Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that enables the secure recording and verification of transactions across multiple computers. Originally developed as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a versatile platform with applications across various sectors. Its key features—transparency, security, and immutability—make it an attractive solution for numerous challenges in today’s digital landscape.
Features of Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where each participant (node) has access to the entire database. This reduces the risk of single points of failure and enhances security.
2. Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are recorded in a public ledger that is accessible to all participants. This transparency fosters trust among users and allows for real-time auditing of transactions.
3. Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network participants. This feature ensures the integrity of the data and prevents fraud.
4. Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link between them. This makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the data.
5. Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code on the blockchain. They automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
How Blockchain Works?
The functioning of blockchain can be summarized in several steps:
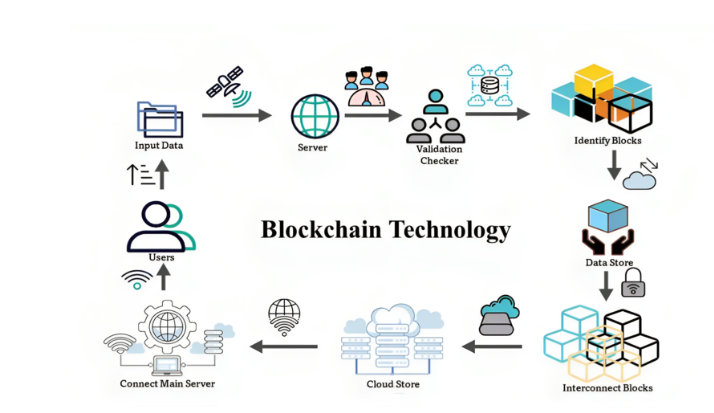
1. Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is then broadcasted to the network.
2. Validation: Network nodes validate the transaction using consensus mechanisms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake).
3. Block Creation: Once validated, transactions are grouped together into a block.
4. Chain Addition: The new block is added to the existing blockchain after consensus is achieved.
5. Update: All nodes in the network update their copies of the blockchain to reflect the new transaction.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has diverse applications across various sectors:
1. Finance and Banking: Blockchain enables faster and cheaper cross-border payments by eliminating intermediaries. Companies like Ripple leverage this technology for real-time international money transfers.
2. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains by recording every transaction related to goods from production to delivery. Companies like IBM and Maersk are using blockchain to streamline logistics and reduce fraud.
3. Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, ensuring that they are accessible only to authorized personnel while maintaining privacy compliance (e.g., HIPAA). It also facilitates secure sharing of clinical trial data among stakeholders.
4. Voting Systems: Blockchain can improve electoral processes by providing secure, transparent voting systems that reduce fraud and increase voter confidence in election outcomes.
5. Digital Identity Verification: Blockchain can provide a decentralized solution for identity verification, allowing individuals to control their personal information and share it securely with service providers without compromising privacy.
6. Real Estate Transactions: By recording property titles on a blockchain, real estate transactions can become more efficient, reducing paperwork and fraud while ensuring clear ownership records.
7. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs represent ownership of unique digital assets (e.g., art, music) on a blockchain, enabling creators to monetize their work while ensuring provenance and authenticity.
8. Insurance: Smart contracts can automate claims processing in insurance by verifying conditions and executing payouts without manual intervention, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
9. Energy Trading: Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading systems where consumers can buy and sell excess energy generated from renewable sources directly with one another.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Technology
Despite its potential, several challenges hinder widespread adoption:
1. Scalability: Many blockchain networks face scalability issues due to limited transaction throughput compared to traditional systems like Visa or Master card.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear regulatory frameworks can create uncertainty for businesses looking to invest in blockchain technologies.
3. Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms (e.g., Proof of Work) consume significant amounts of energy, raising environmental concerns about sustainability.
4. Interoperability: Different blockchain systems often operate in silos without seamless integration capabilities, limiting their utility across platforms.
5. Public Perception and Trust: Misunderstandings about blockchain technology and its association with cryptocurrencies can hinder acceptance among businesses and consumers.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology looks promising as it continues to evolve:
-
- Increased Adoption Across Industries: As organizations recognize its benefits beyond cryptocurrencies, more sectors will adopt blockchain solutions for transparency and efficiency.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: The convergence of blockchain with AI, IoT, and big data will create innovative applications that enhance operational efficiencies.
- Development of Regulatory Frameworks: Governments are beginning to establish clearer regulations surrounding blockchain use, which will foster trust and encourage investment.
- Focus on Sustainability: Efforts are underway to develop more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms that reduce environmental impacts while maintaining security.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a significant advancement in how we record and verify transactions across various sectors. Its unique features—decentralization, transparency, immutability, and security—offer solutions to many challenges faced by traditional systems today. As industries continue to explore its potential applications while addressing inherent challenges, blockchain is poised to play a transformative role in shaping the future economy.
Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Examination
Q.1 Critically assess the implications of blockchain technology for financial systems. How can it transform traditional banking practices and what are the risks involved? Discuss.
(Answer in 250 Words, 10 Marks)
Spread the Word



