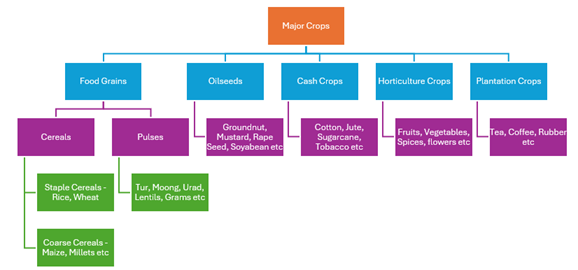
Note: Food crops include cereals, millets, pulses, fruits and vegetables
Foodgrain production in India – Statistics
-
- Total foodgrain production in India has increased from 51 million tonnes in 1951 to more than 325 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- Rice has the largest share of foodgrains with an estimated production of more than 130 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- Wheat production in India is largely about 110 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- Under coarse cereals, maize constitute more than 38 million tonnes out of total 57 million tonnes coarse cereals production in 2022-23. It is more than 60% of total coarse cereals production in India.
- Total oilseed production in 2022-23 has substantially increased to more than 413 lakh tonnes. Despite record production, India is largely an edible oil importer with India’s edible oil imports having increased from 11.6 mt (valued at Rs 60,750 crore) in 2013-14 to 16.5 mt (Rs 138,424 crore) in 2022-23.
Cropping Seasons in India
There are three crop patterns or seasons in India which are Rabi, Kharif, and Zaid. Rabi crops are those which are grown in the winter season like wheat, gram, mustard, pea, etc. Kharif crops are sown in the rainy season. These include rice, sugarcane, cotton, etc. Zaid crops are the summer crops such as cucumber, watermelon, etc.
Spread the Word



