularly shares the Mobile Number Revocation List (MNRL) with stakeholders, detailing numbers disconnected due to cybercrime links, failed re-verification, or misuse—many of which are tied to financial frauds.
- Banks and financial institutions can use FRI in real time to take preventive measures such as declining suspicious transactions, issuing alerts or warnings to customers, and delaying transactions flagged as high risk.
- The system’s utility has already been demonstrated with leading institutions such as PhonePe, Punjab National Bank, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Paytm, and India Post Payments Bank actively using the platform.
- Significance: The FRI allows for swift, targeted, and collaborative action against suspected frauds in both telecom and financial domains.
Source: PIB
Topic- 3: C-FLOOD: A Unified Inundation Forecasting System
GS-3: Disaster Management
The context:
Union Minister of Jal Shakti inaugurated C-FLOOD, a web-based Unified Inundation Forecasting System, developed through collaboration between the Central Water Commission (CWC), C-DAC Pune, and NRSC, under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) jointly led by MeitY and DST.
Significance and Importance of C-FLOOD (Unified Inundation Forecasting System)
-
- C-FLOOD is a web-based, state-of-the-art platform that delivers two-day advance flood inundation forecasts down to the village level.
- It provides detailed flood inundation maps and water level predictions, enhancing early warning capabilities and disaster preparedness.
- The platform integrates national and regional flood modelling data, creating a unified system for informed decision-making in flood-prone areas.
- The system is currently operational in the Mahanadi, Godavari, and Tapi river basins, with plans for pan-India expansion.
- It uses advanced 2D hydrodynamic flood modelling simulations, run on High-Performance Computing (HPC) infrastructure under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM).
- The initiative exemplifies multi-agency collaboration involving CWC, C-DAC Pune, and NRSC, demonstrating inter-ministerial synergy in technological disaster management.
- Developed under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM), jointly steered by MeitY and DST, it reflects India’s growing technological prowess in disaster resilience.
- The portal aims to support national disaster response agencies by providing near-real-time data for early response, mitigation, and evacuation planning.
- The Minister of Jal Shakti has directed that C-FLOOD be integrated with the National Disaster Management Emergency Response Portal (NDEM) for real-time use in emergencies.
- Widespread awareness and accessibility of the C-FLOOD system are expected to improve community-level preparedness, especially in vulnerable rural and low-lying regions.
- The project signifies a major leap forward in flood risk reduction under India’s broader goals of climate resilience and proactive disaster management.
- The system reinforces India’s commitment to the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and the SDG targets on climate resilience (SDG 13).
Source: PIB
Topic- 4: High-Efficiency Lanthanum-Doped Supercapacitor Material
GS-3: Science and technology
The context:
On 2nd July 2025, Indian researchers from the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Bengaluru, in collaboration with Aligarh Muslim University, have engineered a next-generation lanthanum-doped silver niobate (AgNbO₃) material that significantly enhances supercapacitor performance—a critical component in energy storage technology.
Significance & Importance of the Research
-
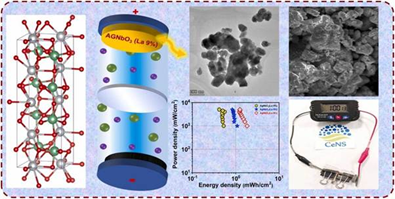
- The research introduces a breakthrough in materials science by engineering a lead-free, environmentally friendly energy storage material using lanthanum-doped silver niobate (AgNbO₃).
- It addresses a key challenge in energy storage by significantly enhancing the energy density of supercapacitors without compromising charge-discharge speed or lifespan.
- The material demonstrates 118% energy retention and 100% coulombic efficiency, showcasing exceptional performance and minimal energy loss.
- The innovation supports India’s clean energy goals by offering a sustainable alternative to conventional batteries and toxic materials.
- It contributes to the development of advanced supercapacitors that can power a range of technologies—from portable electronics to electric vehicles and grid-level storage.
- The research highlights the potential of rare-earth element doping, particularly lanthanum, in tuning the electrochemical properties of perovskite-based nanomaterials.
- It strengthens India’s indigenous scientific capabilities through collaboration between CeNS Bengaluru and Aligarh Muslim University under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The successful prototype powering an LCD display marks a crucial step toward real-world applications and commercialization of the technology.
- The development supports India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives by promoting local innovation in strategic technologies.
- The findings pave the way for future research in nano-engineered energy materials and hold promise for scalable, high-efficiency energy storage solutions globally.
Source: PIB
Topic- 5: Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development
GS-1 & 2: History and Governance & Development
The context:
The National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development (NIPCCD) has been renamed as the Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development, honouring the legacy of social reformer Savitribai Phule.
The Important Key Points:
-
- The National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development (NIPCCD) has been renamed as the Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development.
- The renaming is a tribute to Savitribai Phule, one of India’s foremost social reformers, and reflects a renewed commitment to women and child-centric development.
- The new centre will cater to the training and research needs of Mission Shakti, Mission Vatsalya, and Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 in the eastern region.
- It will specifically serve the states of Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, and West Bengal, which were previously dependent on distant centres in Guwahati and Lucknow.
- The Ranchi centre will enhance accessibility for over seven lakh frontline functionaries spread across 115 districts in these four states.
- It will also offer an Advance Diploma in Child Guidance and Counselling, alongside support for research and mental health-related services.
- This decentralised approach is expected to enable region-specific interventions and better utilisation of resources at the grassroots level.
- The Institute, headquartered in New Delhi, now has regional centres in Bangalore, Guwahati, Lucknow, Indore, Mohali, and the newly added Ranchi centre.
About Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development:
-
- A premier autonomous body under the Ministry of Women and Child Development, serving as the national apex institute for training, research, and capacity-building in women and child welfare.
Historical Legacy
-
- Renamed from NIPCCDto honour Savitribai Phule, one of India’s earliest women educationists and social reformers.
- Reflects a renewed commitment to inclusive and region-specific developmentof women and children.
-
- Headquarters:New Delhi
- Existing Regional Centres: Bangalore, Guwahati, Lucknow, Indore, Mohali
- New Centre:Ranchi (to serve Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal)
- Objectives:
- To strengthen capacity buildingfor the implementation of women and child development schemes.
- To support region-specific interventionsaligned with national missions like Mission Shakti, Vatsalya, Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0.
- Functions:
- Training:Conducts in-service and induction training for ICDS, Poshan, and other related staff.
- Research & Extension:Develops contextual solutions for gender, mental health, and adolescent welfare.
- Policy Support:Offers evidence-based insights to strengthen WCD schemes at national and regional levels.
- Documentation & Innovation:Archives best practices, module development, and digital training innovations.
- Frontline Empowerment:Serves over 7 lakh field workers by enhancing local access to training and counselling.
- Academic Programmes:Offers specialised diplomas like Child Guidance and Counselling, especially at the new Ranchi Centre.
- Significance:
- Decentralized Capacity Building: Reduces dependency on distant centres for training in Eastern India.
- Empowerment at Grassroots: Enhances last-mile delivery of services and strengthens local governance systems like Panchayats.
- Holistic Approach: Integrates mental health, education, and nutritionfor overall child and women welfare.
- Headquarters:New Delhi
Source: PIB
Spread the Word



