APPROACH
Introduction: Explain basics about river linking project in India.
THE BODY
-
- Mention the positives of interlinking of rivers for multi-dimensional inter-related problems.
- Mention the negatives of interlinking of rivers for multi-dimensional inter-related problems.
Conclusion: Conclude by taking a balanced path. Suggest improvements in the project along with alternatives of efficient water use in India.
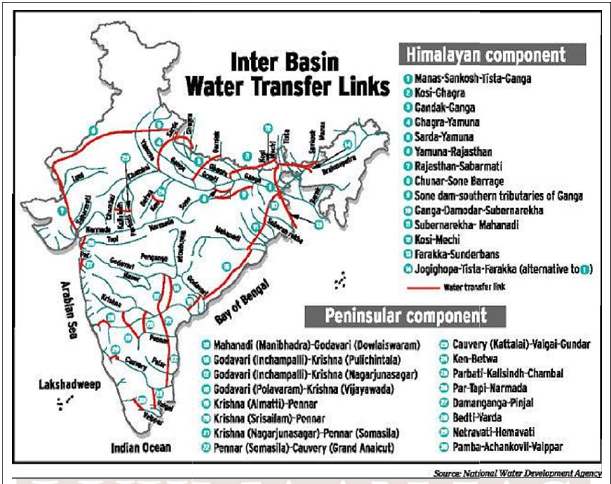
The National Perspective Plan (NPP) presented the development of water resources through the inter-basin transfer of water and the transferring of water from water-surplus basins to water-deficit basins. The interlinking of rivers is a large-scale civil engineering project that aims to effectively manage water resources in India under the NPP.
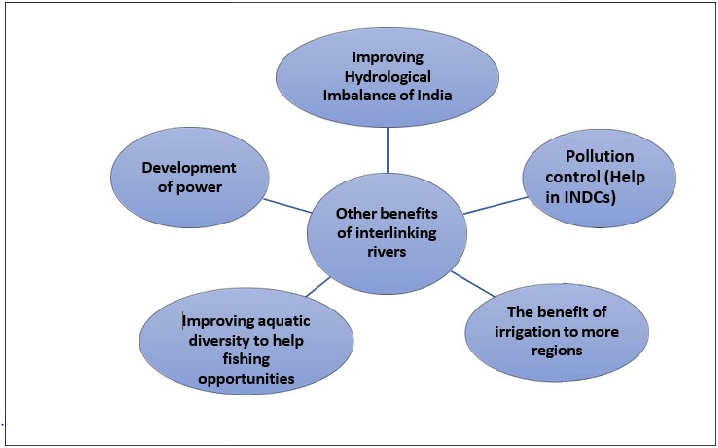
Positives of interlinking of rivers for multi-dimensional inter-related problems:
| Droughts |
|
| Floods |
|
| Improve the inland navigation |
|
Negatives of interlinking of rivers for multi-dimensional inter-related problems:
- Ecological challenges: The ambitious project will induce diversion of forest areas and submergence of fertile land leading to deforestation and soil- erosion. For example, the Ken- Betwa link projects has reduced 8% of forest land of Panna National Park. Also, river diversion may bring significant changes in the physical and chemical compositions of the sediment load, river morphology and the shape of the delta formed at the river basin.
- Social challenges: Reconstruction and rehabilitation of millions of people in and around the river catchments could face significant psychological damage which could result in social unrest and protests in the initial stages itself.
- Political challenges: The inter-state river doesn’t have a bright history in India (for example,Cauvery River dispute). Further, water being a state subject demands cooperation which may be a challenge given the diversity India offers.
Way forward:
- The interlinking of rivers in India has both pros and cons. Implementing the project in its entirety may be a challenge in present times.Therefore, government must opt a decentralized method of implementation instead of a centralized one.
- Inter-linking projects should receive the nod only after appropriate EIA and environmental clearances.
- Further, we must look for alternatives of efficient water use in India. For instance, measures like efficient water use in agriculture (per drop more crop), resourceful rain water harvesting in drought prone areas and so on can be looked upon to liberate India from the persistent water stress.