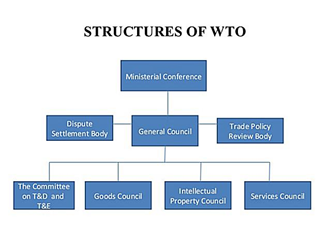
Microeconomics
-
- Microeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals, households, and businesses in their decision-making processes regarding the allocation of scarce resources.
- It examines how these entities interact in markets, determining the prices of goods and services, the supply and demand dynamics, and the production and consumption patterns within specific sectors or industries.
- Microeconomics also analyses the impact of government policies, market structures, and competition on these interactions.
Macroeconomics
-
- Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies broader economic factors and the overall functioning of national or global economies.
- It explores aggregate indicators such as GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, interest rates, national income, and economic growth.
- Macroeconomics seeks to understand and explain economic trends and patterns, and to develop policies that can influence the economy.
- Macroeconomics is essential for policymakers, economists, and business leaders to make informed decisions that affect broader economic outcomes.
Note: It is the macroeconomics branch of economics which is loosely the syllabus for Economy from the perspective of UPSC
| Basis | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Individual/Firm | Whole Economy |
| Prices level | Individual goods and services | General inflation level |
| Labour | Individual labour market | Employment indicators |
| Demand | Individual consumption level | Aggregate Demand |
| Supply | Firms’ production level | Aggregate supply and productivity |
Spread the Word