Day-752
Quiz-summary
0 of 20 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 20 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
Consider the following statements about the Islands of India:
1. The islands of the Bay of Bengal are formed entirely from coral deposits.
2. The islands of the Arabian sea have elevated portions of submarine mountains.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?Correct
Answer. C
Explanation- There are a number of islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian sea. Those in the Bay of Bengal are much larger and more habitable. The Bay of Bengal islands have a different origin than those in the Arabian sea.
The Bay of Bengal Island groups consist of about 572 islands/islets. These are situated roughly between 6°N-14°N and 92°E -94°E. The two principal groups of islets include the Ritchie’s archipelago and the Labrynth island. The entire group of islands is divided into two broad categories – the Andaman in the north and the Nicobar in the south. They are separated by a water body which is called the Ten-degree channel.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The islands of the Bay of Bengal are elevated portions of submarine mountains. However, some smaller islands are volcanic in origin.
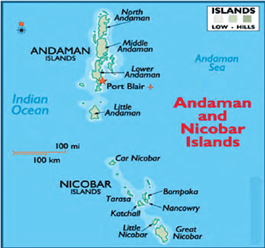

Statement 2 is incorrect- The islands of the Arabian sea include Lakshadweep and Minicoy. These are scattered between 8°N-12°N and 71°E -74°E longitude. They are entirely built of coral deposits.
Lakshadweep islands are considered as an atoll.
Source- NCERT Class 11, India Physical GeographyIncorrect
Answer. C
Explanation- There are a number of islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian sea. Those in the Bay of Bengal are much larger and more habitable. The Bay of Bengal islands have a different origin than those in the Arabian sea.
The Bay of Bengal Island groups consist of about 572 islands/islets. These are situated roughly between 6°N-14°N and 92°E -94°E. The two principal groups of islets include the Ritchie’s archipelago and the Labrynth island. The entire group of islands is divided into two broad categories – the Andaman in the north and the Nicobar in the south. They are separated by a water body which is called the Ten-degree channel.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The islands of the Bay of Bengal are elevated portions of submarine mountains. However, some smaller islands are volcanic in origin.



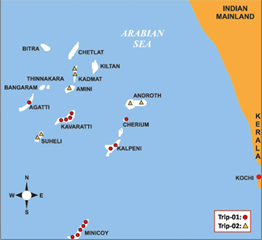
Statement 2 is incorrect- The islands of the Arabian sea include Lakshadweep and Minicoy. These are scattered between 8°N-12°N and 71°E -74°E longitude. They are entirely built of coral deposits.
Lakshadweep islands are considered as an atoll.
Source- NCERT Class 11, India Physical Geography -
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
Consider the following pairs:
Tributary of Indus – Source
1. Jhelum – Verinag, Pir Panjal
2. Beas – Rohtang pass, Kulli hills
3. Satluj – Mansarovar lake, Tibet
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation- Indus forms an important Himalayan River which has five main tributaries together forming Punjnad- Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Satluj and Beas.


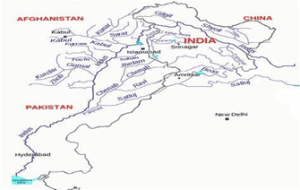
Tributary of Indus – Source
Jhelum – Verinag spring, Pir Panjal range, Kashmir valley
Beas – Rohtang pass, Kulli hills, Himachal Pradesh
Satluj – Rakas lake, Tibet
Ravi – Rohtang pass, Kullu hills, Himachal Pradesh
Chenab Baralacha la pass, Lahaul and Spiti valley, Himachal PradeshIncorrect
Answer. B
Explanation- Indus forms an important Himalayan River which has five main tributaries together forming Punjnad- Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Satluj and Beas.



Tributary of Indus – Source
Jhelum – Verinag spring, Pir Panjal range, Kashmir valley
Beas – Rohtang pass, Kulli hills, Himachal Pradesh
Satluj – Rakas lake, Tibet
Ravi – Rohtang pass, Kullu hills, Himachal Pradesh
Chenab Baralacha la pass, Lahaul and Spiti valley, Himachal Pradesh -
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Sunrise is experienced earlier in Japan than in New Zealand.
2. The circular shadow cast by the earth on the moon supports the spherical shape of the earth.
3. The varying length of seasons is an outcome of the earth’s rotation on its own axis.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation-
Statement 1 is incorrect- The sunrise is first observed in the eastern-most country of New Zealand as compared to Japan.
Statement 2 is correct- The evidences supporting the spherical shape of the earth are as follows:
● Circum-navigation of the earth in which sailors do not come across any abrupt edge or fall from earth
● Circular horizon, which is visible from the deck of a ship at sea and it becomes wider with increase in altitude. This could only be seen on a spherical body
● Ship’s visibility with its top being seen/disappearing first
● Places on the east witnessing sunrise earlier than those in the west.
● Circular shadow of the earth cast on the moon during lunar eclipse
● Driving poles on level ground on a curved earth: The centre pole normally projects slightly above the poles at either end because of the curvature of the earth
● Aerial photographs taken by satellites which clearly show the curved edges of the earth
Statement 3 is incorrect- The varying duration of day and night is caused by the earth’s rotation on its axis while the earth’s revolution around the sun causes seasons.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation-
Statement 1 is incorrect- The sunrise is first observed in the eastern-most country of New Zealand as compared to Japan.
Statement 2 is correct- The evidences supporting the spherical shape of the earth are as follows:
● Circum-navigation of the earth in which sailors do not come across any abrupt edge or fall from earth
● Circular horizon, which is visible from the deck of a ship at sea and it becomes wider with increase in altitude. This could only be seen on a spherical body
● Ship’s visibility with its top being seen/disappearing first
● Places on the east witnessing sunrise earlier than those in the west.
● Circular shadow of the earth cast on the moon during lunar eclipse
● Driving poles on level ground on a curved earth: The centre pole normally projects slightly above the poles at either end because of the curvature of the earth
● Aerial photographs taken by satellites which clearly show the curved edges of the earth
Statement 3 is incorrect- The varying duration of day and night is caused by the earth’s rotation on its axis while the earth’s revolution around the sun causes seasons. -
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
Consider the following statements:
1. The Himalayas were formed after the Ganga plains.
2. The Dravidian rocks are found in the Himalayas.
3. Deccan traps contain both sedimentary and igneous rocks.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation-
Statement 1 is incorrect- The Ganga plains are of recent origin, less than 2 million years old. The origin of Himalayas can be traced back to the Tertiary period as an outcome of the thrusting of the Indo-Australian plate under the Eurasian plate.
The Great Plains of which Ganga plains form a part, were formed after the upliftment of the Himalayas took place and the deposits from erosion of the mountains were deposited by the rivers Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
Statement 2 is correct- The Dravidian rocks do not occur in the Peninsular Plateau because of its location above the sea level at that time but these rocks are found in continuous sequence in the Himalayas.
The tertiary rocks are found mostly in the Himalayas.
DRAVIDIAN ROCKS were formed about 600 – 300 million years ago. They are abundant in fossils and are found in the Extra Peninsular region (Himalayas and Ganga plain). They are very rare in Peninsular India.
The rocks of Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian and Carboniferous periods fall under the Dravidian system.
Statement 3 is correct- Towards the end of the Mesozoic era, an intensive volcanic activity took place which flooded with lava, vast areas of Maharashtra and other parts of the Deccan. Known as Deccan Traps, the volcanic rocks contain some thin fossiliferous sedimentary layers found between the lava flows, this indicates that the lava flows were not continuous.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation-
Statement 1 is incorrect- The Ganga plains are of recent origin, less than 2 million years old. The origin of Himalayas can be traced back to the Tertiary period as an outcome of the thrusting of the Indo-Australian plate under the Eurasian plate.
The Great Plains of which Ganga plains form a part, were formed after the upliftment of the Himalayas took place and the deposits from erosion of the mountains were deposited by the rivers Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
Statement 2 is correct- The Dravidian rocks do not occur in the Peninsular Plateau because of its location above the sea level at that time but these rocks are found in continuous sequence in the Himalayas.
The tertiary rocks are found mostly in the Himalayas.
DRAVIDIAN ROCKS were formed about 600 – 300 million years ago. They are abundant in fossils and are found in the Extra Peninsular region (Himalayas and Ganga plain). They are very rare in Peninsular India.
The rocks of Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian and Carboniferous periods fall under the Dravidian system.
Statement 3 is correct- Towards the end of the Mesozoic era, an intensive volcanic activity took place which flooded with lava, vast areas of Maharashtra and other parts of the Deccan. Known as Deccan Traps, the volcanic rocks contain some thin fossiliferous sedimentary layers found between the lava flows, this indicates that the lava flows were not continuous. -
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
In the context of chemical weathering processes, consider the following statements:
1. The process of chemical addition of water in minerals is known as a solution.
2. Oxidation takes place in a waterlogged environment.
3. The carbonates of sodium and calcium are soluble in water containing carbonic acid.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation- A group of weathering processes viz; solution, carbonation, hydration, oxidation and reduction act on the rocks to decompose, dissolve or reduce them to a fine clastic state through chemical reactions by oxygen, surface and/or soil water and other acids.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The process of chemical addition of water to a mineral is known as hydration.
Minerals take up water and expand; this expansion causes an increase in the volume of the material itself or rock. Calcium sulphate on taking in water turns into gypsum which is unstable than calcium sulphate. The process is reversible and long, continued repetition of this process causes fatigue in the rocks and may lead to their disintegration.
Solution is the process in which minerals such as nitrates, sulphates and potassium etc. are dissolved with water or acid. This process involves the removal oof solids in solution and depends upon solubility of a mineral in water or weak acids.
Statement 2 is incorrect- In weathering, oxidation means a combination of a mineral with oxygen to form oxides or hydroxides. Oxidation occurs when there is ready access to the atmosphere and oxygenated waters.
Reduction is the process which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Therefore, when the oxidised minerals are placed in anaerobic environments, reduction takes place. such conditions exist usually below the water table, in areas of stagnant water and waterlogged ground. The red colour of iron upon reduction turns to greenish or bluish grey.
Statement 3 is correct- The carbonates of sodium and calcium are soluble in water containing carbonic acid. This happens in the process of carbonation in which reaction of carbonate and bicarbonate takes place with minerals. It is a common process that facilitates the breakdown of feldspars and carbonate minerals.
Calcium carbonates and magnesium carbonates are dissolved in carbonic acid and are removed in a solution without leaving any residue resulting in cave formation.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation- A group of weathering processes viz; solution, carbonation, hydration, oxidation and reduction act on the rocks to decompose, dissolve or reduce them to a fine clastic state through chemical reactions by oxygen, surface and/or soil water and other acids.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The process of chemical addition of water to a mineral is known as hydration.
Minerals take up water and expand; this expansion causes an increase in the volume of the material itself or rock. Calcium sulphate on taking in water turns into gypsum which is unstable than calcium sulphate. The process is reversible and long, continued repetition of this process causes fatigue in the rocks and may lead to their disintegration.
Solution is the process in which minerals such as nitrates, sulphates and potassium etc. are dissolved with water or acid. This process involves the removal oof solids in solution and depends upon solubility of a mineral in water or weak acids.
Statement 2 is incorrect- In weathering, oxidation means a combination of a mineral with oxygen to form oxides or hydroxides. Oxidation occurs when there is ready access to the atmosphere and oxygenated waters.
Reduction is the process which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Therefore, when the oxidised minerals are placed in anaerobic environments, reduction takes place. such conditions exist usually below the water table, in areas of stagnant water and waterlogged ground. The red colour of iron upon reduction turns to greenish or bluish grey.
Statement 3 is correct- The carbonates of sodium and calcium are soluble in water containing carbonic acid. This happens in the process of carbonation in which reaction of carbonate and bicarbonate takes place with minerals. It is a common process that facilitates the breakdown of feldspars and carbonate minerals.
Calcium carbonates and magnesium carbonates are dissolved in carbonic acid and are removed in a solution without leaving any residue resulting in cave formation. -
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
“The soils swell when wet and shrink when dried. So, during dry seasons, soils develop wide cracks where loosened soil particles may get accumulated. There occurs a kind of self-ploughing.”
Identify the type of soil based on the description given above:Correct
Answer. C
Explanation- Black soil covers most of the Deccan Plateau which includes parts of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and some parts of Tamil Nadu. In the upper reaches of the Godavari and the Krishna, and the northwestern part of the Deccan Plateau, the black soil is very deep. These soils are also known as the ‘Regur Soil’ or the ‘Black Cotton Soil’. The black soils are generally clayey, deep and impermeable. They swell and become sticky when wet and shrink when dried. So, during the dry season, these soils develop wide cracks. Thus, there occurs a kind of ‘self-ploughing’.
Because of this character of slow absorption and loss of moisture, the black soil retains the moisture for a very long time, which helps the crops, especially the rain fed ones, to sustain even during the dry season.Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation- Black soil covers most of the Deccan Plateau which includes parts of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and some parts of Tamil Nadu. In the upper reaches of the Godavari and the Krishna, and the northwestern part of the Deccan Plateau, the black soil is very deep. These soils are also known as the ‘Regur Soil’ or the ‘Black Cotton Soil’. The black soils are generally clayey, deep and impermeable. They swell and become sticky when wet and shrink when dried. So, during the dry season, these soils develop wide cracks. Thus, there occurs a kind of ‘self-ploughing’.
Because of this character of slow absorption and loss of moisture, the black soil retains the moisture for a very long time, which helps the crops, especially the rain fed ones, to sustain even during the dry season. -
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the degradation of soils:
1. The removal of organic and mineral content of soils is called soil erosion.
2. Mulching and contour bunding are helpful in controlling soil erosion.
3. Overirrigation increases the alkalinity of soils.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation- Several factors contribute to soil degradation.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The removal of the soil by running water in wet areas and wind in dry areas is referred to as soil erosion and the removal of organic and mineral content of soils is called soil exhaustion.
Statement 2 is correct- Contour bunding, contour terracing, regulated forestry, controlled forestry, controlled overgrazing and jhumming, selective weeding, cover cropping, mixed farming, crop rotation and mulching are some of the remedial measures which are often adapted to reduce soil erosion.
Statement 3 is correct- A fairly good amount of arable land in the irrigated zones of India is becoming saline and alkaline because of over-irrigation. The salt lodged in the lower profiles of the soil comes to the surface and destroys the fertility.
Chemical fertilizers are also harmful to the soil. Unless soils get enough humus, chemicals harden it and reduce its fertility in the long run. This problem is common in all the command areas of the river valley projects which were the first beneficiaries of the green revolution.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation- Several factors contribute to soil degradation.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The removal of the soil by running water in wet areas and wind in dry areas is referred to as soil erosion and the removal of organic and mineral content of soils is called soil exhaustion.
Statement 2 is correct- Contour bunding, contour terracing, regulated forestry, controlled forestry, controlled overgrazing and jhumming, selective weeding, cover cropping, mixed farming, crop rotation and mulching are some of the remedial measures which are often adapted to reduce soil erosion.
Statement 3 is correct- A fairly good amount of arable land in the irrigated zones of India is becoming saline and alkaline because of over-irrigation. The salt lodged in the lower profiles of the soil comes to the surface and destroys the fertility.
Chemical fertilizers are also harmful to the soil. Unless soils get enough humus, chemicals harden it and reduce its fertility in the long run. This problem is common in all the command areas of the river valley projects which were the first beneficiaries of the green revolution. -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
In the context of vegetation, consider the following statements:
1. Virgin vegetation is the plant community which grows naturally and is undisturbed by humans for a long time.
2. Rubber and mulberry are trees found in tropical evergreen forests.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation-
Statement 1 is correct- Natural vegetation refers to a plant community which has grown naturally without human aid and has been left undisturbed by humans for a long time. This is termed as virgin vegetation. Thus, cultivated crops and fruits, orchards form part of vegetation but not natural vegetation.
Statement 2 is incorrect- Some of the commercially important trees of tropical evergreen forests are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona.
Teak is the most important species of the moist deciduous forests. Other commercially important trees of this forest are Bamboo, Sal, Shisham, Sandalwood, Khair, Kusum, Arjun and Mulberry.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation-
Statement 1 is correct- Natural vegetation refers to a plant community which has grown naturally without human aid and has been left undisturbed by humans for a long time. This is termed as virgin vegetation. Thus, cultivated crops and fruits, orchards form part of vegetation but not natural vegetation.
Statement 2 is incorrect- Some of the commercially important trees of tropical evergreen forests are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona.
Teak is the most important species of the moist deciduous forests. Other commercially important trees of this forest are Bamboo, Sal, Shisham, Sandalwood, Khair, Kusum, Arjun and Mulberry. -
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
Consider the following statements about the tropical deciduous forests:
1. The rainier parts of the Peninsular Plateau of India have moist deciduous forests.
2. Both tropical evergreen forests and deciduous forests are found in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation- On the basis of the availability of water, the deciduous forests are divided into moist and dry deciduous. The former is found in areas receiving rainfall between 200 and 100 cm. These forests exist, therefore, mostly in the eastern part of the country – northeastern states, along the foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Orissa and Chhattisgarh, and on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. Teak is the most dominant species of this forest. Bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair, kusum, arjun, mulberry are other commercially important species.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The dry deciduous forests are found in areas having rainfall between 70 cm and 100 cm. These forests are found in the rainier parts of the peninsular plateau and the plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. There are open stretches in which Teak, Sal, Peepal, Neem grow.
Statement 2 is correct- The moist deciduous forests are common in the Andamans but they are almost absent in the Nicobar islands.
The middle and North Andaman are characterized by moist deciduous and wet evergreen forests respectively.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation- On the basis of the availability of water, the deciduous forests are divided into moist and dry deciduous. The former is found in areas receiving rainfall between 200 and 100 cm. These forests exist, therefore, mostly in the eastern part of the country – northeastern states, along the foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Orissa and Chhattisgarh, and on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. Teak is the most dominant species of this forest. Bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair, kusum, arjun, mulberry are other commercially important species.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The dry deciduous forests are found in areas having rainfall between 70 cm and 100 cm. These forests are found in the rainier parts of the peninsular plateau and the plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. There are open stretches in which Teak, Sal, Peepal, Neem grow.
Statement 2 is correct- The moist deciduous forests are common in the Andamans but they are almost absent in the Nicobar islands.
The middle and North Andaman are characterized by moist deciduous and wet evergreen forests respectively. -
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
Which among the following ocean currents does not belong to the Atlantic Ocean?
Correct
Answer. A
Explanation- The following ocean currents are found within the Atlantic Ocean:


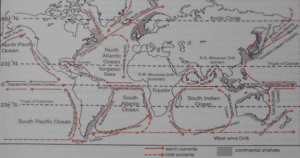
Warm ocean currents include Cayenne current, Florida current, Gulf stream, North Atlantic drift and Brazilian current.
Cold currents include Irminger current, Labrador current, Benguela current, Canaries current.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation- The following ocean currents are found within the Atlantic Ocean:



Warm ocean currents include Cayenne current, Florida current, Gulf stream, North Atlantic drift and Brazilian current.
Cold currents include Irminger current, Labrador current, Benguela current, Canaries current. -
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
The term “buyous” can be best understood as:
Correct
Answer. C
Explanation- Rivers during their mature stage in the lower course, undergo intense meandering on plains and often cut ox-bow lakes which are called cut-offs or bayous in the Mississippi basin.
Ox-bow Lake is also known as mortlake or dead lake. After cutting an ox-bow lake, the river becomes straight. The ox-bow lake often degenerates into a swamp through subsequent floods that may silt up the lake. It becomes marshy and may dry up eventually.Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation- Rivers during their mature stage in the lower course, undergo intense meandering on plains and often cut ox-bow lakes which are called cut-offs or bayous in the Mississippi basin.
Ox-bow Lake is also known as mortlake or dead lake. After cutting an ox-bow lake, the river becomes straight. The ox-bow lake often degenerates into a swamp through subsequent floods that may silt up the lake. It becomes marshy and may dry up eventually. -
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
Consider the following pairs:
Volcanoes – location
1. Mt. Vesuvius – Italy
2. Mt. Krakatoa – Indonesia
3. Mt. Merapi – Ecuador
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation-
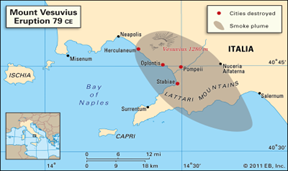
● Mt. Vesuvius – Italy


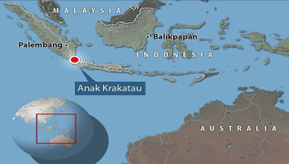
● Mt. Krakatoa – Indonesia


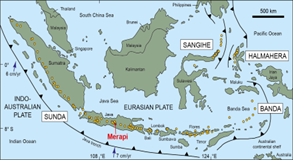
● Mt. Merapi – Sumatra, Indonesia


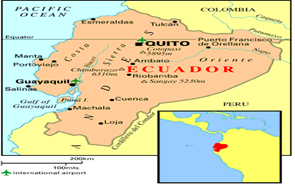
● Mt. Catapoxi (near Quito) – Ecuador


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation-
● Mt. Vesuvius – Italy



● Mt. Krakatoa – Indonesia



● Mt. Merapi – Sumatra, Indonesia



● Mt. Catapoxi (near Quito) – Ecuador



-
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
Which one of the following plateaus is formed due to tectonic forces?
Correct
Answer. D
Explanation- Tibetan Plateau, the highest in the world, is believed to have been formed through tectonic process when the Indian and Eurasian plates collided with each other.
Plateau are elevated uplands with extensive level surfaces and usually descend steeply to the surrounding lowland. They are also known as tablelands. According to their mode of formation and their physical characteristics, plateau can be classified into three types:


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation- Tibetan Plateau, the highest in the world, is believed to have been formed through tectonic process when the Indian and Eurasian plates collided with each other.
Plateau are elevated uplands with extensive level surfaces and usually descend steeply to the surrounding lowland. They are also known as tablelands. According to their mode of formation and their physical characteristics, plateau can be classified into three types:



-
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
Regarding the cold weather season in India, consider the following statements:
1. The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is positioned at 25-degree North latitude.
2. The winds become westerly over peninsular India.
3. Western disturbances cause rainfall and snow in northwest India.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation- The cold weather season begins in December and continues till February.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is positioned at 25-degree North latitude during summers and not winters. Due to the apparent movement of the sun, the ITCZ shifts southward from 25-degree North latitude.
Statement 2 is incorrect- The sun shines vertically over the Tropic of Capricorn. The northwestern part of India located far inland, away from the marine influences, experiences low temperature and high atmospheric pressure. The dry winds blow from the northwest part of India towards the surrounding ocean. Over North India in Ganga valley, the winds become westerly. They become northerly over central India and northeasterly over Peninsular India.
Statement 3 is correct- A unique characteristic of the winter season of India is the influx of Western Disturbances. These are extra-tropical cyclonic storms which originate in the Mediterranean Sea, are carried by the Westerly winds and cause rainfall and snow in the northwestern part of India. The cold weather rainfall is small in amount but is of great economic significance for the rabi crops such as wheat.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation- The cold weather season begins in December and continues till February.
Statement 1 is incorrect- The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is positioned at 25-degree North latitude during summers and not winters. Due to the apparent movement of the sun, the ITCZ shifts southward from 25-degree North latitude.
Statement 2 is incorrect- The sun shines vertically over the Tropic of Capricorn. The northwestern part of India located far inland, away from the marine influences, experiences low temperature and high atmospheric pressure. The dry winds blow from the northwest part of India towards the surrounding ocean. Over North India in Ganga valley, the winds become westerly. They become northerly over central India and northeasterly over Peninsular India.
Statement 3 is correct- A unique characteristic of the winter season of India is the influx of Western Disturbances. These are extra-tropical cyclonic storms which originate in the Mediterranean Sea, are carried by the Westerly winds and cause rainfall and snow in the northwestern part of India. The cold weather rainfall is small in amount but is of great economic significance for the rabi crops such as wheat. -
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
Consider the following pairs:
Soil types – Parent Rock
1. Sandy soil – Sandstone
2. Clayey soil – Limestone
3. Alluvial soil – Gneiss
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation- Parent rocks play a definite role in the case of derived soils. The Peninsular soils reflect the parent rocks very much. For example, the soils derived from the lava rocks are of black colour.
Soil type – Parent Rock
Sandy soil – Sandstone
Clayey soil – Gneiss
Alluvial soil – limestoneIncorrect
Answer. A
Explanation- Parent rocks play a definite role in the case of derived soils. The Peninsular soils reflect the parent rocks very much. For example, the soils derived from the lava rocks are of black colour.
Soil type – Parent Rock
Sandy soil – Sandstone
Clayey soil – Gneiss
Alluvial soil – limestone -
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
Consider the following statements about the saline soils:
1. Saline soils are rich in nitrogen, sodium, magnesium and calcium.
2. They are found in the deltas of the eastern coast of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation- Saline soils are also known as Usara soils. They have more salts, largely because of dry climate and poor drainage. They occur in arid and semi-arid regions, and in waterlogged and swampy areas. Their structure ranges from sandy to loamy.
Statement 1 is incorrect- Saline soils contain a larger proportion of sodium, potassium and magnesium, and thus, they are infertile, and do not support any vegetative growth. They lack nitrogen and calcium.
Statement 2 is correct- Saline soils are more widespread in western Gujarat, deltas of the eastern coast and in Sundarbans areas of West Bengal. Seawater intrusions in the deltas promote the occurrence of saline soils.
In the Rann of Kachchh, the Southwest Monsoon brings salt particles and deposits there as a crust. In the areas of intensive cultivation with excessive use of irrigation, especially in areas of green revolution, the fertile alluvial soils are becoming saline.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation- Saline soils are also known as Usara soils. They have more salts, largely because of dry climate and poor drainage. They occur in arid and semi-arid regions, and in waterlogged and swampy areas. Their structure ranges from sandy to loamy.
Statement 1 is incorrect- Saline soils contain a larger proportion of sodium, potassium and magnesium, and thus, they are infertile, and do not support any vegetative growth. They lack nitrogen and calcium.
Statement 2 is correct- Saline soils are more widespread in western Gujarat, deltas of the eastern coast and in Sundarbans areas of West Bengal. Seawater intrusions in the deltas promote the occurrence of saline soils.
In the Rann of Kachchh, the Southwest Monsoon brings salt particles and deposits there as a crust. In the areas of intensive cultivation with excessive use of irrigation, especially in areas of green revolution, the fertile alluvial soils are becoming saline. -
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
The barani soils can be best understood as:
Correct
Answer. A
Explanation- Soils in the ancient times were majorly classified into two main groups- Urvara which were fertile and Usara which were sterile. In the 16th century, soils were classified on the basis of their inherent characteristics and external features such as texture and colour of soils, slope of land and availability of water.
Soils dependent on rainwater were called Barani, that on well-irrigation Chari, that on canal irrigation Nahari and that on river percolation Sailabi.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation- Soils in the ancient times were majorly classified into two main groups- Urvara which were fertile and Usara which were sterile. In the 16th century, soils were classified on the basis of their inherent characteristics and external features such as texture and colour of soils, slope of land and availability of water.
Soils dependent on rainwater were called Barani, that on well-irrigation Chari, that on canal irrigation Nahari and that on river percolation Sailabi. -
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
The red colour of ‘Red and Yellow soils’ can be best explained by which of the following reasons?
Correct
Answer. D
Explanation- Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern part of the Deccan Plateau. Along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghat, long stretch of area is occupied by red loamy soil. Yellow and red soils are also found in parts of Odisha and Chattisgarh and in the southern parts of the middle Ganga plain.
The soil develops a reddish colour due to a wide diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks (resulting into presence of iron oxides). It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form. The fine-grained red and yellow soils are normally fertile, whereas coarse-grained soils found in dry upland areas are poor in fertility. They are generally poor in nitrogen, phosphorous and humus.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation- Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern part of the Deccan Plateau. Along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghat, long stretch of area is occupied by red loamy soil. Yellow and red soils are also found in parts of Odisha and Chattisgarh and in the southern parts of the middle Ganga plain.
The soil develops a reddish colour due to a wide diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks (resulting into presence of iron oxides). It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form. The fine-grained red and yellow soils are normally fertile, whereas coarse-grained soils found in dry upland areas are poor in fertility. They are generally poor in nitrogen, phosphorous and humus. -
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
Which of the following statements is correct?
Correct
Answer. C
Explanation-


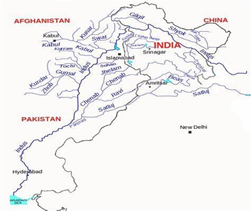
Statement 1 is incorrect- Jhelum flows through Srinagar and Wular lakes before entering Pakistan through a narrow gorge. It runs along the Indo-Pak border between Muzzafarabad and Mangla. It joins the Chenab near Jhang in Pakistan.
Statement 2 is incorrect- The river Indus originates from Bokhar Chau glacier in Tibet near Mansarovar lake. Flowing west, the river after cutting the Himalayan range enters India near Demchok in Ladakh, not Jammu and Kashmir.
Statement 3 is correct- The catchment area of the Indus is 11,65,000 sq. km. Out of this, 3,21,290 sq. km is in India which makes up 20%(one-fifth) of the total catchment area.
Statement 4 is incorrect- Ravi drains the area between the southeastern part of Pir Panjal and the Dhaoladhar ranges. Ravi flows through the Chamba valley of Himachal Pradesh and has a drainage area of 5,957 sq.km.Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation-



Statement 1 is incorrect- Jhelum flows through Srinagar and Wular lakes before entering Pakistan through a narrow gorge. It runs along the Indo-Pak border between Muzzafarabad and Mangla. It joins the Chenab near Jhang in Pakistan.
Statement 2 is incorrect- The river Indus originates from Bokhar Chau glacier in Tibet near Mansarovar lake. Flowing west, the river after cutting the Himalayan range enters India near Demchok in Ladakh, not Jammu and Kashmir.
Statement 3 is correct- The catchment area of the Indus is 11,65,000 sq. km. Out of this, 3,21,290 sq. km is in India which makes up 20%(one-fifth) of the total catchment area.
Statement 4 is incorrect- Ravi drains the area between the southeastern part of Pir Panjal and the Dhaoladhar ranges. Ravi flows through the Chamba valley of Himachal Pradesh and has a drainage area of 5,957 sq.km. -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
Regarding river Ganga and its tributaries, consider the following statements:
1. Akaknanda rises from the Gaumukh glacier in Uttarakhand.
2. The rivers Son, Yamuna and Punpun originate from the Central Highlands.
3. River Chambal, after rising from the Malwa plateau, flows northwards.
4. The river Kosi along with its tributary Arun, forms Saptkosi.
Which of the statements given above are correct?Correct
Answer. D
Explanation- The Ganga is the most important river of India both from the viewpoint of its basin and cultural significance.
Statement 1 is incorrect- It is Bhagirathi and not Alaknanda that rises from the Gaumukh glacier in the Gangotri.
● The Ganga rises in the Gangotri glacier near Gaumukh in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand. Here, it is known as the Bhagirathi. It cuts through the Central and Lesser Himalayas in narrow gorges.
● At Devprayag, Bhagirathi meets the Alaknanda; from here it is known as the Ganga.
● The Alaknanda has its own source in the Satopanth glacier above Badrinath.


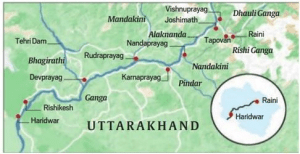
Statement 2 is correct- The major right bank tributaries of Ganga are Yamuna, Son and Punpun, all of which originate in the Central Highlands and Kaimur ranges.


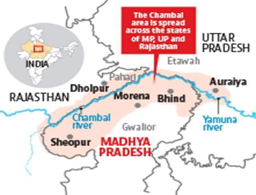
Statement 3 is correct- The Chambal rises near Mhow in the Malwa plateau of Madhya Pradesh and flows northwards through a gorge up to Kota in Rajasthan; the Gandhinagar dam has been constructed here. From Kota, it traverses down Bundi, Sawai Madhopur and Dholpur to finally join the Yamuna.
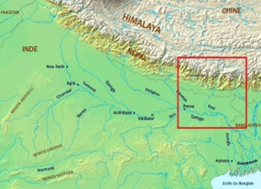
Statement 4 is correct- The Kosi is an antecedent river with its source to the north of Mount Everest in Tibet where its main stream Arun rises. After crossing the Central Himalayas in Nepal, it is joined by the Sun Kosi from the west and Tamur kosi from the east. It forms Sapt Kosi after uniting with the Arun River.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation- The Ganga is the most important river of India both from the viewpoint of its basin and cultural significance.
Statement 1 is incorrect- It is Bhagirathi and not Alaknanda that rises from the Gaumukh glacier in the Gangotri.
● The Ganga rises in the Gangotri glacier near Gaumukh in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand. Here, it is known as the Bhagirathi. It cuts through the Central and Lesser Himalayas in narrow gorges.
● At Devprayag, Bhagirathi meets the Alaknanda; from here it is known as the Ganga.
● The Alaknanda has its own source in the Satopanth glacier above Badrinath.



Statement 2 is correct- The major right bank tributaries of Ganga are Yamuna, Son and Punpun, all of which originate in the Central Highlands and Kaimur ranges.



Statement 3 is correct- The Chambal rises near Mhow in the Malwa plateau of Madhya Pradesh and flows northwards through a gorge up to Kota in Rajasthan; the Gandhinagar dam has been constructed here. From Kota, it traverses down Bundi, Sawai Madhopur and Dholpur to finally join the Yamuna.
Statement 4 is correct- The Kosi is an antecedent river with its source to the north of Mount Everest in Tibet where its main stream Arun rises. After crossing the Central Himalayas in Nepal, it is joined by the Sun Kosi from the west and Tamur kosi from the east. It forms Sapt Kosi after uniting with the Arun River.







