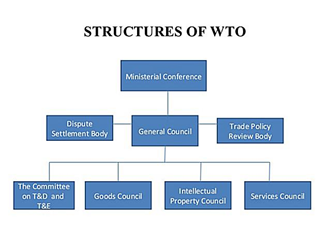
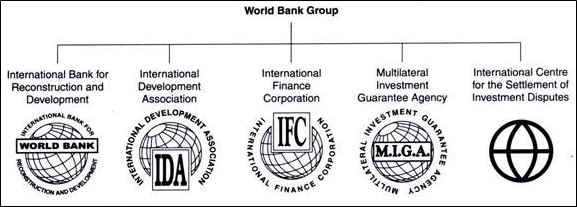
-
Land Acquisition and Clearances:
-
- Delays in land acquisition and clearances affect infrastructure sectors.
- Issues with onboarding digital land records.
- Greenfield airport projects face time-intensive processes due to site selection and approvals.
-
-
Skill Demands:
-
- Limited technical knowledge in aviation sectors like MRO operations and manufacturing.
- Specialized skills needed for project development and management.
- Effective public-private partnerships are essential for skill development.
-
-
Private Sector Participation:
-
- High capital investment and long payback periods deter private involvement.
- Project structuring issues, delays in clearances, lack of independent regulators, and contractual issues impact participation.
-
-
Climate and Environmental Sustainability:
-
- Aviation sector faces compliance challenges with CORSIA from 2027.
- No ICAO-approved emissions unit programs in India.
- Cost of sustainable aviation fuel is significantly higher than fossil fuel.
-
-
Aggregation of Financial Flows:
-
- Complex financing structure with multiple stakeholders and instruments.
- Inconsistent reporting formats and sectoral splits make aggregation difficult.
- Lack of comprehensive data on capital expenditure and fund flows.
-
-
Monitoring Infrastructure Progress:
-
-
- No single source for tracking physical progress of infrastructure projects.
- Coordination needed between central, state governments, and project authorities to evaluate progress.
-
Conclusion and Outlook
-
- Infrastructure Growth: India has seen transformative changes in infrastructure with significant advancements in road, rail, air connectivity, sanitation, and digital infrastructure.
- Public Sector Dominance: Between FY19 and FY23, Central and State Governments contributed 49% and 29% of total infrastructure investments, respectively, while the private sector contributed 22%.
- Private Sector Role: Increased private sector financing and innovative resource mobilisation, like pooled financing and asset recycling, are crucial for sustaining infrastructure development.
- Data and Reporting Improvements: Enhanced data capture and reporting mechanisms are needed to track infrastructure demand, utilisation, and financial flows across sectors and instruments.
- Database Consolidation: Developing a unified mechanism for consolidating infrastructure data and financial flows, with regular updates and sectoral bifurcation, will aid in better policymaking and resource allocation.