Human Development
Human development is defined as the process of enlarging people’s freedoms and opportunities and improving their well-being. The human development concept was developed by economist Mahbub ul Haq. Central to the human development approach is the concept of capabilities.
Pillars of Human Development
-
- Equality
- Sustainability
- Productivity
- Empowerment
Human Development Index (HDI)
-
- Human Development Reports (HDRs) have been released since 1990 and have explored different themes through the human development approach.
- The first HDR was launched in 1990 by the Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and Indian Nobel laureate Amartya Sen.
- The reports produced by the Human Development Report Office for the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) are ensured of editorial independence by the United Nations General Assembly.
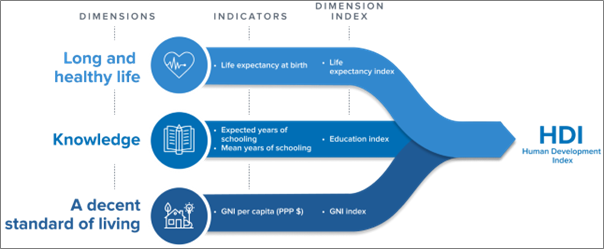
-
- The HDI is the geometric mean of normalised indices for each of the three dimensions.
- The HDI sets a minimum and a maximum for each dimension, called “goalposts”, then shows where each country stands in relation to these goalposts.
- This is expressed as a value between 0 and 1. The higher a country’s human development, the higher its HDI value.
- Geometric Mean of

- The HDI is the geometric mean of normalised indices for each of the three dimensions.
Four categories of countries (As per HDI)
-
- Very High – 0.800 and above
- High – 0.700 to 0.799
- Medium – 0.550 to 0.699
- Low – below 0.550
Human Development Report 2023-24
-
- Theme of the Report: The 2023-24 HDR was titled “Breaking the Gridlock: Reimagining Cooperation in a Polarized World.”
- India’s Ranking: India’s ranking in the Human Development Index (HDI) improved slightly from 134 in 2022 to 133 in 2023-24.
- India’s Category: India remained in the medium human development category.
- India’s HDI Progress: Between 1990 and 2022, India’s HDI value increased by 48.4%, from 0.434 to 0.644.
- Life Expectancy: India’s life expectancy at birth improved slightly from 67.2 years in 2021 to 67.7 years in 2022.
- Expected Years of Schooling (EYS): There was a notable increase of 5.88% in EYS, from 11.9 years to 12.6 years, resulting in an improvement of 18 places.
- Gross National Income (GNI) per Capita: GNI per capita also improved from $6,542 to $6,951.
- Performance of India’s Neighbours: Sri Lanka and China were ranked higher in the High Human Development category, while Bhutan and Bangladesh were ranked lower than India. Nepal and Pakistan were ranked even lower.
- Progress in Reducing Gender Inequality: India made progress in reducing gender inequality, ranking 108 out of 166 countries in the Gender Inequality Index (GII) 2022. The GII value of 0.437 was better than the global and South Asian averages.
- Reproductive Health: India’s performance in reproductive health was better than other countries in the medium human development group or South Asia.
- Adolescent Birth Rate: India’s adolescent birth rate in 2022 improved to 16.3 births per 1,000 women ages 15-19, down from 17.1 in 2021.
- Gender Gap in Labor Force Participation: India still faced challenges with a large gender gap in the labour force participation rate, with a 47.8 percentage point difference between women (28.3%) and men (76.1%).




