Topic- 1: Ayush Nivesh Saarthi Portal
GS- 3: Science and Technology
The context:
In a historic move to position India as the global epicenter for traditional medicine and wellness, the Government of India launched ‘the Ayush Nivesh Saarthi portal on 29th May 2025 during the Ayush Stakeholder/Industry Interaction Meet held at Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
About Ayush Suraksha Portal
-
- The portal was jointly unveiled by the Union Minister of Commerce & Industry and Union Minister of State (Independent Charge), Ministry of Ayush with the technical support of the Central Council for Research in Siddha (CCRS).
- It is a dedicated, investor-centric digital platform developed by the Ministry of Ayush in collaboration with Invest India.
- This portal represents a significant advancement in pharmacovigilance and regulatory convergence within the Ayush ecosystem.
- It is aligned with the National Pharmacovigilance Program, allows consumers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory authorities to report and monitor misleading advertisements and adverse drug reactions through a seamless digital process.
- The system integrates multiple authorities, including the Ayush vertical under CDSCO, MoI&B, CCPA, NCISM, NCH, PCI, FSSAI, and State Licensing Authorities, ensuring coordinated response and enforcement.
Significance of the Ayush Suraksha Portal
-
- The portal is a strategic enabler designed to attract both domestic and global investors into India’s Ayush sector, aligning with the vision of making India a global hub for traditional medicine.
- With the Ayush industry recording a 17% annual growth between 2014 and 2020, the platform leverages this momentum to further strengthen the sector’s contribution to the national economy.
- The portal aligns with the rising global demand for natural, preventive, and wellness-based healthcare, positioning Ayush as a central player in global lifestyle transformation.
- It promotes FDI and Ease of Doing Business with 100% FDI through the automatic route and offering investor-friendly features, the Ayush Nivesh Saarthi initiative signals India’s openness to innovation and collaboration in holistic healthcare.
- It showcases India’s natural wealth, including over 8,000 medicinal plant species, as a unique advantage for investment in traditional medicine and wellness.
- The Ayush sector plays a significant role in India’s USD 13 billion MVT economy, ranking among the top five health services and attracting international wellness tourism.
- The launch reaffirms the Government of India’s commitment to making Ayush a dual engine of public health and economic development.
- It positions India as a trusted global leader in traditional medicine, offering a compelling investment narrative backed by policy support, heritage, and market potential.
- With the launch of Ayush Nivesh Saarthi, the Government of India has reaffirmed its vision of making Ayush a pillar of both public health and economic growth.
Source: PIB
Topic- 2: Digital Transformation in Electoral Statistics: ECI’s Index Card Upgrade
GS-2: Polity and Governance
The context:
In June 2025, the Election Commission of India (ECI), under the leadership of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) announced the digitization and streamlining of Index Cards and Statistical Reports.
-
- This upgraded mechanism replaces the traditional manual methods, which were often time-consuming and prone to delays. By leveraging automation and data integration, the new system ensures faster reporting.
About the Index Card:
-
- It is a non-statutory, post-election Statistical Reporting Format developed as a suo moto initiative by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to promote accessibility of election-related data at the constituency level for all stakeholders, including researchers, academia, policymakers, journalists, and the general public.
- It is designed to disseminate data across multiple dimensions—such as candidates, electors, votes polled, votes counted, party-wise and candidate-wise vote share, gender-based voting patterns, regional variations, and performance of political parties—the Index Card forms the foundation for generating about 35 Statistical Reports for Lok Sabha elections and 14 for State Assembly elections.
- These reports cover variables like State/PC/AC-wise elector details, number of polling stations, state and constituency-wise voter turnout, participation of women electors, performance of national/state parties and Registered Unrecognized Political Parties (RUPPs), winning candidates’ analysis, detailed constituency-wise results, and summary data reports.
- This rich, data-driven resource enhances the capacity for deep electoral research contributing to a stronger democratic discourse.
- However, these statistical reports are meant solely for academic and research purposes and are based on secondary data from Index Cards, while the primary and final data remains in the statutory forms maintained by the concerned Returning Officers.
Earlier, this information was manually filled at the Constituency level using various statutory formats in Physical Index Cards. These physical Index Cards were subsequently used for data entry into the online system to facilitate the generation of statistical reports. This manual, multi-layered process was time-consuming and frequently led to delays in data availability and dissemination.
Source: PIB
Topic- 3: World Environment Day 2025
GS-3: Environmental Conservation
The context:
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, 06th June 2025 celebrated World Environment Day 2025 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, under the slogan ‘One Nation, One Mission: End Plastic Pollution’.
Key Highlights: National Plastic Pollution Reduction Campaign & Related Initiatives
-
- The Government of India reiterated that maintaining environmental balance is intrinsic to Indian culture, and highlighted India’s early proactive steps on plastic pollution before it gained global attention.
- The event was attended by dignitaries including the Union Environment Minister, Lieutenant Governor of Delhi, Chief Minister of NCT of Delhi, and other senior officials, reflecting the ‘Whole of Government’ and ‘Whole of Society’ approach.
The Union Minister for Environment emphasized:
-
- The role of electric buses in tackling Delhi’s vehicular pollution.
- The need for collective state action to address pollution in River Yamuna.
- The importance of banning plastic carry bags below 120 microns and avoiding single-use plastics.
- The necessity of recycling technologies and linking innovation with business opportunities to promote circular economy.
- Adoption of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) guidelines and Mission LiFE principles to reduce the use of virgin resources.
- An increase in Delhi’s tree cover over the past three years.
- The importance of greening the Aravalli region.
- The need for collective behavioural change to address plastic pollution.
- The role of innovation and technology in developing eco-friendly alternatives.
Major Launches and Publications:
-
-
Two key publications were released:
-
-
-
- Government Initiatives on Ending Plastic Pollution – documents collective efforts by Government and Industry.
- Compendium on Eco-alternatives to Single Use Plastics – a national-level compilation of sustainable alternatives.
-
-
-
National Plastic Waste Reporting Portal was launched:
-
-
-
- Replaces manual, multi-step processes with digitized online reporting.
- Tracks the full plastic waste management ecosystem from collection to disposal.
- Enables data transparency and supports better planning by Urban Local Bodies and District Panchayats.
-
-
-
- The National Plastic Pollution Reduction Campaign, which includes: Targeted initiatives in Tiger Reserves, urban/rural areas, and government offices (under Special Campaign 5.0) and Hackathon for eco-alternatives to single-use plastics.
- Youth engagement through poem and slogan writing, and street plays (Nukkad Nataks).
- 21 winners of the Ideas4LiFE initiative were felicitated, under seven LiFE themes.
- Pre-campaign outreach saw 69,000 events with participation of over 21 lakh people nationwide.
-
-
-
National Expo on Eco-alternatives:
- A National Expo was held showcasing:
- Participation from 150 startups, recyclers, and local bodies.
- Innovations in eco-alternatives and plastic waste management.
- A separate pavilion dedicated to Mission LiFE.
- Display of student paintings on environmental themes by NMNH.
- A National Expo was held showcasing:
-
Source: PIB
Topic- 4: EnviStats India 2025: Environment Statistics
GS-3: Environmental Conservation
The context:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), Government of India, released the 8th issue of the publication titled “EnviStats India 2025: Environment Statistics” during the National Workshop on Using Alternate Data Sources and Frontier Technologies for Policy Making on 5th June, 2025 in New Delhi.
Key highlights of the publication
-
- Thermal power generation has increased from 7,92,053 GWh to 13,26,549 GWh and Electricity generation from renewable energy sources has increased from 65520 GWh to 2,25,835 GWh during 2013-14 to 2023-24.
-
- Inland fish production has increased from 61.36 lakh tonnes to 139.07 lakh tonnes during 2013-14 to 2023–24.
- Since 2018, the National Statistics Office (NSO) has been publishing “EnviStats India” in alignment with the Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) 2013.
- The data presented in the publication are compiled based on the data, sourced from various Ministries, Departments, and Organizations of the Government of India.
EnviStats India 2025: Environment Statistics
-
- It is a key resource for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders, offering a comprehensive overview of the country’s environmental landscape. Through the analysis of key environmental indicators, the publication highlights emerging environmental trends, identifies pressing challenges, and supports the development of evidence-based policies aimed at achieving environmental sustainability and resilience.
This year’s publication introduced several changes in its formation and structure, which inter alia includes:
1. An expert group comprising representatives from line Ministries/Departments and domain experts in the field of environment was constituted to consult on potential improvements to the publication, including expanding its scope, identifying potential data sources, and suggesting refinements in its design and presentation.
2. The publication has been restructured to provide information in a component-wise format.
3. The concordance of indicators collected for EnviStats 2025 was mapped vis-à-vis FDES 2013. The comprehensive list of indicators under the Basic Set of Environment Statistics from FDES 2013 is also included in the publication.
4. New data on the population’s access to electricity, transport, and sanitation is included. An indicator containing List of Ramsar Sites was compiled based on the Expert Group’s recommendations.
Important Highlights of the publication “EnviStats India 2025: Environment Statistics”
-
- The annual mean temperature increased from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024. Similarly, the annual minimum and maximum temperature rose from 19.32°C to 20.24°C and 30.78°C to 31.25°C respectively, during the same period.
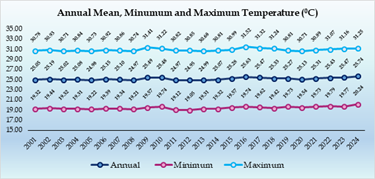
-
- The annual rainfall data from 2001 to 2024 highlights significant year-to-year variability influenced by monsoon patterns. Despite this variability, the data does not indicate any clear long-term upward or downward trend in total annual rainfall.
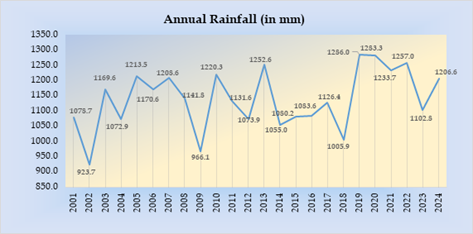
-
- Globally, there are 2,47,605 marine faunal species, while India accounts for 20,613. India has 9,436 freshwater species, 5,023 species in the Indian Mangrove System, 3,383 species in the Estuarine Ecosystem, and a notable 22,404 species in its Soil Ecosystem. When considering the total count of faunal species, the world has 16,73,627 species of which 1,04,561 are found in India. This data underscores India’s significant contribution to global faunal diversity across different habitats and high number of soil species in India is also noteworthy.
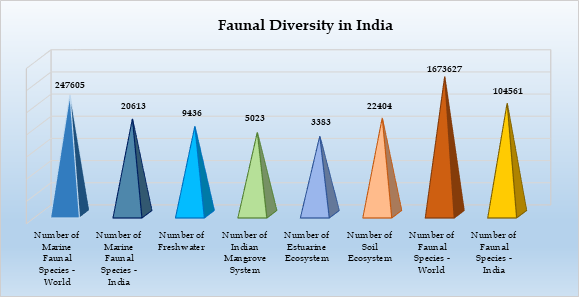
-
- Inland fish production has increased from 61.36 lakh tonnes in 2013-14 to 139.07 lakh tonnes in 2023–24, possibly indicating inland aquaculture and freshwater fisheries. With a slower growth, Marine production has also increased from 34.43 lakh tonnes to 44.95 lakh tonnes during the same period.
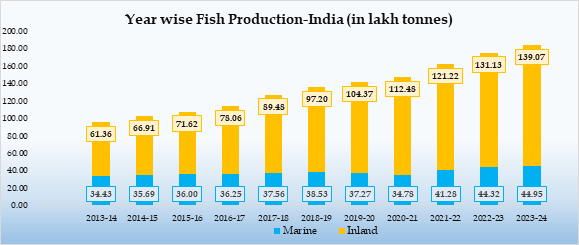
-
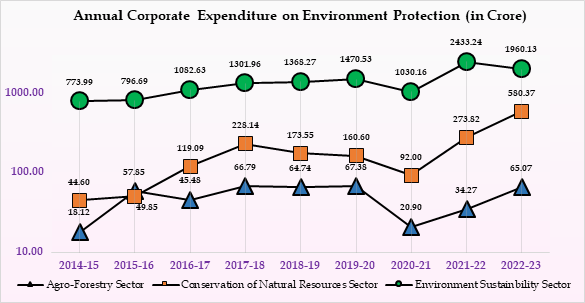
- The Environment Sustainability Sector shows the highest expenditure share as Rs. 2433.24 crore in 2021-22. The Conservation of Natural Resource Sector shows an upward trend and the Agro-Forestry Sector exhibits the lowest expenditure among the three sectors: Agro-Forestry, Conservation of Natural Resources, and Environment Sustainability.
Source: PIB
Spread the Word
