Day-674
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. With reference to the Battery Waste Management Rules 2022, consider the following statements:
1. The Rules cover electric vehicle batteries, portable batteries, automotive batteries and industrial batteries.
2. While incineration may be used for disposal of waste batteries, there is prohibition on their disposal in landfills.
3. The Central Pollution Control Board can cancel the registration or/and impose environmental compensation in case of non-compliance with the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) targets set under the Rules.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation: Battery Waste Management (BWM) Rules, 2022 would replace Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001.
Statement 1 is correct: The 2001 Rules covered only lead-acid batteries whereas the new rules 2022 now cover all types of batteries, viz. electric vehicle batteries, portable batteries, automotive batteries and industrial batteries.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The BWMR, 2022 rules function based on the concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) where the producers (including importers) of batteries are responsible for collection and recycling/refurbishment of waste batteries and use of recovered materials from wastes into new batteries. EPR mandates that all waste batteries be collected and sent for recycling/refurbishment, and it prohibits disposal in landfills and incineration.
● To meet the EPR obligations, producers may engage themselves or authorise any other entity for collection, recycling or refurbishment of waste batteries.
● The rules will enable setting up a mechanism and centralized online portal for exchange of EPR certificates between producers and recyclers/refurbishers to fulfil the obligations of producers.
Statement 3 is correct: In case of non-compliance with the set EPR targets/obligations under the rules, CPCB has been empowered to even suspend/cancel the registration of producers of batteries.
● On the principle of Polluter Pays Principle, environmental compensation will be imposed by CPCB for non-fulfilment of Extended Producer Responsibility targets, responsibilities and obligations set out in the rules. The funds collected under environmental compensation shall be utilised in collection and refurbishing or recycling of uncollected and non-recycled waste batteries.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation: Battery Waste Management (BWM) Rules, 2022 would replace Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001.
Statement 1 is correct: The 2001 Rules covered only lead-acid batteries whereas the new rules 2022 now cover all types of batteries, viz. electric vehicle batteries, portable batteries, automotive batteries and industrial batteries.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The BWMR, 2022 rules function based on the concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) where the producers (including importers) of batteries are responsible for collection and recycling/refurbishment of waste batteries and use of recovered materials from wastes into new batteries. EPR mandates that all waste batteries be collected and sent for recycling/refurbishment, and it prohibits disposal in landfills and incineration.
● To meet the EPR obligations, producers may engage themselves or authorise any other entity for collection, recycling or refurbishment of waste batteries.
● The rules will enable setting up a mechanism and centralized online portal for exchange of EPR certificates between producers and recyclers/refurbishers to fulfil the obligations of producers.
Statement 3 is correct: In case of non-compliance with the set EPR targets/obligations under the rules, CPCB has been empowered to even suspend/cancel the registration of producers of batteries.
● On the principle of Polluter Pays Principle, environmental compensation will be imposed by CPCB for non-fulfilment of Extended Producer Responsibility targets, responsibilities and obligations set out in the rules. The funds collected under environmental compensation shall be utilised in collection and refurbishing or recycling of uncollected and non-recycled waste batteries. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Global Flaring and Methane Reduction Partnership (GFMR) focuses on helping developing countries cut carbon dioxide and methane emissions generated by the oil and gas industry. It is an initiative of:
Correct
Answer. C
Explanation: At COP28 of the UNFCCC, the World Bank launched the Global Flaring and Methane Reduction (GFMR) Partnership, a new multi-donor trust fund focused on helping developing countries cut carbon dioxide and methane emissions generated by the oil and gas industry. GFMR will provide more than $250 million and mobilize billions from the private sector to support those countries with the least capacity and resources to address these emissions. The partnership will focus on providing grant funding, technical assistance, policy and regulatory reform advisory services, institutional strengthening, and mobilizing financing to support action by governments and operators.Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation: At COP28 of the UNFCCC, the World Bank launched the Global Flaring and Methane Reduction (GFMR) Partnership, a new multi-donor trust fund focused on helping developing countries cut carbon dioxide and methane emissions generated by the oil and gas industry. GFMR will provide more than $250 million and mobilize billions from the private sector to support those countries with the least capacity and resources to address these emissions. The partnership will focus on providing grant funding, technical assistance, policy and regulatory reform advisory services, institutional strengthening, and mobilizing financing to support action by governments and operators. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Recently, the production and use of ‘Ketoprofen’ has been banned in the country. It is widely used as:
Correct
Answer. D
Explanation: The Union Health Ministry has banned the veterinary use of painkiller aceclofenac and ketoprofen and its formulations, in August 2023. These are two of three “vulture-toxic” drugs that conservationists have been seeking a ban on. The third drug is nimesulide. Conservationists point to meloxicam and tolfenamic acid as safe alternatives.
About 16 years ago, India had banned the veterinary use of diclofenac, as it was found to be toxic for vultures. It has been established by researchers that aceclofenac metobalises into diclofenac in the body of large animals, and vultures feed on their carcass. The use of aceclofenac and ketoprofen threaten the already critically endangered Gyps vultures in South Asia.
Ketoprofen is ubiquitously used in both human and veterinary medicine for treating pain, inflammation, and fever.
Ketoprofen, a bicyclic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug commonly used in human and veterinary medicine, has recently been cited as an environmental contaminant that raises concerns for ecological well-being. It is bioaccumulated and biomagnified throughout the food chain, threatening the ecosystem function.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation: The Union Health Ministry has banned the veterinary use of painkiller aceclofenac and ketoprofen and its formulations, in August 2023. These are two of three “vulture-toxic” drugs that conservationists have been seeking a ban on. The third drug is nimesulide. Conservationists point to meloxicam and tolfenamic acid as safe alternatives.
About 16 years ago, India had banned the veterinary use of diclofenac, as it was found to be toxic for vultures. It has been established by researchers that aceclofenac metobalises into diclofenac in the body of large animals, and vultures feed on their carcass. The use of aceclofenac and ketoprofen threaten the already critically endangered Gyps vultures in South Asia.
Ketoprofen is ubiquitously used in both human and veterinary medicine for treating pain, inflammation, and fever.
Ketoprofen, a bicyclic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug commonly used in human and veterinary medicine, has recently been cited as an environmental contaminant that raises concerns for ecological well-being. It is bioaccumulated and biomagnified throughout the food chain, threatening the ecosystem function. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. With reference to the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, and its amendments, consider the following statements:
1. The State Biodiversity Boards advise the state governments regarding the selection and management of heritage sites.
2. It is mandatory for the AYUSH practitioners to pay compensation under the Access and Benefit Sharing clause of the Act.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer. D
Explanation: The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 focuses on the conservation of biological resources, managing its sustainable use and enabling fair and equitable sharing benefits arising out of the use and knowledge of biological resources with the local communities. It seeks to check biopiracy, protect biological diversity and local growers through a three-tier structure of central and state boards and local committees. The Act provides for setting up of a National Biodiversity Authority (NBA), State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs) and Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) in local bodies.
Statement 1 is incorrect: The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) is a statutory body established in 2003 and tasked with the role of advising the Central Government on matters relating to biodiversity conservation, sustainable use of its components, and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of biological resources. It advises state governments on the selection of areas of biodiversity importance to be notified as heritage sites under Subsection (1) of Section 37, as well as measures for managing such heritage sites.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Act, 2023, encourages the Indian system of medicine by exempting AYUSH practitioners and people accessing traditional knowledge from giving prior intimation to state biodiversity boards. Thus, they are exempted from paying Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS), a compensatory amount paid to tribal and other communities who traditionally gather, protect, and use herbs and medicinal plants that are also important for the AYUSH industry.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation: The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 focuses on the conservation of biological resources, managing its sustainable use and enabling fair and equitable sharing benefits arising out of the use and knowledge of biological resources with the local communities. It seeks to check biopiracy, protect biological diversity and local growers through a three-tier structure of central and state boards and local committees. The Act provides for setting up of a National Biodiversity Authority (NBA), State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs) and Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) in local bodies.
Statement 1 is incorrect: The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) is a statutory body established in 2003 and tasked with the role of advising the Central Government on matters relating to biodiversity conservation, sustainable use of its components, and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of biological resources. It advises state governments on the selection of areas of biodiversity importance to be notified as heritage sites under Subsection (1) of Section 37, as well as measures for managing such heritage sites.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Act, 2023, encourages the Indian system of medicine by exempting AYUSH practitioners and people accessing traditional knowledge from giving prior intimation to state biodiversity boards. Thus, they are exempted from paying Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS), a compensatory amount paid to tribal and other communities who traditionally gather, protect, and use herbs and medicinal plants that are also important for the AYUSH industry. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. The term ‘carbon insetting’, sometimes mentioned in news, is seen in the context of which one of the following?
Correct
Answer. A
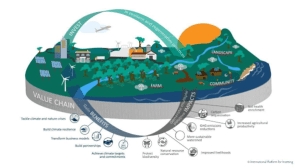
Explanation: Put simply, carbon ‘insetting’ focuses on doing more good rather than doing less bad within a value chain. Carbon insetting is the implementation of nature-based solutions such as reforestation, agroforestry, renewable energy and regenerative agriculture. The battle with soaring temperatures will, however, not be won until organizations start decarbonising their own value chains to include more nature-positive solutions and operations.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation: Put simply, carbon ‘insetting’ focuses on doing more good rather than doing less bad within a value chain. Carbon insetting is the implementation of nature-based solutions such as reforestation, agroforestry, renewable energy and regenerative agriculture. The battle with soaring temperatures will, however, not be won until organizations start decarbonising their own value chains to include more nature-positive solutions and operations.


