Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, improving response times and saving bandwidth. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the volume of data generated at the “edge” of networks—such as sensors, devices, and local data centers—has increased exponentially. Edge computing addresses the limitations of traditional cloud computing by enabling real-time data processing and analysis at or near the source of data generation.
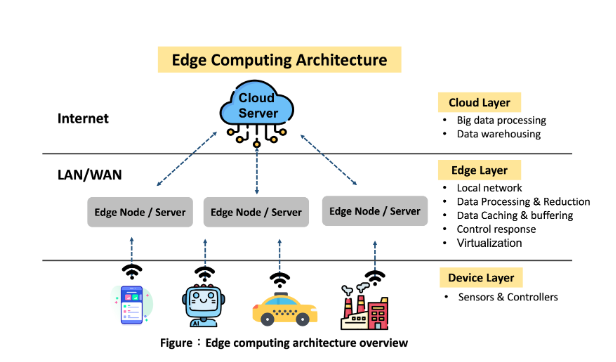
Features of Edge Computing
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing significantly reduces latency, which is critical for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing minimizes the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to centralized cloud servers, reducing bandwidth consumption and costs associated with data transfer.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Processing sensitive data locally can enhance security by reducing exposure to potential breaches during data transmission. This is particularly important in industries like healthcare and finance.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows organizations to scale their operations more efficiently by distributing computing resources across multiple locations rather than relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure.
- Improved Reliability: Local processing can continue even if connectivity to the central cloud is lost, ensuring that critical applications remain operational.
How Edge Computing Works?
Edge computing operates through a network of devices that process data at the edge rather than in centralized data centers. The process generally involves:
- Data Generation: Devices such as sensors, cameras, and IoT devices generate vast amounts of data.
- Local Processing: Edge devices analyze and process this data locally using algorithms and machine learning models.
- Decision Making: Based on the processed data, immediate decisions can be made without needing to communicate with a central server.
- Data Transmission: Only relevant or summarized data is sent to the cloud for further analysis or storage, optimizing bandwidth usage.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries:
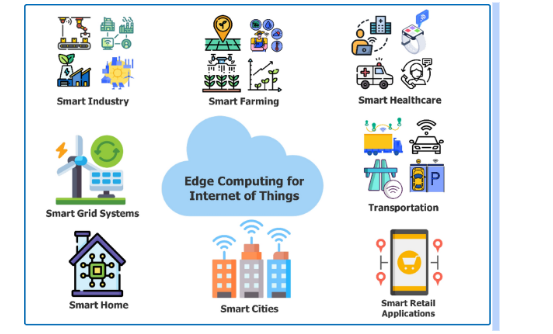
- Healthcare: Real-time patient monitoring systems utilize edge computing to process vital signs from wearable devices, enabling immediate alerts for abnormal conditions.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on edge computing for real-time processing of sensor data (e.g., LIDAR, cameras) to make split-second driving decisions.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing supports smart infrastructure by processing data from traffic sensors, surveillance cameras, and environmental monitors locally to enhance urban management.
- Retail: Retailers use edge computing for real-time inventory management and personalized customer experiences through smart shelves and in-store analytics.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In manufacturing, edge computing enables predictive maintenance by analyzing equipment performance data locally to prevent downtime.
- Energy Management: Smart grids leverage edge computing to monitor energy consumption patterns in real-time, optimizing energy distribution and reducing waste.
Facts and Statistics Supporting Edge Computing
- Market Growth: The global edge computing market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach around $84 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of about 29% .
- Data Generation Projections: According to IDC, by 2025, approximately 175 zettabytes of data will be created globally, with a significant portion processed at the edge .
- Latency Reduction: Edge computing can reduce latency from several hundred milliseconds (typical in cloud processing) to less than 10 milliseconds, which is crucial for applications like autonomous driving .
- IoT Device Proliferation: The number of connected IoT devices is expected to exceed 30 billion by 2025, driving demand for edge computing solutions that can handle local processing needs .
- Cost Savings: Organizations implementing edge computing solutions can save up to 30% on bandwidth costs, according to industry estimates.
- Adoption Rates: A survey conducted by Spiceworks reported that about 80% of organizations are expected to adopt edge computing solutions by 2023, highlighting its growing importance in IT strategies.
Challenges Facing Edge Computing
Despite its advantages, several challenges exist:
- Security Concerns: With multiple devices operating at the edge, ensuring consistent security measures across all endpoints can be challenging.
- Management Complexity: Managing a distributed network of edge devices requires advanced orchestration tools and strategies to ensure seamless operation.
- Interoperability Issues: Different devices may use various protocols and standards, complicating integration efforts across platforms.
- Limited Processing Power: While edge devices are becoming more powerful, they may still lack the computational resources available in centralized cloud environments for complex tasks.
Way Forward
The future of edge computing looks promising as it continues to evolve:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Combining edge computing with AI will enable more sophisticated analytics at the source of data generation.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance the capabilities of edge computing by providing faster connectivity and enabling more devices to connect seamlessly.
- Standardization Efforts: As adoption increases, efforts towards standardizing protocols for interoperability among devices will likely gain traction.
- Focus on Sustainability: Edge computing can contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource usage and reducing energy consumption in various applications.
Conclusion
Edge computing represents a significant shift in how we process and analyze data in an increasingly connected world. By bringing computation closer to where it is needed most, it enhances efficiency, reduces latency, and enables real-time decision-making across various industries. As technology continues to advance, addressing challenges related to security, management complexity, and interoperability will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of edge computing in shaping the future digital landscape.
Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Examination
Q1. Discuss the role of edge computing in enhancing operational efficiency across various sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. What challenges does it face in widespread implementation?
(Answer in 250 Words, 10 Marks)
Spread the Word



