Day-770
Quiz-summary
0 of 20 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 20 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
Which of the following actions can help in reducing India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD)?
1) Reduction in oil imports
2) Promotion of agricultural exports
3) Importing more gold
Choose the correct option given below:Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 2 are correct:
● To reduce CAD, India needs to promote exports and slow down consumption imports such as fuels, electronic items and gold.
● Reduction of fuel subsidies will also reduce the demand for imported fuel and thus trade balance.
Additional Information:
● A current account deficit (CAD) occurs when the country’s expenditure is more than its income. CAD may occur when the country’s expenditure in imports is more than its income from exports of goods and services.
● CAD records every transaction including foreign investment in an Indian company or transfer of money made by an individual back home in India over a period.
● CAD is an important tool to measure the health of a country’s economy. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) releases the CAD data every financial quarter, which is measured in the U.S. dollar and as a percentage of the gross domestic product (GDP).Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 2 are correct:
● To reduce CAD, India needs to promote exports and slow down consumption imports such as fuels, electronic items and gold.
● Reduction of fuel subsidies will also reduce the demand for imported fuel and thus trade balance.
Additional Information:
● A current account deficit (CAD) occurs when the country’s expenditure is more than its income. CAD may occur when the country’s expenditure in imports is more than its income from exports of goods and services.
● CAD records every transaction including foreign investment in an Indian company or transfer of money made by an individual back home in India over a period.
● CAD is an important tool to measure the health of a country’s economy. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) releases the CAD data every financial quarter, which is measured in the U.S. dollar and as a percentage of the gross domestic product (GDP). -
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the World Bank Group:
1) International Development Association (IDA) promotes private sector investments in developing countries.
2) International Finance Corporation (IFC) is responsible for providing long term, interest free loans to poor nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
● Statement 1 is not correct: International Development Association (1960) –aims to reduce poverty by providing loans (called “credits”) and grants for programs that boost economic growth, reduce inequalities, and improve people’s living conditions. IDA is responsible for providing long term, interest free loans to poor nations. IDA repayments are stretched for 25-40 years, including a grace period also.
● Statement 2 is not correct: International Finance Corporation (1956): It is the largest global development institution focused exclusively on the private sector in developing countries. It is a private-sector arm of the World Bank Group, to advance economic development by investing in for-profit and commercial projects for poverty reduction and promoting development.
Additional Information:
The World Bank Group consists of five organizations:
The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
● The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) lends to governments of middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries.
The International Development Association
● The International Development Association (IDA) provides interest-free loans — called credits — and grants to governments of the poorest countries.
Together, IBRD and IDA make up the World Bank.
The International Finance Corporation
● The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is the largest global development institution focused exclusively on the private sector. It helps developing countries achieve sustainable growth by financing investment, mobilizing capital in international financial markets, and providing advisory services to businesses and governments.
The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
● The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) was created in 1988 to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries to support economic growth, reduce poverty, and improve people’s lives. MIGA fulfils this mandate by offering political risk insurance (guarantees) to investors and lenders.
The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes
● The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) provides international facilities for conciliation and arbitration of investment disputes.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
● Statement 1 is not correct: International Development Association (1960) –aims to reduce poverty by providing loans (called “credits”) and grants for programs that boost economic growth, reduce inequalities, and improve people’s living conditions. IDA is responsible for providing long term, interest free loans to poor nations. IDA repayments are stretched for 25-40 years, including a grace period also.
● Statement 2 is not correct: International Finance Corporation (1956): It is the largest global development institution focused exclusively on the private sector in developing countries. It is a private-sector arm of the World Bank Group, to advance economic development by investing in for-profit and commercial projects for poverty reduction and promoting development.
Additional Information:
The World Bank Group consists of five organizations:
The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
● The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) lends to governments of middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries.
The International Development Association
● The International Development Association (IDA) provides interest-free loans — called credits — and grants to governments of the poorest countries.
Together, IBRD and IDA make up the World Bank.
The International Finance Corporation
● The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is the largest global development institution focused exclusively on the private sector. It helps developing countries achieve sustainable growth by financing investment, mobilizing capital in international financial markets, and providing advisory services to businesses and governments.
The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
● The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) was created in 1988 to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries to support economic growth, reduce poverty, and improve people’s lives. MIGA fulfils this mandate by offering political risk insurance (guarantees) to investors and lenders.
The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes
● The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) provides international facilities for conciliation and arbitration of investment disputes. -
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
Consider the following:
1. Borrowing capacity of a member country
2. Financial resources that the member country is obliged to provide IMF
3. Voting Rights
4. SDR allocation to member countries
How many of the above are dependent on the “QUOTA” assigned by the IMF to its member countries?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statements 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct:
● Quota subscriptions are a central component of the IMF’s financial resources.
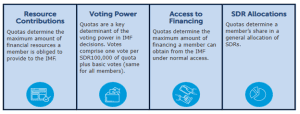
● A member country’s quota determines:
⮚ Its maximum financial commitment to the IMF – A member’s quota subscription determines the maximum amount of financial resources the member is obliged to provide to the IMF.
⮚ A member must pay its subscription in full upon joining the Fund: up to 25 percent must be paid in SDRs or other members’ currencies specified by the IMF, and the rest is paid in the member’s own currency.
⮚ Voting power – each member gets an equal share of what are called “basic votes,” plus additional votes based on quota.
⮚ Access to IMF financing
⮚ Quotas also determine how SDRs are allocated to countries.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statements 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct:
● Quota subscriptions are a central component of the IMF’s financial resources.
● A member country’s quota determines:
⮚ Its maximum financial commitment to the IMF – A member’s quota subscription determines the maximum amount of financial resources the member is obliged to provide to the IMF.
⮚ A member must pay its subscription in full upon joining the Fund: up to 25 percent must be paid in SDRs or other members’ currencies specified by the IMF, and the rest is paid in the member’s own currency.
⮚ Voting power – each member gets an equal share of what are called “basic votes,” plus additional votes based on quota.
⮚ Access to IMF financing
⮚ Quotas also determine how SDRs are allocated to countries.


-
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Executive Board of the IMF:
1. The Executive Board conducts the day-to-day functions of the IMF.
2. It is a 24-member body elected by the Board of Governors.
3. The IMF is led by a managing director, who serves as the Chairman of the executive board.
4. Five of the seats on the Executive Board are reserved for the Directors appointed by the members with the five largest quotas.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
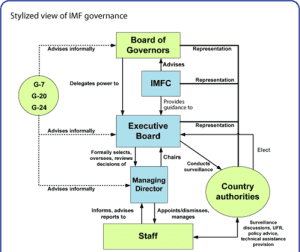
Statement 1 is correct:
● The Executive Board (the Board) is responsible for conducting the day-to-day business of the IMF.
Statements 2 and 3 are correct:
● It is composed of 24 Directors, who are elected by the member countries or by groups of countries, and the Managing Director, who serves as its Chairman.
● The Board usually meets several times each week.
● It carries out its work largely on the basis of papers prepared by IMF management and staff.
Statement 4 is incorrect:
After reforms completed in 2016, for the first time, all seats on the IMF Executive Board are held by Executive Directors elected by IMF member countries.
● Previously, five of the seats on the Executive Board were reserved for Directors appointed by the members with the five largest quotas.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
● The Executive Board (the Board) is responsible for conducting the day-to-day business of the IMF.
Statements 2 and 3 are correct:
● It is composed of 24 Directors, who are elected by the member countries or by groups of countries, and the Managing Director, who serves as its Chairman.
● The Board usually meets several times each week.
● It carries out its work largely on the basis of papers prepared by IMF management and staff.
Statement 4 is incorrect:
After reforms completed in 2016, for the first time, all seats on the IMF Executive Board are held by Executive Directors elected by IMF member countries.
● Previously, five of the seats on the Executive Board were reserved for Directors appointed by the members with the five largest quotas.

-
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
Consider the following statements regarding India’s position in IMF after reforms of 2016:
1. India’s quota share increased from 2.44% to 2.75 %.
2. India is the 8th largest quota holding country in the IMF.
3. India’s voting rights increased from 2.3% to 2.6%.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
IMF Reforms:
IMF reforms related to member’s Quota and Voting power are done under General Review of Quota mechanism.
14th General Review of Quota was implemented in year 2016-17, and new position of India in IMF in terms of Quota and Voting share are as follow:
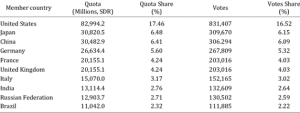
Statement 1 is correct:
● India’s quota share increased to 2.75 % (from 2.44%).
Statement 2 is correct:
● India is the 8th largest quota holding country in the IMF.
Statement 3 is correct:
● In comparison, China and the US hold quotas of 6.4 % and 17.43 %, respectively.
● India’s voting rights increased to 2.63% (from 2.3%).
Some of the top countries with their Quota and Voting share are shown in given figure below:


The 15th General Review of Quotas concluded in 2020 with no increase in quotas and provided guidance for the 16th Review. The 16th Review is currently ongoing and expected to be completed by mid-December 2023.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
IMF Reforms:
IMF reforms related to member’s Quota and Voting power are done under General Review of Quota mechanism.
14th General Review of Quota was implemented in year 2016-17, and new position of India in IMF in terms of Quota and Voting share are as follow:
Statement 1 is correct:
● India’s quota share increased to 2.75 % (from 2.44%).
Statement 2 is correct:
● India is the 8th largest quota holding country in the IMF.
Statement 3 is correct:
● In comparison, China and the US hold quotas of 6.4 % and 17.43 %, respectively.
● India’s voting rights increased to 2.63% (from 2.3%).
Some of the top countries with their Quota and Voting share are shown in given figure below:



The 15th General Review of Quotas concluded in 2020 with no increase in quotas and provided guidance for the 16th Review. The 16th Review is currently ongoing and expected to be completed by mid-December 2023. -
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
With reference to the credit facilities of the IMF, consider the following statements:
1. The Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI) provides fast concessional financial assistance to low-income countries (LICs) facing an urgent balance of payments need.
2. The Rapid Credit Facility (RCF) provides prompt financial assistance to any IMF member country facing an urgent balance of payments need.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI):
● RFI provides prompt financial assistance to any IMF member country facing an urgent balance of payments need.
Purpose:
● Provide rapid, low-access financial assistance to countries facing urgent balance of payments needs that, if not addressed, would result in an immediate and severe economic disruption.
● Respond to situations where a full-fledged economic program is not necessary because the need is transitory and limited in nature, or not feasible because of policy design, capacity and other implementation constraints.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Rapid Credit Facility (RCF):
● RCF provides fast concessional financial assistance to low-income countries (LICs) facing an urgent balance of payments need.
● The RCF is one of the facilities under the Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust (PRGT) that provide flexible financial support tailored to the diverse needs of LICs, including in times of crisis.
Purpose:
● Provide concessional, rapid, and low-access financial assistance to qualifying LICs facing an urgent balance of payments need from a wide variety of circumstances, including external shocks, natural disasters, and emergencies connected to fragility.
● Respond to situations where a full-fledged economic program is not necessary because the need is transitory and limited in nature, or not feasible, including when facing capacity constraints of policy implementation.
● Provide policy support that may help catalyze foreign aid.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI):
● RFI provides prompt financial assistance to any IMF member country facing an urgent balance of payments need.
Purpose:
● Provide rapid, low-access financial assistance to countries facing urgent balance of payments needs that, if not addressed, would result in an immediate and severe economic disruption.
● Respond to situations where a full-fledged economic program is not necessary because the need is transitory and limited in nature, or not feasible because of policy design, capacity and other implementation constraints.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Rapid Credit Facility (RCF):
● RCF provides fast concessional financial assistance to low-income countries (LICs) facing an urgent balance of payments need.
● The RCF is one of the facilities under the Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust (PRGT) that provide flexible financial support tailored to the diverse needs of LICs, including in times of crisis.
Purpose:
● Provide concessional, rapid, and low-access financial assistance to qualifying LICs facing an urgent balance of payments need from a wide variety of circumstances, including external shocks, natural disasters, and emergencies connected to fragility.
● Respond to situations where a full-fledged economic program is not necessary because the need is transitory and limited in nature, or not feasible, including when facing capacity constraints of policy implementation.
● Provide policy support that may help catalyze foreign aid. -
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
Arrange the following agencies in the chronological order of their year of establishment:
1. National Stock Exchange (NSE)
2. Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
3. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
4. National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
Choose the correct option given below:Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) – 1875
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) – Established in 1988, became a statutory body in 1992.
National Stock Exchange (NSE) – 1992
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) – 1996
Additional Information:
National Stock Exchange (NSE):
● The National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE) is India’s largest financial market.
● Incorporated in 1992.
● The NSE has developed into a sophisticated, electronic market, which ranked fourth in the world by equity trading volume.
● Trading commenced in 1994 with the launch of the wholesale debt market and a cash market
segment shortly thereafter.
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
● BSE Limited, also known as the Bombay Stock Exchange is an Indian stock exchange which is located on Dalal Street in Mumbai.
● Established in 1875 by cotton merchant Premchand Roychand, it is the oldest stock exchange in Asia, and also the tenth oldest in the world.
● The BSE is one of the world’s largest stock exchanges by market capitalization with a market cap of US$ 3.8 trillion as of June 2023.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI):
● It was constituted as a non-statutory body on April 12, 1988 through a resolution of the Government of India.
● The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established as a statutory body in the year 1992 and the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 came into force on January 30, 1992.
● Functions of SEBI: To protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of and to regulate the securities market.
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL):
● It is an Indian central securities depository under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance based in Mumbai.
● The enactment of Depositories Act in August 1996 paved the way for establishment of NSDL.
● It was established in 1996 as the first electronic securities depository in India with national coverage.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) – 1875
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) – Established in 1988, became a statutory body in 1992.
National Stock Exchange (NSE) – 1992
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) – 1996
Additional Information:
National Stock Exchange (NSE):
● The National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE) is India’s largest financial market.
● Incorporated in 1992.
● The NSE has developed into a sophisticated, electronic market, which ranked fourth in the world by equity trading volume.
● Trading commenced in 1994 with the launch of the wholesale debt market and a cash market
segment shortly thereafter.
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
● BSE Limited, also known as the Bombay Stock Exchange is an Indian stock exchange which is located on Dalal Street in Mumbai.
● Established in 1875 by cotton merchant Premchand Roychand, it is the oldest stock exchange in Asia, and also the tenth oldest in the world.
● The BSE is one of the world’s largest stock exchanges by market capitalization with a market cap of US$ 3.8 trillion as of June 2023.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI):
● It was constituted as a non-statutory body on April 12, 1988 through a resolution of the Government of India.
● The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established as a statutory body in the year 1992 and the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 came into force on January 30, 1992.
● Functions of SEBI: To protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of and to regulate the securities market.
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL):
● It is an Indian central securities depository under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance based in Mumbai.
● The enactment of Depositories Act in August 1996 paved the way for establishment of NSDL.
● It was established in 1996 as the first electronic securities depository in India with national coverage. -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) was Asia’s second stock exchange established after Tokyo Stock Exchange of Japan.
2. The National Stock Exchange (NSE) was the first stock exchange of India on which trading took place electronically.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
About Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
● BSE Ltd was established in 1875 and was Asia’s first Stock Exchange.
● It was granted permanent recognition under the Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956.
● It has contributed to the growth of the corporate sector by providing a platform for raising capital.
● It is known as BSE Ltd but was established as the Native Share Stock Brokers Association in 1875.
Objectives:
(a) To provide an efficient and transparent market for trading in equity, debt instruments, derivatives, and mutual funds.
(b) To provide a trading platform for equities of small and medium enterprises.
(c) To ensure active trading and safeguard market integrity through an electronically-driven exchange.
(d) To provide other services to capital market participants, like risk management, clearing, settlement, market data, and education.
(e) To conform to international standards.
● The exchange has about 5000 companies listed from all over the country and outside, and has the largest market capitalisation in India.
Statement 2 is correct:
About National Stock Exchange (NSE):
● The National Stock Exchange is the latest, most modern and technology driven exchange.
● It was incorporated in 1992 and was recognised as a stock exchange in April 1993.
● It started operations in 1994, with trading on the wholesale debt market segment.
● Subsequently, it launched the capital market segment in November 1994 as a trading platform for equities and the futures and options segment in June 2000 for various derivative instruments.
● It was the first stock exchange on which trading took place electronically.
Objectives:
a) Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
b) Ensuring equal access to investors all over the country through an appropriate communication network.
c) Providing a fair, efficient and transparent securities market using electronic trading system.
d) Enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements.
e) Meeting international benchmarks and standards.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
About Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
● BSE Ltd was established in 1875 and was Asia’s first Stock Exchange.
● It was granted permanent recognition under the Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956.
● It has contributed to the growth of the corporate sector by providing a platform for raising capital.
● It is known as BSE Ltd but was established as the Native Share Stock Brokers Association in 1875.
Objectives:
(a) To provide an efficient and transparent market for trading in equity, debt instruments, derivatives, and mutual funds.
(b) To provide a trading platform for equities of small and medium enterprises.
(c) To ensure active trading and safeguard market integrity through an electronically-driven exchange.
(d) To provide other services to capital market participants, like risk management, clearing, settlement, market data, and education.
(e) To conform to international standards.
● The exchange has about 5000 companies listed from all over the country and outside, and has the largest market capitalisation in India.
Statement 2 is correct:
About National Stock Exchange (NSE):
● The National Stock Exchange is the latest, most modern and technology driven exchange.
● It was incorporated in 1992 and was recognised as a stock exchange in April 1993.
● It started operations in 1994, with trading on the wholesale debt market segment.
● Subsequently, it launched the capital market segment in November 1994 as a trading platform for equities and the futures and options segment in June 2000 for various derivative instruments.
● It was the first stock exchange on which trading took place electronically.
Objectives:
a) Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
b) Ensuring equal access to investors all over the country through an appropriate communication network.
c) Providing a fair, efficient and transparent securities market using electronic trading system.
d) Enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements.
e) Meeting international benchmarks and standards. -
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
The General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) covers four modes of supplying services.
Regarding this, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Consumption abroad means services availed by a tourist in another country.
2. Commercial presence means when persons of one member country enter into the territory of another country to supply a service.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
The GATS distinguishes between four modes of supplying services:
⮚ cross-border trade
⮚ consumption abroad
⮚ commercial presence
⮚ presence of natural persons
1. Cross-border supply –
● It is defined to cover services flows from the territory of one member into the territory of another member (e.g. banking or architectural services transmitted via telecommunications or mail).
Statement 1 is correct:
2. Consumption abroad –
● It refers to situations where a service consumer (e.g. tourist or patient) moves into another member’s territory to obtain a service.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
3. Commercial presence –
● It implies that a service supplier of one member establishes a territorial presence, including through ownership or lease of premises, in another member’s territory to provide a service (e.g. domestic subsidiaries of foreign insurance companies or hotel chains).
4. Presence of natural persons –
● It consists of persons of one member entering the territory of another member to supply a service (e.g. accountants, doctors or teachers).Additional Information on GATS:
● It is a treaty of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) that entered into force in 1995.
● All members of the WTO are parties to the GATS.
● The fundamental principles of the GATS apply, in principle, to all service sectors.
The objectives are:
● To create a reliable and predictable system of international rules for trade in services.
● To facilitate the progressive liberalisation of services markets.
The fundamental principles of the GATS apply, in principle, to all service sectors.
● There are two exceptions:
a) Services supplied in the exercise of governmental authority on a con-commercial basis, such as social security schemes, public health, education.
b) Services related to air transport.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
The GATS distinguishes between four modes of supplying services:
⮚ cross-border trade
⮚ consumption abroad
⮚ commercial presence
⮚ presence of natural persons
1. Cross-border supply –
● It is defined to cover services flows from the territory of one member into the territory of another member (e.g. banking or architectural services transmitted via telecommunications or mail).
Statement 1 is correct:
2. Consumption abroad –
● It refers to situations where a service consumer (e.g. tourist or patient) moves into another member’s territory to obtain a service.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
3. Commercial presence –
● It implies that a service supplier of one member establishes a territorial presence, including through ownership or lease of premises, in another member’s territory to provide a service (e.g. domestic subsidiaries of foreign insurance companies or hotel chains).
4. Presence of natural persons –
● It consists of persons of one member entering the territory of another member to supply a service (e.g. accountants, doctors or teachers).Additional Information on GATS:
● It is a treaty of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) that entered into force in 1995.
● All members of the WTO are parties to the GATS.
● The fundamental principles of the GATS apply, in principle, to all service sectors.
The objectives are:
● To create a reliable and predictable system of international rules for trade in services.
● To facilitate the progressive liberalisation of services markets.
The fundamental principles of the GATS apply, in principle, to all service sectors.
● There are two exceptions:
a) Services supplied in the exercise of governmental authority on a con-commercial basis, such as social security schemes, public health, education.
b) Services related to air transport. -
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Balance of Payment (BoP) Account:
1. Autonomous items are the reasons for the imbalances in the Balance of Payment Account while accommodating items are intended to restore the balance in the Balance of Payment Account.
2. Autonomous items fall in the capital account only while accommodating items fall in both the current account and the capital account.
Which of the above given statement is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Autonomous Items –
● They are those international transactions which happen due to profit earning motive.
● Also known as ‘above the line items’.
● Autonomous transactions are called ‘autonomous’ because they happen on their own accord and not because of a country’s BOP scenario.’
Accommodating Items
● They are those international transactions which originate to ‘accommodate’ the BOP scenario.
● Also known as ‘below the line items’
● If there is BOP surplus or deficit then accommodating transactions are carried out in a deliberate manner to balance out the surplus/ deficit BOP.
● Accommodating transactions compensate the surplus or deficit brought about by autonomous transactions. It seeks to bring equality between the payments and receipts of foreign exchange.
From above, we can conclude that Autonomous items are the reason for the imbalances in the Balance of Payment Account.
On the other hand, Accommodating items are intended to restore the balance in the Balance of Payment Account.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Autonomous items/transactions:
● These transactions fall on both the current account and the capital account.
● In the case of the current account, the autonomous transactions cover exports and imports.
● Also, it covers unilateral transfers, though they are not commercial items, as they don’t result in a balance in the balance of payment.
● In the case of capital account, autonomous transactions include long-term capital movements, as they are commercial transactions that aim to earn profit.
Examples
⮚ Export of rubber to the USA
⮚ A loan raised by a company from a foreign bank
Accommodating items/transactions:
⮚ These transactions fall in the capital account only.
⮚ Usually we have BOP deficit and that is accommodated by bringing in flow of foreign exchange in the form of FDI/ loan from IMF etc. to balance out the deficit or to lower the deficit.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
Autonomous Items –
● They are those international transactions which happen due to profit earning motive.
● Also known as ‘above the line items’.
● Autonomous transactions are called ‘autonomous’ because they happen on their own accord and not because of a country’s BOP scenario.’
Accommodating Items
● They are those international transactions which originate to ‘accommodate’ the BOP scenario.
● Also known as ‘below the line items’
● If there is BOP surplus or deficit then accommodating transactions are carried out in a deliberate manner to balance out the surplus/ deficit BOP.
● Accommodating transactions compensate the surplus or deficit brought about by autonomous transactions. It seeks to bring equality between the payments and receipts of foreign exchange.
From above, we can conclude that Autonomous items are the reason for the imbalances in the Balance of Payment Account.
On the other hand, Accommodating items are intended to restore the balance in the Balance of Payment Account.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Autonomous items/transactions:
● These transactions fall on both the current account and the capital account.
● In the case of the current account, the autonomous transactions cover exports and imports.
● Also, it covers unilateral transfers, though they are not commercial items, as they don’t result in a balance in the balance of payment.
● In the case of capital account, autonomous transactions include long-term capital movements, as they are commercial transactions that aim to earn profit.
Examples
⮚ Export of rubber to the USA
⮚ A loan raised by a company from a foreign bank
Accommodating items/transactions:
⮚ These transactions fall in the capital account only.
⮚ Usually we have BOP deficit and that is accommodated by bringing in flow of foreign exchange in the form of FDI/ loan from IMF etc. to balance out the deficit or to lower the deficit. -
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
1. Indian stock exchanges follow a “T+2” settlement system.
2. Faster rolling of funds and stocks helps investors in reducing the overall capital requirements.
3. India will commence it’s “T+1” settlement system from January, 2024.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 3 are incorrect:
India has started to follow “Trade Plus One” or “T+1” settlement system in top listed securities from January, 2023 itself.
● After China, India became the second country in the world to start the ‘trade-plus-one’ (T+1) settlement cycle in top listed securities in January, 2023.
● The United States, United Kingdom and Eurozone markets are yet to move to the T+1 system.Statement 2 is correct:In the T+1 format, if an investor sells a share, she will get the money within a day, and the buyer will get the shares in her demat account also within a day. It will also help investors in reducing the overall capital requirements with the margins getting released on T+1 day, and in getting the funds in the bank account within 24 hours of the sale of shares. Therefore, it will boost operational efficiency as the rolling of funds and stocks will be faster.
The shorter trade settlement cycle augurs well for the Indian equity markets from a liquidity perspective.
It shows how well a country has grown on the digital journey to ensure seamless settlements within 24 hours.
Additional Information:
T+1 settlement plan-
● The T+1 settlement cycle means that trade-related settlements must be done within a day, or 24 hours, of the completion of a transaction.
⮚ For example, under T+1, if a customer bought shares on Wednesday, they would be credited to the customer’s demat account on Thursday.
⮚ This is different from T+2, where they will be settled on Friday.
⮚ Until 2001, stock markets had a weekly settlement system. The markets then moved to a rolling settlement system of T+3, and then to T+2 in 2003.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 3 are incorrect:
India has started to follow “Trade Plus One” or “T+1” settlement system in top listed securities from January, 2023 itself.
● After China, India became the second country in the world to start the ‘trade-plus-one’ (T+1) settlement cycle in top listed securities in January, 2023.
● The United States, United Kingdom and Eurozone markets are yet to move to the T+1 system.Statement 2 is correct:In the T+1 format, if an investor sells a share, she will get the money within a day, and the buyer will get the shares in her demat account also within a day. It will also help investors in reducing the overall capital requirements with the margins getting released on T+1 day, and in getting the funds in the bank account within 24 hours of the sale of shares. Therefore, it will boost operational efficiency as the rolling of funds and stocks will be faster.
The shorter trade settlement cycle augurs well for the Indian equity markets from a liquidity perspective.
It shows how well a country has grown on the digital journey to ensure seamless settlements within 24 hours.
Additional Information:
T+1 settlement plan-
● The T+1 settlement cycle means that trade-related settlements must be done within a day, or 24 hours, of the completion of a transaction.
⮚ For example, under T+1, if a customer bought shares on Wednesday, they would be credited to the customer’s demat account on Thursday.
⮚ This is different from T+2, where they will be settled on Friday.
⮚ Until 2001, stock markets had a weekly settlement system. The markets then moved to a rolling settlement system of T+3, and then to T+2 in 2003. -
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements:
1. Project OASIS report became the basis for the introduction of the New Pension Scheme (NPS) in India.
2. Only the government employees are eligible for receiving pension after retirement under the Old Pension Scheme (OPS).
3. The New Pension Scheme (NPS) is implemented and regulated by the Employee Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
● In 1998, the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment commissioned a report for an Old Age Social and Income Security (OASIS) project. The report became the basis for the introduction of the New Pension Scheme (NPS) in India.
● Chairman of the committee was S. A. Dave.
● An expert committee submitted the report in January 2000.
● The primary objective of OASIS was targeted at unorganised sector workers who had no old age income security, so the OASIS project was not meant to reform the government pension system.
Statement 2 is correct: Only government employees are eligible for receiving a pension after retirement under the Old Age Pension Scheme which was applicable before NPS was kicked in (i.e. before January, 2004).
● Pension to government employees at the Centre as well as states was fixed at 50 per cent of the last drawn basic pay.
● Income under the old pension scheme doesn’t attract tax.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The NPS is prudently regulated by PFRDA which is a statutory regulatory body established by the Government of India through the PFRDA Act 2013 to promote old age income security by establishing, regulating and developing pension funds to protect the interest of subscribers to schemes of pension funds.
● Contribution made to the NPS Tier-I account is eligible for tax deduction under the Income Tax Act, 1961. An additional tax rebate of Rs.50000 is also allowed for contributions made to NPS Tier-I under Section 80CCD (1B) of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
● Subscribers can withdraw up to 25% of their own contributions before attaining age of superannuation, subject to certain conditions.
● PFRDA has increased the maximum age limit from 60 years to 65 years for joining NPS.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct:
● In 1998, the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment commissioned a report for an Old Age Social and Income Security (OASIS) project. The report became the basis for the introduction of the New Pension Scheme (NPS) in India.
● Chairman of the committee was S. A. Dave.
● An expert committee submitted the report in January 2000.
● The primary objective of OASIS was targeted at unorganised sector workers who had no old age income security, so the OASIS project was not meant to reform the government pension system.
Statement 2 is correct: Only government employees are eligible for receiving a pension after retirement under the Old Age Pension Scheme which was applicable before NPS was kicked in (i.e. before January, 2004).
● Pension to government employees at the Centre as well as states was fixed at 50 per cent of the last drawn basic pay.
● Income under the old pension scheme doesn’t attract tax.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The NPS is prudently regulated by PFRDA which is a statutory regulatory body established by the Government of India through the PFRDA Act 2013 to promote old age income security by establishing, regulating and developing pension funds to protect the interest of subscribers to schemes of pension funds.
● Contribution made to the NPS Tier-I account is eligible for tax deduction under the Income Tax Act, 1961. An additional tax rebate of Rs.50000 is also allowed for contributions made to NPS Tier-I under Section 80CCD (1B) of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
● Subscribers can withdraw up to 25% of their own contributions before attaining age of superannuation, subject to certain conditions.
● PFRDA has increased the maximum age limit from 60 years to 65 years for joining NPS. -
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
With reference to PM Vishwakarma Scheme, consider the following statements:
1. The scheme aims to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools.
2. It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
3. The scheme has a provision for collateral free credit facility.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: PM Vishwakarma was launched on 17th September, 2023 to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools. The Scheme covers artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades, which are:
● Carpenter (Suthar/Badhai), Boat Maker, Armourer, Blacksmith (Lohar), Hammer and Tool Kit Maker, Locksmith, Goldsmith (Sonar), Potter (Kumhaar), Sculptor (Moortikar, stone carver), Stone breaker, Cobbler (Charmkar)/ Shoesmith/Footwear artisan, Mason (Rajmistri), Basket/Mat/Broom Maker/Coir Weaver, Doll & Toy Maker (Traditional), Barber (Naai), Garland maker (Malakaar), Washerman (Dhobi), Tailor (Darzi) and Fishing Net Maker.
Statement 2 is incorrect: PM Vishwakarma is a Central Sector Scheme launched on 17th September, 2023 by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
Statement 3 is correct: Credit Support under the scheme is ensured through collateral-free ‘Enterprise Development Loans’ of upto Rs. 3 lakhs in two tranches of Rs. 1 lakh and Rs. 2 lakhs with tenures of 18 months and 30 months, respectively, at a concessional rate of interest fixed at 5%, with Government of India subvention to the extent of 8%. Beneficiaries who have completed Basic Training will be eligible to avail the first tranche of credit support of upto Rs. 1 lakh. The second loan tranche will be available to beneficiaries who have availed the 1st tranche and maintained a standard loan account and have adopted digital transactions in their business or have undergone Advanced Training.
Additional Information:
Other benefits to artists and craftspersons promised under the scheme are as follows:
● Recognition: Recognition of artisans and craftspeople through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
● Skill Upgradation: Basic Training of 5-7 days and Advanced Training of 15 days or more, with a stipend of Rs. 500 per day.
● Toolkit Incentive: A toolkit incentive of upto Rs. 15,000 in the form of e-vouchers at the beginning of Basic Skill Training.
● Incentive for Digital Transaction: An amount of Re. 1 per digital transaction, upto maximum 100 transactions monthly will be credited to the beneficiary’s account for each digital pay-out or receipt.
● Marketing Support: in the form of quality certification, branding, onboarding on e-commerce platforms such as GeM, advertising, publicity and other marketing activities to improve linkage to value chain.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: PM Vishwakarma was launched on 17th September, 2023 to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools. The Scheme covers artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades, which are:
● Carpenter (Suthar/Badhai), Boat Maker, Armourer, Blacksmith (Lohar), Hammer and Tool Kit Maker, Locksmith, Goldsmith (Sonar), Potter (Kumhaar), Sculptor (Moortikar, stone carver), Stone breaker, Cobbler (Charmkar)/ Shoesmith/Footwear artisan, Mason (Rajmistri), Basket/Mat/Broom Maker/Coir Weaver, Doll & Toy Maker (Traditional), Barber (Naai), Garland maker (Malakaar), Washerman (Dhobi), Tailor (Darzi) and Fishing Net Maker.
Statement 2 is incorrect: PM Vishwakarma is a Central Sector Scheme launched on 17th September, 2023 by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
Statement 3 is correct: Credit Support under the scheme is ensured through collateral-free ‘Enterprise Development Loans’ of upto Rs. 3 lakhs in two tranches of Rs. 1 lakh and Rs. 2 lakhs with tenures of 18 months and 30 months, respectively, at a concessional rate of interest fixed at 5%, with Government of India subvention to the extent of 8%. Beneficiaries who have completed Basic Training will be eligible to avail the first tranche of credit support of upto Rs. 1 lakh. The second loan tranche will be available to beneficiaries who have availed the 1st tranche and maintained a standard loan account and have adopted digital transactions in their business or have undergone Advanced Training.
Additional Information:
Other benefits to artists and craftspersons promised under the scheme are as follows:
● Recognition: Recognition of artisans and craftspeople through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
● Skill Upgradation: Basic Training of 5-7 days and Advanced Training of 15 days or more, with a stipend of Rs. 500 per day.
● Toolkit Incentive: A toolkit incentive of upto Rs. 15,000 in the form of e-vouchers at the beginning of Basic Skill Training.
● Incentive for Digital Transaction: An amount of Re. 1 per digital transaction, upto maximum 100 transactions monthly will be credited to the beneficiary’s account for each digital pay-out or receipt.
● Marketing Support: in the form of quality certification, branding, onboarding on e-commerce platforms such as GeM, advertising, publicity and other marketing activities to improve linkage to value chain. -
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
In the context of economy, Gresham’s Law is related to:
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
● Gresham’s law is a principle that states that “bad money drives out good” and can be applied to the currency markets. The law observes that legally overvalued currency will drive legally undervalued currency out of circulation. The law observes the effects of currency debasement.Additional Information
Currency debasement:
● Debasement refers to lowering the value of a currency.
● It is primarily associated with coins made from precious metals, such as gold and silver.
● A currency is debased when the coins are made with a mix of precious metals and base metals as opposed to purely precious metals.The law stemmed from the historical use of precious metals to manufacture coins and their subsequent value. Since the abandonment of metallic currency standards, the theory often describes the stability and movement of different currencies in global markets.
Historically, mints manufactured coins from gold, silver, and other precious metals, which gave the coins their value. Issuers of coins sometimes lowered the level of the precious metals used and passed the coins as full-value coins. New coins with less metal content had less market value and traded at a discount. The old coins retained a higher value.
However, legal tender laws mandated that new coins with less metal content have the same face value as older coins. The new coins were legally overvalued, and the old coins were legally undervalued. Governments, rulers, and other coin issuers often implemented this policy to obtain revenue and repay debts borrowed in old coins using new coins at par value.
Legally forced to treat both types of coins as the same monetary unit, buyers passed along their less valued coins as quickly as possible and held onto the old coins, thus debasing the currency, creating a fall in the purchasing power of the currency units.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
● Gresham’s law is a principle that states that “bad money drives out good” and can be applied to the currency markets. The law observes that legally overvalued currency will drive legally undervalued currency out of circulation. The law observes the effects of currency debasement.Additional Information
Currency debasement:
● Debasement refers to lowering the value of a currency.
● It is primarily associated with coins made from precious metals, such as gold and silver.
● A currency is debased when the coins are made with a mix of precious metals and base metals as opposed to purely precious metals.The law stemmed from the historical use of precious metals to manufacture coins and their subsequent value. Since the abandonment of metallic currency standards, the theory often describes the stability and movement of different currencies in global markets.
Historically, mints manufactured coins from gold, silver, and other precious metals, which gave the coins their value. Issuers of coins sometimes lowered the level of the precious metals used and passed the coins as full-value coins. New coins with less metal content had less market value and traded at a discount. The old coins retained a higher value.
However, legal tender laws mandated that new coins with less metal content have the same face value as older coins. The new coins were legally overvalued, and the old coins were legally undervalued. Governments, rulers, and other coin issuers often implemented this policy to obtain revenue and repay debts borrowed in old coins using new coins at par value.
Legally forced to treat both types of coins as the same monetary unit, buyers passed along their less valued coins as quickly as possible and held onto the old coins, thus debasing the currency, creating a fall in the purchasing power of the currency units. -
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
Consider the following statements in respect of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for automobile and auto components:
1. 50% domestic value addition is demanded to receive the incentives under the scheme.
2. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry is the nodal ministry for the scheme.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: The government approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Automobile and Auto Component Industry on 15.09.2021.
The PLI Scheme for the auto sector envisages to overcome the cost disabilities of the industry for manufacture of Advanced Automotive Technology products in India. The incentive structure will encourage industry to make fresh investments for indigenous global supply chain of Advanced Automotive Technology products.Statement 1 is correct: According to the scheme guidelines, applicants must achieve a Domestic Value Addition (DVA) of 50% to claim incentives under the scheme.
● The auto companies and component makers are required to calculate and present the DVA across their supply chain and present these details to the testing agencies.
● This is being done to promote the Make in India campaign and boost domestic manufacturing of advanced automotive products.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Ministry of Heavy Industries is the nodal ministry for the scheme.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: The government approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Automobile and Auto Component Industry on 15.09.2021.
The PLI Scheme for the auto sector envisages to overcome the cost disabilities of the industry for manufacture of Advanced Automotive Technology products in India. The incentive structure will encourage industry to make fresh investments for indigenous global supply chain of Advanced Automotive Technology products.Statement 1 is correct: According to the scheme guidelines, applicants must achieve a Domestic Value Addition (DVA) of 50% to claim incentives under the scheme.
● The auto companies and component makers are required to calculate and present the DVA across their supply chain and present these details to the testing agencies.
● This is being done to promote the Make in India campaign and boost domestic manufacturing of advanced automotive products.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Ministry of Heavy Industries is the nodal ministry for the scheme. -
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. The Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme allows individuals to invest in gold in a paperless form as an alternative to physical gold investments.
2. It helps in addressing the issue of Current Account Deficit.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Government of India (Ministry of Finance) launched Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme in November, 2015, as an alternative to purchasing metal gold. The scheme intends to reduce the demand for physical gold. It allows individuals to invest in gold in a paperless form. These bonds are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on behalf of the Government of India.The SGBs will be sold through Scheduled Commercial banks (except Small Finance Banks, Payment Banks and Regional Rural Banks), Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL), Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL), designated post offices, and recognised stock exchanges viz., National Stock Exchange of India Limited and Bombay Stock Exchange Limited.
The SGBs will be restricted for sale to resident individuals, HUFs, Trusts, Universities and Charitable Institutions. Minimum permissible investment will be One gram of gold.The maximum limit of subscription shall be 4 Kg for individual, 4 Kg for HUF and 20 Kg for trusts and similar entities per fiscal year (April-March) notified by the Government from time to time.
Statement 2 is correct: The Government of India introduced it as an alternative to physical gold investments and to reduce the demand for imported gold, which significantly impacts India’s trade deficit.
Fact: India’s gold imports plunged 24.15 per cent in 2022-23 to $35.01 billion from $46.16 billion in 2021-22.
Additional Information:
Other key features of the Sovereign Gold Bonds Scheme:
● Assured returns of 2.5% p.a. payable half-yearly: Investors receive a fixed annual return of 2.5% on the nominal value of the bonds. This return is paid out semi-annually, providing a predictable income stream.
● No storage hassles like physical gold: Unlike physical gold, there is no need to worry about storage when investing in SGBs. This eliminates security concerns associated with holding physical gold.
● No Capital Gain Tax on Redemption: SGBs offer the advantage of exemption from Capital Gain Tax upon redemption. This can help maximize returns for investors.
● Liquidity: SGBs can be easily traded on stock exchanges within two weeks of issuance, as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) specified. This scheme provides investors with the flexibility to exit their investments if needed.
● Gold Bonds can be used as collateral for loans: Gold Bonds can be used to secure loans. The loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is set in line with the RBI’s guidelines for ordinary gold loans. Authorized banks mark the lien on the bonds in the depository.
● No GST and making charges: SGBs are not subject to goods and services tax (GST), unlike gold coins and bars. Compared to digital gold, which incurs a 3% GST, investing in SGBs offers a tax advantage. Additionally, there are no making charges associated with SGBs.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Government of India (Ministry of Finance) launched Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme in November, 2015, as an alternative to purchasing metal gold. The scheme intends to reduce the demand for physical gold. It allows individuals to invest in gold in a paperless form. These bonds are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on behalf of the Government of India.The SGBs will be sold through Scheduled Commercial banks (except Small Finance Banks, Payment Banks and Regional Rural Banks), Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL), Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL), designated post offices, and recognised stock exchanges viz., National Stock Exchange of India Limited and Bombay Stock Exchange Limited.
The SGBs will be restricted for sale to resident individuals, HUFs, Trusts, Universities and Charitable Institutions. Minimum permissible investment will be One gram of gold.The maximum limit of subscription shall be 4 Kg for individual, 4 Kg for HUF and 20 Kg for trusts and similar entities per fiscal year (April-March) notified by the Government from time to time.
Statement 2 is correct: The Government of India introduced it as an alternative to physical gold investments and to reduce the demand for imported gold, which significantly impacts India’s trade deficit.
Fact: India’s gold imports plunged 24.15 per cent in 2022-23 to $35.01 billion from $46.16 billion in 2021-22.
Additional Information:
Other key features of the Sovereign Gold Bonds Scheme:
● Assured returns of 2.5% p.a. payable half-yearly: Investors receive a fixed annual return of 2.5% on the nominal value of the bonds. This return is paid out semi-annually, providing a predictable income stream.
● No storage hassles like physical gold: Unlike physical gold, there is no need to worry about storage when investing in SGBs. This eliminates security concerns associated with holding physical gold.
● No Capital Gain Tax on Redemption: SGBs offer the advantage of exemption from Capital Gain Tax upon redemption. This can help maximize returns for investors.
● Liquidity: SGBs can be easily traded on stock exchanges within two weeks of issuance, as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) specified. This scheme provides investors with the flexibility to exit their investments if needed.
● Gold Bonds can be used as collateral for loans: Gold Bonds can be used to secure loans. The loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is set in line with the RBI’s guidelines for ordinary gold loans. Authorized banks mark the lien on the bonds in the depository.
● No GST and making charges: SGBs are not subject to goods and services tax (GST), unlike gold coins and bars. Compared to digital gold, which incurs a 3% GST, investing in SGBs offers a tax advantage. Additionally, there are no making charges associated with SGBs. -
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Riyadh Conference of 1960 resulted into the establishment of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
2. The World Energy Outlook is the report published by the OPEC.
3. Russia is a founding member of OPEC.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a permanent intergovernmental Organization created at the Baghdad Conference on September 10–14, 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
Currently, the Organization has a total of 13 Member Countries. The countries which joined after the 5 founding member countries are Qatar (1961), Indonesia (1962), Libya (1962), the United Arab Emirates (1967), Algeria (1969), Nigeria (1971), Ecuador (1973), Gabon (1975), Angola (2007), Equatorial Guinea (2017) and Congo (2018).
● OPEC as an organisation aims to manage the supply of oil in an effort to set the price of oil in the world market, in order to avoid fluctuations that might affect the economies of both producing and purchasing countries.
● It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
● OPEC membership is open to any country that is a substantial exporter of oil and which shares the ideals of the organization.Statement 2 is incorrect: World Energy Outlook is a report published by the International energy Agency (IEA).
Reports published by OPEC are as follows-
● Monthly oil market report
● World Oil Outlook
Statement 3 is incorrect:
Russia is not a member of OPEC, but it is considered as a part of “OPEC Plus”.
About OPEC Plus-
● In 2016, largely in response to dramatically falling oil prices driven by significant increases in U.S. shale oil output, OPEC signed an agreement with 10 other oil-producing countries to create what is now known as OPEC+.
● The non-OPEC countries which export crude oil are termed as OPEC plus countries. OPEC plus countries include Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan.
● Among these 10 countries was the world’s third-largest oil producer in 2022, Russia, which produced 13% of the world’s total oil production.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect:
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a permanent intergovernmental Organization created at the Baghdad Conference on September 10–14, 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
Currently, the Organization has a total of 13 Member Countries. The countries which joined after the 5 founding member countries are Qatar (1961), Indonesia (1962), Libya (1962), the United Arab Emirates (1967), Algeria (1969), Nigeria (1971), Ecuador (1973), Gabon (1975), Angola (2007), Equatorial Guinea (2017) and Congo (2018).
● OPEC as an organisation aims to manage the supply of oil in an effort to set the price of oil in the world market, in order to avoid fluctuations that might affect the economies of both producing and purchasing countries.
● It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
● OPEC membership is open to any country that is a substantial exporter of oil and which shares the ideals of the organization.Statement 2 is incorrect: World Energy Outlook is a report published by the International energy Agency (IEA).
Reports published by OPEC are as follows-
● Monthly oil market report
● World Oil Outlook
Statement 3 is incorrect:
Russia is not a member of OPEC, but it is considered as a part of “OPEC Plus”.
About OPEC Plus-
● In 2016, largely in response to dramatically falling oil prices driven by significant increases in U.S. shale oil output, OPEC signed an agreement with 10 other oil-producing countries to create what is now known as OPEC+.
● The non-OPEC countries which export crude oil are termed as OPEC plus countries. OPEC plus countries include Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan.
● Among these 10 countries was the world’s third-largest oil producer in 2022, Russia, which produced 13% of the world’s total oil production. -
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
Consider the following:
1. Medium- and long-term loans for purchasing agriculture machinery and equipment
2. Loans to Small and Marginal farmers for purchasing agricultural land
3. Loans to the start-ups engaged in agriculture
4. Loans to the Food Processing Industries
How many of the above can be categorised as priority sector loans under the agriculture sector?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
All of the 4 activities mentioned in the options are eligible for priority sector loans under the agriculture sector.
Priority Sector Lending (PSL) refers to a regulatory framework implemented by central banks or financial authorities in many countries to ensure that a certain portion of bank loans are directed towards specific sectors of the economy that are considered to be important for overall development and inclusive growth.
● The RBI mandates banks to lend a certain portion of their funds to specified sectors, like agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), food processing industries, export credit, education, housing, social infrastructure, renewable energy among others.
● The idea behind this is to ensure that adequate institutional credit reaches some of the vulnerable sectors of the economy, which otherwise may not be attractive for banks from the profitability point of view.
The categories under priority sector are as follows:
⮚ Agriculture
⮚ Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
⮚ Export Credit
⮚ Education
⮚ Housing
⮚ Social Infrastructure
⮚ Renewable Energy
⮚ As per RBI’s Master Directions dated 04.09.2020, all food & agro- processing activities have been included as eligible under Priority Sector Lending (PSL).
⮚ Others
In Agriculture-
● The lending to agriculture sector will be categorized as
(i) Farm Credit (which will include short-term crop loans and medium/long-term credit to farmers)
(ii) Agriculture Infrastructure and
(iii) Ancillary Activities.
● All scheduled commercial banks and foreign banks (with a sizable presence in India) are mandated to set aside 40% of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANDC) for lending to these sectors. The Regional rural banks, co-operative banks and small finance banks have to allocate 75% of ANDC to PSL.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
All of the 4 activities mentioned in the options are eligible for priority sector loans under the agriculture sector.
Priority Sector Lending (PSL) refers to a regulatory framework implemented by central banks or financial authorities in many countries to ensure that a certain portion of bank loans are directed towards specific sectors of the economy that are considered to be important for overall development and inclusive growth.
● The RBI mandates banks to lend a certain portion of their funds to specified sectors, like agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), food processing industries, export credit, education, housing, social infrastructure, renewable energy among others.
● The idea behind this is to ensure that adequate institutional credit reaches some of the vulnerable sectors of the economy, which otherwise may not be attractive for banks from the profitability point of view.
The categories under priority sector are as follows:
⮚ Agriculture
⮚ Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
⮚ Export Credit
⮚ Education
⮚ Housing
⮚ Social Infrastructure
⮚ Renewable Energy
⮚ As per RBI’s Master Directions dated 04.09.2020, all food & agro- processing activities have been included as eligible under Priority Sector Lending (PSL).
⮚ Others
In Agriculture-
● The lending to agriculture sector will be categorized as
(i) Farm Credit (which will include short-term crop loans and medium/long-term credit to farmers)
(ii) Agriculture Infrastructure and
(iii) Ancillary Activities.
● All scheduled commercial banks and foreign banks (with a sizable presence in India) are mandated to set aside 40% of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANDC) for lending to these sectors. The Regional rural banks, co-operative banks and small finance banks have to allocate 75% of ANDC to PSL. -
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
Consider the following steps:
1. Imposition of higher import duties.
2. Restrictions on Capital Outflows.
3. Selling dollars from the forex reserves.
How many of the above steps are likely to be taken in order to counter rupee depreciation?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation: All the steps 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
Under a flexible exchange rate system, the exchange value of a currency frequently appreciates or depreciates depending upon the demand for and supply of a currency.
Rupee Depreciation takes place when there is shortage of domestic currency in the Indian economy, often due to the relative rise in capital outflows driven by higher interest rates offered by market abroad(for instance, attractive US Fed interest rates). Hence, to counter rupee depreciation, we would have to increase demand for domestic currency(rupee).
This can be done through multiple ways –
⮚ Imposition of higher import duties
⮚ Boost Exports
⮚ Encouraging Foreign Investment into the Indian economy
⮚ Restrictions on Capital outflows
⮚ Selling dollars from the Forex Reserves.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation: All the steps 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
Under a flexible exchange rate system, the exchange value of a currency frequently appreciates or depreciates depending upon the demand for and supply of a currency.
Rupee Depreciation takes place when there is shortage of domestic currency in the Indian economy, often due to the relative rise in capital outflows driven by higher interest rates offered by market abroad(for instance, attractive US Fed interest rates). Hence, to counter rupee depreciation, we would have to increase demand for domestic currency(rupee).
This can be done through multiple ways –
⮚ Imposition of higher import duties
⮚ Boost Exports
⮚ Encouraging Foreign Investment into the Indian economy
⮚ Restrictions on Capital outflows
⮚ Selling dollars from the Forex Reserves. -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
Which among the following best describes the term “Currency Manipulation”?
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Currency Manipulation:
● The term Currency Manipulation means ‘Devaluation of the Currencies’ to gain unfair trade advantage. For example, countries may deliberately devalue their currencies to boost exports, reduce imports and thus, achieve higher trade surplus. China is doing it to boost exports.
● Devaluation is the deliberate downward adjustment of the value of a country’s money relative to another currency or standard. It is a monetary policy tool used by countries with a fixed exchange rate or semi-fixed exchange rate.
● By devaluing its currency, a country makes its money cheaper and boosts exports, rendering them more competitive in the global market. Conversely, foreign products become more expensive, so the demand for imports falls.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Currency Manipulation:
● The term Currency Manipulation means ‘Devaluation of the Currencies’ to gain unfair trade advantage. For example, countries may deliberately devalue their currencies to boost exports, reduce imports and thus, achieve higher trade surplus. China is doing it to boost exports.
● Devaluation is the deliberate downward adjustment of the value of a country’s money relative to another currency or standard. It is a monetary policy tool used by countries with a fixed exchange rate or semi-fixed exchange rate.
● By devaluing its currency, a country makes its money cheaper and boosts exports, rendering them more competitive in the global market. Conversely, foreign products become more expensive, so the demand for imports falls.




