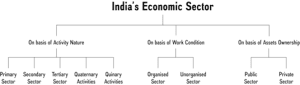
On the basis of Sectors of Economy
- Primary Sector: It includes the production of goods and services using natural resources. Eg- Agriculture and allied activities, Mining and Quarrying
- Secondary Sector: It includes processing of natural resources into value added goods. Eg- Manufacturing, Construction
- Tertiary Sector: These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. This is also known as the service sector. Eg – Transportation, traders, banking etc.
- Quaternary Activities: Intellectual and knowledge-based activities. Eg – R&D, Project consulting and assessment.
- Quinary Activities: High-level decision making. Eg- Top management in an industry, Policy makers etc.
Government of India classification
Agriculture and Allied Sector: It includes Agriculture, Livestock, Forestry and Fishing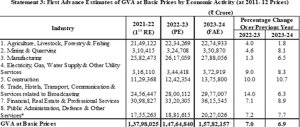
Industries: It includes Mining and Quarrying; Manufacturing; Electricity, Gas, Water Supply and Other Utility Services; Construction.
Services: This sector includes Trade, Hotels, Transport, Communication and services related to Broadcasting; Financial, Real Estate and Professional Services; Public Administration, Defence and Other Services.
On the basis of working condition
-
- Organised sector
-
-
- The employment term is regular.
- Workers enjoy the security of employment.
- Firms must comply with the laws and regulations set out in various laws, including the Minimum Wages Act, Factories Act, the Gratuity Payment Act, the Shops and Establishments Act, and so on.
-
-
-
Unorganised sector
-
-
-
- It is characterised by small and scattered units, which are largely outside the control of the government.
- Jobs are low-paid and often not regular.
-
Government of India classification: As per National Commission for Enterprises in Unorganized Sector (NCEUS) classification, the unorganised sector consists of all unincorporated private enterprises owned by individuals or households engaged in the sale and production of goods and services operated on a proprietary or partnership basis and with less than ten total workers.
However, informal workers consist of those working in the unorganised enterprises or households, excluding regular workers with social security benefits, and the workers in the formal sector without any employment benefits/social security provided by the employers.
On the basis of ownership
- Public Sector: Ownership of assets in government hands. For example: Indian Railways, BSNL etc.
- Private Sector: Individuals or Firms own the assets. For example: Reliance Industries, Tata Motors etc.