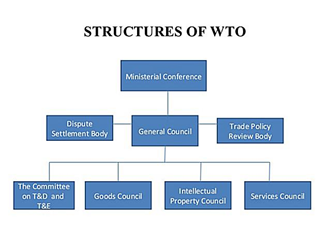
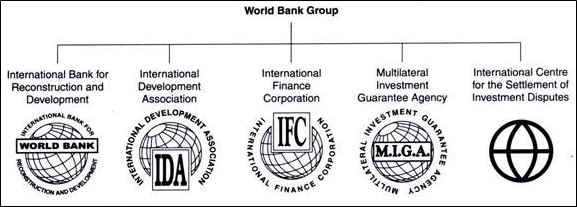
Economic planning refers to various policies, schemes and strategies of the government to achieve high and sustained economic growth. It is tasked with efficient allocation of scarce resources – physical, financial and human, for holistic and equitable development in an economy.
Types of Economic Planning
1. Imperative Planning: Socialist economy, Centralisation of planning
2. Indicative Planning: Mixed economy, Government as facilitator and private sector participation is encouraged
3. Perspective Planning: Long-term plans of 15-20 years which are broken into various short-term and medium-term goals.
4. Rolling Plan: Every year three types of plans are created (short-term, medium-term, long-term), but there is no fixed date of achieving it. Moreover, the targets are revised every year.
Note: The planning under the NITI Aayog is somewhere between Perspective and Rolling Planning.
Economic Planning before Independence
| Name of Plan | Year | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Visvesvaraya Plan | 1934 | Shift from agriculture to industrialisation. Focus on employment generation |
| National Planning Committee | 1938 | Focus on raising standard of living of masses |
| Bombay Plan | 1944 | Focus on state intervention in planning |
| Gandhian Plan | 1944 | Economic decentralisation and focus on cottage industries |