TAG: GS-2: EDUCATION INSTITUTIONS & MISCELLANEOUS
CONTEXT: The QS Asia University Rankings 2025 have been released. Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IITD) has achieved the highest position in India. It ranks 44th overall in Asia.
EXPLANATION:
- The QS World University Rankings is one of the most widely recognised and respected global rankings of universities, published annually by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS).
- These rankings are influential in assessing the relative performance of universities around the world across various dimensions of academic and research excellence.
- The QS World University Rankings includes both global rankings and regional rankings (e.g., QS Asia, QS Latin America, QS Arab Region, etc.), which provide information on the performance of universities in different regions.
India’s Top 10 Universities in QS Asia Rankings 2025:
1. IIT Delhi – Rank 44
2. IIT Bombay – Rank 48
3. IIT Madras – Rank 56
4. IIT Kharagpur – Rank 60
5. Indian Institute of Science (IISc) – Rank 62
6. IIT Kanpur – Rank 67
7. University of Delhi – Rank 81
8. IIT Guwahati – Rank 104
9. IIT Roorkee – Rank 108
10. Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) – Rank 110
IIT Delhi, IIT Bombay, and IIT Madras stand as India’s premier institutions, recognized for their academic standards, research outputs, and reputational impact. Each institute brings unique strengths that contribute to their high rankings, cementing their status as world-class universities.The Growing Influence of Indian Universities:
- Research and Development: Enhanced funding has been allocated to promote research output and innovation.
- International Collaboration: Many Indian universities are collaborating with global institutions to enhance academic and research opportunities.
- Reforms in Higher Education: Recent initiatives, such as the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, have laid the groundwork for expanding India’s educational framework, focusing on critical thinking, research, and innovation.
In 2025, 21 new Indian institutions were added to the QS Asia Rankings, reflecting the growing emphasis on improving academic standards and global presence.
QS Asia 2025 Rankings for South Asia:
- Seven Indian universities have made it to the top 10 in South Asia, notably the National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, tied for 6th place with IIT Kanpur, indicating healthy regional competition and collaboration within South Asia.
- South Asian universities, mainly from India, dominate the top spots in the Southern Asia category, with seven institutions making it to the top 100.
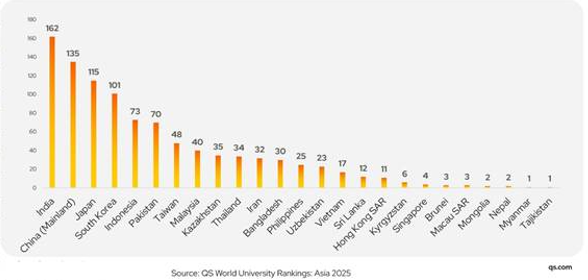
- India is the most represented country in the rankings, reflecting its strong commitment to advancing its higher education system.
- It has seen impressive growth over the past decade, with the number of institutions in the QS rankings increasing by 318%.
- Universities such as the University of Petroleum and Energy Studies (UPES) have significantly improved, climbing 70 spots to 148th place because of improved performance in metrics such as international research networks and citations per paper.
- Anna University scored perfect in citations per faculty, underscoring its research excellence.
- The University of Colombo represents Sri Lanka (ranked in the 551-600 band), with the University of Peradeniya also showing progress in the regional rankings.
- Pakistan’s Quaid-e-Azam University (QAUM) is a prominent representative, while universities such as Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS) are also in the middle range of the rankings.
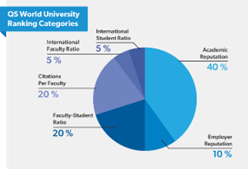
Key Criteria for QS Rankings:
- Academic Reputation: This is the most significant criterion, contributing to 40% of the overall score. It is based on an academic survey where universities are ranked according to the quality of their teaching and research as perceived by scholars worldwide.
- Faculty/Student Ratio: This metric (20%) assesses the teaching quality, measured by the number of academic staff relative to the number of students.
- Citations per Faculty: This metric (20%) measures the impact and quality of the research produced by the university, as indicated by the number of citations in academic papers per faculty member.
- Employer Reputation: This accounts for 10% of the ranking and reflects how highly employers regard the university’s graduates.
- International Faculty and Student Ratio: This measures the diversity of the university’s staff and student body, reflecting its international outlook and ability to attract talent from around the world (5% each).
Additional Focus Areas:
-
- Research Output: Universities are also assessed based on the volume and impact of their published research, with some rankings (such as QS by Subject) focusing specifically on research strengths in individual disciplines.
- Internationalization: The QS rankings often highlight how well universities are connected to the global academic community, based on faculty and student mobility, as well as international collaborations and partnerships.
Challenges for Indian Universities in Competing Globally:
- Funding and Resources: Many Indian universities have limited funding compared to top institutions in other countries, impacting research capabilities and faculty recruitment.
- Global Engagement: Indian universities often lag in international faculty and student ratios, affecting their global outreach and reputation.
- Innovation and Research Output: There is a need for increased emphasis on research output and faculty-student engagement to compete with leading universities in Asia.
- Faculty-Student Ratio: Many Indian institutions struggle to maintain an optimal faculty-student ratio, which affects student support and learning quality.
Conclusion:
The QS Asia University Rankings 2025 is a milestone for Indian higher education, with India becoming the most represented country in Asia. This achievement underlines the impact of recent educational reforms, increased funding and government initiatives aimed at strengthening India’s global presence.
Source:
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2072018
Spread the Word



