Answer:
APPROACH AND STRUCTURE
1. Introduce NPM.
2. Write some basics about NPM on rationalism lines.
3. Then write how NPM borrows its features from different schools.
4. Give some practices of NPM.
5. Comment part: some flaws of NPM.
6. Conclude.
INTRODUCTION: NPM is considered as 2nd reinvention of the government which emerged as a dominant paradigm during 1990s.
BODY: The term “New Public Management” was first coined by Christopher Hood in his book ‘A Public Management for all Seasons’ in 1991. He described NPM as a ‘Marriage of opposites’, one of which is the new institutional economics and the other is ‘a set of successive waves of business-type managerialism’. The book Reinventing Government: How the Entrepreneurial Spirit is Transforming the Public Sector by Osborne and Gaebler, published in 1992, takes this new trend of public administration, the New Public Management, much further.
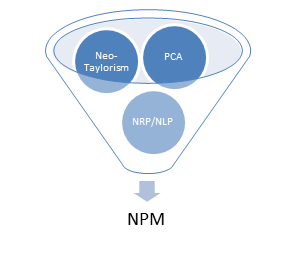
NPM has its root in neo‐Taylorism and PCA.
| Neo‐Taylorism | PCA |
| 1. Taylorism Plus | 1. Privatisation. |
| 2. Personnel Management | 2. Liberalisation. |
| 3. Performance Management/Appraisal | 3. Regulation |
| 4. Performance Incentivisation | 4. Facilitation |
| 5. Managerialism | 5. Marketisation |
The principles of NPM are:
-
- The main principle of NPM is to emphasize economy, efficiency, and effectiveness by downplaying the importance of regulation.
- Reorganizing the bureaucracy into different agencies.
- Increase competition through the introduction of quasi-market systems and contract systems.
- Expenses reduce and facilitate income growth.
- Shift to greater competition in public sectors.
- NPM emphasizes more on private-sector styles of management.
- Managerialism that means the role of the administrator transforms as a manager.
- Increasing the flexibility and mobility of organizational structure, personnel, and working conditions.
- Greater emphasis on consumerism. To NPM citizens are considered as consumers.
Dunleavy’s view, there are three important features of NPM which are diagrammatically represented.
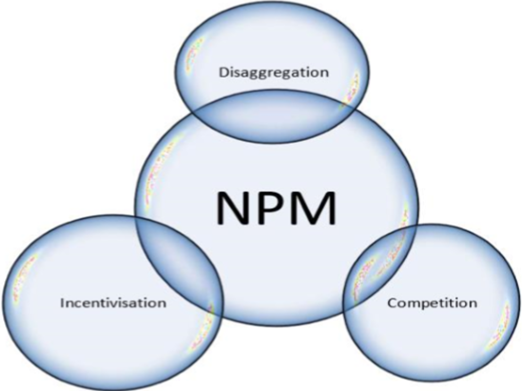
Economic Rationalism: It deals with the application of rationality in terms of
-
- Performance output
- Result-orientation
- Disaggregation-dividing govt. into multiple institutions
- Incentivisation
- Hands on management
- No mystical or normative notions
NPM also possesses these characteristics. NPM is a business/management process theory which has its roots in Taylorism and Scientific Management Theory. It’s the political-economic concept which explains how rationally designed processes can increase the 3Es of the govt. how the PA can increase its performance through management science.
Novel Approaches to PA and management: Some practical examples:
-
- USA: National performance review an interagency task force to reform US federal administration was constituted under the leadership of Bill Clinton and was headed by Vice-President Al Gore. Under this initiative a report “Creating the Government which cost less and work better” was published. Under NPR, emphasis was given on cutting red tape; cutting expenditure; going back to basics and; focusing on performance than service.
- UK: Executive or “Next Steps” Agencies have been drawn out of ministries and departments to allow “a clear delineation between policy formulation and policy implementation”. Under this initiatives were taken such as, autonomy was given to executive agencies to uphold their accountability on the basis of agreement between ministry/department and executive agencies. Such initiatives resulted into phenomenon of agencification and it became legacy of reform in UK. New localism another major initiative in UK in which NPM has been incorporated in which goals are set at national level and achieved at local level by giving autonomy to local bodies.
- Singapore: Initiative known as SINGAPORE ONE in civil services.
- Japan: Total Quality Management. (TQM)
- Impact on Developing Countries:
- Malaysia: Initiated TQM, Client charter, PEMANDU business-like (Performance Management and Delivery Unit)- successful in reducing corruption in civil services.
- Philippines: CITIZEN FIRST
- South African Countries: Such as Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda took initiative in revenue department. Largely there was increase in their tax to GDP ratio.
India: Fifth pay commission recommended to reduce its workforce in 10 years is considered as reinvention. New Economic Policy took many initiatives such as liberalization, privatization, MOU, PLI scheme, EoDB, Citizen Charter etc. which improved tax to GDP ratio; improved PSU performance and; made economy more business friendly.
Criticism of NPM:
-
- PA can’t be equated with business management.
- Rationalism is essential but Democratic Humanism is also needed.
- Values are epitome of democracy.
- Performance is important so is democratic accountability.
- State can’t be run like business.
CONCLUSION:
NPM may have the epitome of managerial values e.g.3Es but it lacks the ideals of an administrative state. Various post-NPM models like NPS, NWS, NPG etc. have tried to balance NPM with democratic notions by having value aspects. Economic rationalism should be clubbed with democratic idealism to achieve a balanced type of state serving its citizens efficiently.
Spread the Word