TAG: GS:3- ENVIRONMENTAL & ECOLOGY
CONTEXT: Researchers from India studied 13 mangrove species from Kerala and found that the estimated maximum leaf temperatures were higher than the surrounding air temperatures.
EXPLANATION:
What are Mangroves?
- Mangroves are a unique type of coastal ecosystem found in tropical and subtropical regions. They are dense forests of salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that thrive in intertidal zones, where land meets the sea.
- These ecosystems are characterized by their ability to withstand harsh conditions, such as saline water, tidal fluctuations, and muddy, oxygen-poor soils.
-
- Mangrove plants have special roots like prop roots and pneumatophores, which help impede water flow and provide support in the challenging tidal environment.
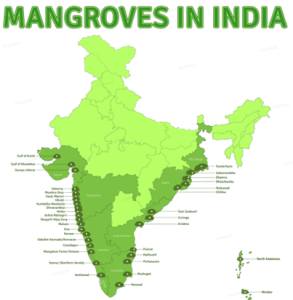
Mangrove Cover in India:
- According to the Indian State Forest Report 2021, Mangrove cover in India is 4992 sq. Km which is 0.15% of the country’s total geographical area.
- Sundarbans in West Bengal are the largest mangrove forest regions in the world. It is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Besides the Sundarbans, the Andamans region, the Kachchh and Jamnagar areas in Gujarat too have substantial mangrove cover.
Significance:
- Biodiversity Conservation:Mangroves provide a unique habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, serving as breeding, nursery, and feeding grounds for numerous marine and terrestrial organisms.
- For example, sundarban hosts the Royal Bengal tiger, Irrawady Dolphin, Rhesus macaque, Leopard cats, Small Indian civet.
- Coastal Protection:Mangroves act as natural buffers against coastal erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis.
- Their dense root systems and tangled network of prop roots stabilize shorelines and reduce the impact of waves and currents.
- During hurricanes and cyclones, mangroves can absorb and dissipate a significant amount of energy, protecting inland areas and human settlements from devastating damage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Mangroves are highly efficient carbon sinks, sequestering large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass and sediments.
- Fisheries and Livelihoods:Mangroves support fisheries by providing nursery areas for fish and shellfish, enhancing fishery productivity and contributing to livelihood and local food security.
- Water Quality Improvement: Mangroves act as natural filters, trapping and removing pollutants and excess nutrients from coastal waters before they reach the open ocean.
- Their role in purifying water contributes to the health of marine ecosystems and helps maintain the balance of fragile coastal ecosystems.
- Tourism and Recreation:Mangroves offer recreational opportunities such as eco-tourism, birdwatching, kayaking, and nature-based activities, which can promote sustainable economic growth for local communities.
Challenges:
- Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation:Mangroves are often cleared for various purposes, including agriculture, urbanization, aquaculture, and infrastructure development.
- Such activities lead to the fragmentation and loss of mangrove habitats, disrupting their ecosystem functioning and biodiversity.
- The conversion of mangroves into shrimp farms and other commercial uses is a significant concern.
- Climate Change and Sea Level Rise:Rising sea levels due to climate change pose a significant threat to mangroves.
- Climate change also brings about extreme weather events, such as cyclones and storms, which can cause severe damage to mangrove forests.
- Pollution and Contamination:Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and improper waste disposal contaminate mangrove habitats.
- Heavy metals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect the flora and fauna of these ecosystems.
- Lack of Integrated Management: Often, mangroves are managed in isolation, without considering their interconnectedness with adjacent ecosystems like coral reefs and seagrass beds.
- Integrated management approaches that consider the broader coastal ecosystem are necessary for effective conservation.
Government Initiatives Related to Mangrove Conservation:
- MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes)
- Sustainable Aquaculture in Mangrove Ecosystem (SAIME) initiative
Source:
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/forests/mangroves-exhibit-exceptional-heat-resilience-study-reveals
Spread the Word



