Answer.
APPROACH
Introduction- Begin with the report highlighting the grave concern over the shrinking of lakes globally. Use key facts and examples.
The Body
-
- Firstly, address the causes behind such drastic reduction in lakes and then discuss in detail its implication on environment, society, economy and politics.
- Suitable examples and linkages should be established.
Conclusion- Suggest the need for preservation of such lakes and how this objective can be achieved.
Introduction:
Based on a three-decade analysis of satellite observations complemented with climate models, researchers have discovered that over half of the world’s largest lakes have shrunk dramatically since the 1990s due to human activities and Climate Change. The cumulative loss of these lakes is estimated to be equivalent to 17 Lake Meads of the USA.
Some of the largest lakes which have diminished include the Aral Sea of Central Asia, Lake Mar Chiquita of Argentina, the Dead Sea of the Middle East, the Salton Sea of California etc. India’s Tso Moriri Lake (Ladakh) has also featured among the worst affected lakes.
The Body-
Factors responsible for the loss of lakes:
Roughly 60% of the lakes have shrunk due to unmindful human activities since the 1960s. the issue has been further exacerbated by the impacts of Climate Change.
1. Faulty land use practices: Humans have encroached upon the lakes under the garb of development. The unsustainable development projects (roads, railways, industries, etc.) and rising demand for land to expand agriculture and establish settlements are serious threats to lakes which are on the verge of extinction from the planet.
2. Sedimentation: Illegal mining for sand and gravel, construction of waterways, unregulated tourism and industrial expansion besides landslides, heavy rainfall cause accumulation of sediments in the lakes. The study has found that more than half of the reservoirs in Peninsular India have their water storage plummeting because of sedimentation.
3. Overconsumption: The increased pressure on lakes for water for drinking water, hydroelectric power projects, fishing etc., have led to the shrinking of the capacity of lakes such as the Aral Sea and Dead Sea, among many others.
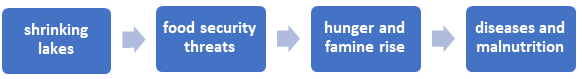
4. Climate Change: The average global temperatures have surpassed 1.1 degrees Celsius of warming, driven mainly by fossil fuel consumption and the hike in the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide. Most of the lakes in the world are experiencing elevated temperatures and, consequently, higher levels of potential evapotranspiration which has led to drastic loss of water from the lakes. Therefore, the drying of lakes from Africa, Mongolia, and other regions, including the Arctic, is a major cause of concern.
The researchers mention Megadrought, having drained two largest reservoirs of the USA, namely Lake Powell and Lake Mead, both of which are fed by the river Colorado. Extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts, etc., in the wake of Climate Change are contributing factors in diminishing lakes across the globe.
Impacts of shrinking lakes:
Environmental impacts:
1. Water cycle: Any disturbance in the elements of the hydrological cycle due to diminishing lakes would be catastrophic as it affects the whole ecosystem and biosphere. The rapidly rising evaporation rates and high moisture losses from lakes such as the Great Lakes of the USA are alleged to increase precipitation in some pockets of the world.
The perturbed water cycle is likely to have uncertain whether implications, with droughts and floods occurring simultaneously in different regions.
2. Carbon cycle: The lakes in the warm environment are known to emit more greenhouse gases. Warm lakes might metabolize a greater proportion of the terrestrial organic carbon entering the warm waters than cool lakes, leading to increased levels of carbon dioxide. The warming lakes are considered a source of methane and carbon dioxide emissions.
3. Loss of biodiversity: With the depletion of surface and groundwater due to the loss of lakes, both terrestrial and aquatic life would face threats of extinction. As per a study, nearly 20% of the endemic biodiversity of Lake Victoria (South America) has been reported as threatened with extinction.
4. Algal bloom: The pollution of lakes like Bellandur (Karnataka) supports the proliferation of harmful algal blooms, which further cause the creation of dead zones and have deadly impacts on fish, molluscs, and other aquatic species.
5. Loss of wetlands: Lakes and ponds are considered vital wetlands which have huge ecological significance. The drastically shrinking lakes have a direct bearing on the areal stretch of wetlands and loss of vital ecological services such as food, clean water, flood regulation, recreation etc.
6. Land degradation: The shrinking of lakes decreases the productivity of lands which depend on them for water. This will also adversely impact the infrastructure near it, such as canals, ports etc., with cascading impacts on the local and national economy.
7. Coastline erosion: The loss of lakes would trigger intense flash floods, thus, leading to erosion of floodplains and coastlines.
Associated Socio-Economic Impacts:
1. Water crisis: The loss of lakes implies water shortage as its direct consequence. UN estimates reveal that about 2 million people lack access to drinking water. This situation will worsen in future due to shrinking lakes.
Lake Chad is a large freshwater lake in Africa which supplies water to nearly 40 million people, but this lake has witnessed shrinkage by over 90%. The subsequent water crisis in the Sahel region (Nigeria, Niger, Cameroon, Chad) is alarming.
2. Social tensions: Water scarcity and increasing water demands, especially in arid and semi-arid regions like the Horn of Africa, would disturb social harmony as ethnic conflicts for control over waters are likely to intensify further.
3. Risks to food security: Not only will the diminishing lakes affect the agricultural productivity of adjunct regions, but it will also result in a loss of quality and quantity of seafood and marine agri-exports.
4. Loss of livelihoods: The turning of lakes into marshes or barren lands eventually will have a direct impact on agriculture, industries and fisheries which rely on lake water for flourishing. The tourism sector witnesses a drag on its growth with lakes losing their existence. This compounds the problem of unemployment and leads to depressed living standards of the affected.
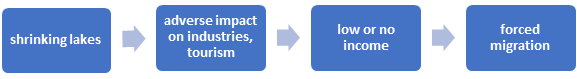
5. Navigation: Lakes such as the Great Lakes of North America hold immense significance from the perspective of transportation (waterways) and trade. But the losses to the lakes due to human activities and global warming are likely to hamper economic growth and development with direct effects on the navigable capacity of the lakes.
6. Energy crisis: Those regions which heavily rely on lakes for generation of hydroelectricity would experience hardships due to decline in water reservoirs. This will also make it difficult for countries (including India) to achieve their targets regarding renewable, green energy.
Associated Political Impacts:
1. International water conflicts: Lakes such as Lake Victoria in Africa act as a source of important rivers like the Nile. With the decline in source waters, the volume of water in rivers will also witness a reduction and aggravate the conflicts among countries for water. Similar disputes will arise from transnational lakes.
2. Inter-state water conflicts: The water disputes will further compound within countries between the provinces/states. For instance, Pulicat Lake is shared by Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
3. Increase in fiscal burden: The rising demands for water, healthcare and social security as an aftermath of shrinking lakes will impinge on the public exchequer. More resources will be required to address the needs and demands of the victims.
4. Rise in Climate migrants: The rising migration of people from regions affected by the shrinking of lakes will add to already brewing tensions between nations and communities. The welfare of those affected will require proactive efforts from governments and the international community.
Conclusion:
Since the impacts of the loss of lakes are multidimensional and interconnected, the need of the hour is to address the issue through an integrated approach. The protection of Ramsar wetlands and all the lakes must be the priority of governments and local communities, following a decentralised, community-based landscape approach. Addressing the root cause of Climate Change underlines the significance of the Paris Climate Agreement and sustainable development goals to ensure the ecology and humans benefit from their interconnected relationship.
Spread the Word



