Day-679
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. With reference to the National Carbon Registry, consider the following statements:
1. It is an initiative of the Union Environment Ministry, launched as part of the ‘Carbon Credit Trading Scheme’.
2. It will allow India to effectively manage national data and processes for trading carbon credits.
3. It will be interoperable with the global Climate Action Data Trust (CAD Trust), launched by the World Bank.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has developed an open-source software which allows countries (India being no exception) to effectively manage national data and processes for trading carbon credits. The software, called the National Carbon Registry, has recently been accredited as a digital public good (DPG). As a DPG, the registry uses open-source code, which allows countries to replicate and adapt the information to fit their own needs and contexts.
Statement 3 is correct: Built as an interoperable digital system, it can be integrated with national measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) systems and international digital systems such as UNDP’s voluntary cooperation platform and the global platform Climate Action Data Trust (CAD Trust) launched by the World Bank. This can result in a broader suite of digital public infrastructure to address climate challenges.
The registry follows national and international best practices based on inputs from countries and is a result of ongoing work by the Digital4Climate (D4C) Working Group, which includes UNDP, the World Bank, the United Nations Framework Convention of Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) among others.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has developed an open-source software which allows countries (India being no exception) to effectively manage national data and processes for trading carbon credits. The software, called the National Carbon Registry, has recently been accredited as a digital public good (DPG). As a DPG, the registry uses open-source code, which allows countries to replicate and adapt the information to fit their own needs and contexts.
Statement 3 is correct: Built as an interoperable digital system, it can be integrated with national measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) systems and international digital systems such as UNDP’s voluntary cooperation platform and the global platform Climate Action Data Trust (CAD Trust) launched by the World Bank. This can result in a broader suite of digital public infrastructure to address climate challenges.
The registry follows national and international best practices based on inputs from countries and is a result of ongoing work by the Digital4Climate (D4C) Working Group, which includes UNDP, the World Bank, the United Nations Framework Convention of Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) among others. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements about Santiago Network:
1. It was officially launched at the UN Climate Conference held in Glasgow, the United Kingdom.
2. It provides technical assistance to developing countries for addressing loss and damage caused by climate change-related extreme weather events.
3. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) hosts the Secretariat of this network.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect while statement 2 is correct: The Santiago Network was established at COP 25 in Madrid as part of the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage (WIM) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change with the objective of “catalysing technical assistance of relevant organisations, bodies, networks and experts, for the implementation of relevant approaches for averting, minimise and addressing loss and damage at the local, national and regional level, in developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change.”
● One of the vital functions of the Santiago network is to catalyse technical assistance of relevant organizations, bodies, networks and experts, for the implementation of relevant approaches for averting, minimize and addressing loss and damage at the local, national and regional level, in developing countries
Statement 3 is incorrect: The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) and United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS) host the Santiago network secretariat, as announced during the UNFCCC COP28 held at Dubai, United Arab Emirates in 2023.
● The UNOPS is a UN agency dedicated to implementing infrastructure and procurement projects for the UN system, international financial institutions, governments and other partners around the world. It is headquartered at the UN City campus in Copenhagen, Denmark.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect while statement 2 is correct: The Santiago Network was established at COP 25 in Madrid as part of the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage (WIM) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change with the objective of “catalysing technical assistance of relevant organisations, bodies, networks and experts, for the implementation of relevant approaches for averting, minimise and addressing loss and damage at the local, national and regional level, in developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change.”
● One of the vital functions of the Santiago network is to catalyse technical assistance of relevant organizations, bodies, networks and experts, for the implementation of relevant approaches for averting, minimize and addressing loss and damage at the local, national and regional level, in developing countries
Statement 3 is incorrect: The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) and United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS) host the Santiago network secretariat, as announced during the UNFCCC COP28 held at Dubai, United Arab Emirates in 2023.
● The UNOPS is a UN agency dedicated to implementing infrastructure and procurement projects for the UN system, international financial institutions, governments and other partners around the world. It is headquartered at the UN City campus in Copenhagen, Denmark. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: In India, wolves are listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Statement II: The breeding of wolves with dogs in India is causing genetic erosion among Indian wolves.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation:
Statements I and II are correct. Statement II explains statement I: Wolves in India are classified under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 thus making them as endangered as tigers in the country. The highest concentration of wolves in India is currently in the state of Madhya Pradesh (772) followed by Rajasthan (532), Gujarat (494), Maharashtra (396) and Chattisgarh (320).
The ancient wolf lineage in the country is threatened by:
● Habitat loss (Wolves’ native habitat is barren wastelands that are now actively prioritised for development activities.)
● Hybridisation with dogs (causing genetic erosion among wolves)
● Diseases and road kills
● Depletion of wild prey populations
● Illegal hunting for trade in its fur and body parts including paws, tongues, heads, and other parts.
Additional information about species of wolves found in India
● The Indian grey wolves are one of the oldest wolf lineages in the world. They are smaller and leaner compared to their European and American counterparts. The Indian wolf is highly adapted to the hot, arid plains of the subcontinent. Listed as ‘Least Concern’ by the IUCN in its Red List.
● Peninsular wolf: Commonly sighted in the plains and Deccan plateau; listed as ‘Endangered’ by the IUCN in its Red List.
● Himalayan wolf: Distributed in Ladakh, Spiti Valley of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim states of India; It was assessed for the first time by the IUCN in January 2024 as ‘Vulnerable’.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation:
Statements I and II are correct. Statement II explains statement I: Wolves in India are classified under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 thus making them as endangered as tigers in the country. The highest concentration of wolves in India is currently in the state of Madhya Pradesh (772) followed by Rajasthan (532), Gujarat (494), Maharashtra (396) and Chattisgarh (320).
The ancient wolf lineage in the country is threatened by:
● Habitat loss (Wolves’ native habitat is barren wastelands that are now actively prioritised for development activities.)
● Hybridisation with dogs (causing genetic erosion among wolves)
● Diseases and road kills
● Depletion of wild prey populations
● Illegal hunting for trade in its fur and body parts including paws, tongues, heads, and other parts.
Additional information about species of wolves found in India
● The Indian grey wolves are one of the oldest wolf lineages in the world. They are smaller and leaner compared to their European and American counterparts. The Indian wolf is highly adapted to the hot, arid plains of the subcontinent. Listed as ‘Least Concern’ by the IUCN in its Red List.
● Peninsular wolf: Commonly sighted in the plains and Deccan plateau; listed as ‘Endangered’ by the IUCN in its Red List.
● Himalayan wolf: Distributed in Ladakh, Spiti Valley of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim states of India; It was assessed for the first time by the IUCN in January 2024 as ‘Vulnerable’. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following statements:
1. Livestock sector emits methane and nitrous oxides.
2. Forest fires and volcanoes are sources of Particulate Matter.
3. Refineries and industrial boilers are sources of ozone pollution.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?Correct
Answer. D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: In addition to greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) arising from enteric fermentation and manure storage, feed production together with the related soil carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions is another important hotspot for the livestock sector.
Soil carbon dioxide emissions are due to soil carbon dynamics (e.g., decomposing plant residues, mineralization of soil organic matter, land use change, etc.), the manufacturing of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and from fossil fuel use in on-farm agricultural operations. Nitrous oxide emissions are emitted when organic and inorganic fertilizers are applied to the soil.
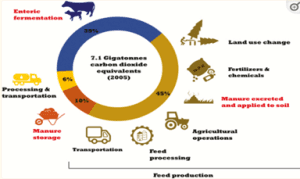
Statement 2 is correct: Sources of Particulate matter pollution include wood stoves, construction sites, forest fires, coal-powered thermal plants, automobiles, sea salt, dust storms, pollen, sulphate aerosols from volcanoes, etc.
Forest fires emit soot/black carbon, a component of particulate air pollution (PM2.5).
Statement 3 is correct: Sources of Ozone pollution include automobiles, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, paints, solvents etc.
Additional information
● Ozone pollution is concerned with unsustainable levels of ground-level ozone in the troposphere which is a secondary air pollutant. Bad ozone as it is popularly known, is formed due to the chemical reactions involving Nitrogen oxides and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in the presence of sunlight.
● Particulate matter refers to the mixture of solid and liquid particles in the air such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke etc. which may or may not be visible to the naked eye. PM10 includes inhalable particles having a diameter of 10 micrometres in general whereas PM2.5 comprises fine inhalable particles which have a diameter of 2.5 mm.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: In addition to greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) arising from enteric fermentation and manure storage, feed production together with the related soil carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions is another important hotspot for the livestock sector.
Soil carbon dioxide emissions are due to soil carbon dynamics (e.g., decomposing plant residues, mineralization of soil organic matter, land use change, etc.), the manufacturing of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and from fossil fuel use in on-farm agricultural operations. Nitrous oxide emissions are emitted when organic and inorganic fertilizers are applied to the soil.

Statement 2 is correct: Sources of Particulate matter pollution include wood stoves, construction sites, forest fires, coal-powered thermal plants, automobiles, sea salt, dust storms, pollen, sulphate aerosols from volcanoes, etc.
Forest fires emit soot/black carbon, a component of particulate air pollution (PM2.5).
Statement 3 is correct: Sources of Ozone pollution include automobiles, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, paints, solvents etc.
Additional information
● Ozone pollution is concerned with unsustainable levels of ground-level ozone in the troposphere which is a secondary air pollutant. Bad ozone as it is popularly known, is formed due to the chemical reactions involving Nitrogen oxides and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in the presence of sunlight.
● Particulate matter refers to the mixture of solid and liquid particles in the air such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke etc. which may or may not be visible to the naked eye. PM10 includes inhalable particles having a diameter of 10 micrometres in general whereas PM2.5 comprises fine inhalable particles which have a diameter of 2.5 mm. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following:
1. Castor seed shells
2. Elephant grass
3. Pine Needle
4. Paddy Straw
How many of the above-mentioned agro products/crops/wastes have been permitted by the Government of India to be used for co-firing in thermal power plants?Correct
Answer. D
Explanation:
Options 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
The Ministry of Power issued modification on 16.06.2023 to revise the biomass policy dated 08.10.2021 and now, it mandates 5% biomass co-firing in Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) from FY 2024-25. This obligation shall increase to 7% from FY 2025-26.
The Ministry of Power through a policy Addendum dated 03-05-2023 has indicated the various type of various agro residues such as stubble/straw/stalk/husk which are surplus and not being used as animal fodder for making the biomass pellets. This includes agro-residue obtained from crops like Paddy, Soya, Arhar, Gwar, Cotton, Gram, Jawar, Bajra, Moong, Mustard, Sesame, Til, Maize, Sunflower, Jute, Coffee, etc. as well as Groundnut Shell, Coconut Shell, Castor Seed Shell etc.
In addition, pellets made from the following agro product/crop/waste can also be used for co-firing in TPPs viz. Bamboo and its by-products, Horticulture waste such as dry leaves and trimmings obtained from maintenance & pruning of trees and plants and other biomass such as Pine Cone/Needle, Elephant Grass, Sarkanda, etc.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation:
Options 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
The Ministry of Power issued modification on 16.06.2023 to revise the biomass policy dated 08.10.2021 and now, it mandates 5% biomass co-firing in Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) from FY 2024-25. This obligation shall increase to 7% from FY 2025-26.
The Ministry of Power through a policy Addendum dated 03-05-2023 has indicated the various type of various agro residues such as stubble/straw/stalk/husk which are surplus and not being used as animal fodder for making the biomass pellets. This includes agro-residue obtained from crops like Paddy, Soya, Arhar, Gwar, Cotton, Gram, Jawar, Bajra, Moong, Mustard, Sesame, Til, Maize, Sunflower, Jute, Coffee, etc. as well as Groundnut Shell, Coconut Shell, Castor Seed Shell etc.
In addition, pellets made from the following agro product/crop/waste can also be used for co-firing in TPPs viz. Bamboo and its by-products, Horticulture waste such as dry leaves and trimmings obtained from maintenance & pruning of trees and plants and other biomass such as Pine Cone/Needle, Elephant Grass, Sarkanda, etc.




