TAG: GS-2: IR & GS-3: ECONOMY
CONTEXT: The Union Commerce and Industry Minister of India recently exchanged MoUs with the United States Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo to ‘expand and diversify critical mineral supply chains’ between India and the US.
EXPLANATION:
What is a Minerals Security Partnership (MSP)?
- Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) is a US-led alliance of 14 developed countries launched in June 2022.
- The elite critical minerals club is also known as the ‘Critical Minerals Alliance’.
- It was set up to ensure that critical minerals are produced, processed and recycled in a way that it secures critical mineral supply chains.
- It also aims to weaken China’s grip on supplies of critical minerals worldwide.
- India is the only developing country to become a part of the MSP.
- Members
- Australia, Canada, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Norway, Republic of Korea, Sweden, United Kingdom, United States, and European Union.
What is the Minerals Security Finance Network?
The MSFN is a US-led initiative aimed at enhancing cooperation among member countries to secure supply chains for critical minerals.
What are Critical Minerals?
- A mineral is critical when the risk of supply shortage and associated impact on the economy is (relatively) higher than other raw materials.
- These minerals are essential for economic development and national security, and their lack of availability/ the concentration of extraction/ processing in a few geographical locations could potentially lead to supply chain vulnerabilities.
- These (such as lithium, graphite, cobalt, titanium, and rare earth elements) are essential for the advancement of many sectors, including high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defence.
- It forms part of multiple strategic value chains, including –
- Clean technologies initiatives such as zero-emission vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels.
- Information and communication technologies, including semiconductors.
- Advanced manufacturing inputs and materials such as defence applications, permanent magnets, ceramics.
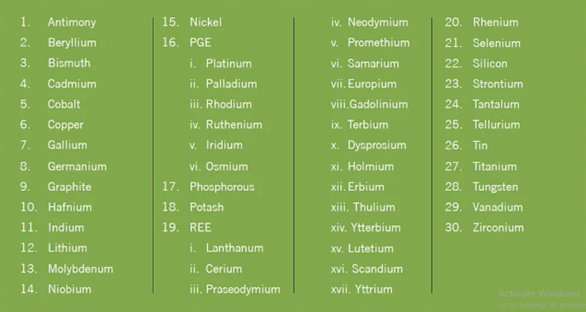
India’s status of critical minerals:
- India is endowed with and produces over 85 minerals.
- Some of the required critical mineral assets are not yet ready to be mined.
- India is dependent on China and other countries to meet its requirement of critical minerals including Rare Earth Elements (REE)
- Currently, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL), is taking charge of ensuring mineral security through facilitating supply chains, mine asset acquisitions, and G2G collaborations.
- Only about 10-20% of India’s critical minerals has been explored.
What are the challenges to critical minerals supply chains?
- China – China being an important player in the critical minerals supply chains and it is yet to overcome the effects of covid-19, and so India faces short falls in the supply
- Russia-Ukraine war – Russia being significant producers of nickel, palladium, titanium sponge, & scandium and Ukraine being producer of titanium, the war has disrupted the supply chains.
- Power shifts – Due to low supply from Russia and china the developed countries have drawn up plans such as Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and G7’s Sustainable Critical Minerals Alliance.
- Demand for green technologies – Since India lacks the critical minerals requirement demand for the green technologies it has depend on other countries.
- Geographic hurdles – The geographic concentration of mining and processing of the minerals may also adversely impact their availability.
- Trade agreements – Lack of trade agreements with other mineral-endowed countries.
- Private sector – Lack of private sector involvement in the critical mining industries.
- Multilateral Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) – India is not a part of it which brings countries together to build robust critical minerals supply chains needed for climate objectives.
- Periodic assessments – Lack of periodic assessments for critical minerals to be sustainable.
Source:
Spread the Word



