Day-658
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Consider the following statements:
Statement – I: Enclosed seas in the low latitudes record relatively higher temperatures than the open seas.
Statement – II: Enclosed seas in the low latitudes experience more evaporation.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
Statement-I is correct:
Factors affecting Temperature Distribution in the oceans-
● The factors which affect the distribution of temperature of ocean water are:
⮚ Latitude
⮚ Prevailing wind
⮚ Ocean currents
⮚ Unequal distribution of land and water
⮚ Continentality
● All these factors influence the temperature of the ocean currents locally.
● The enclosed seas in the low latitudes record relatively higher temperatures than the open seas:
➢ The main reason for this phenomenon is the effect of continentality.
➢ Since the specific heat of continents is lower than that of oceans, the rate of cooling and heating of continents is higher than the water bodies. As the regions of lower latitudes receive a good amount of insolation, the enclosed seas are able to absorb more heat from the surrounding land. This makes the closed seas having higher temperature as compared to the open seas of the same latitudes.
➢ Moreover, enclosed seas are typically surrounded by land masses on most sides, which limits water exchange with the open ocean. This isolation can lead to reduced water movement, making it easier for heat to accumulate in the enclosed sea.
❖ Example – Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea
● whereas the enclosed seas in the high latitudes have lower temperatures than the open seas.
❖ The warming effect of the warm ocean currents seems to be the most pertinent reason for this effect in seas of higher latitudes.
➢ Enclosed seas in high latitudes often have limited exchange with warmer ocean currents. This geographical isolation can lead to slower heat transfer from other parts of the ocean, resulting in cooler temperatures.
➢ Example – Open seas at high latitudes, like the North Atlantic, can be influenced by warm ocean currents (e.g., the Gulf Stream), which carry warmer water from lower latitudes, raising their temperatures. Enclosed seas like the Baltic Sea due to their geographic barriers, don’t benefit from such warm currents.
Statement-II is correct but not an explanation for statement 1:
● Enclosed seas in low latitudes tend to experience more evaporation due to a combination of several factors like high temperatures, longer daylight hours, high humidity, limited freshwater input, and stable atmospheric conditions in low-latitude regions contribute to higher evaporation rates in enclosed seas located in these areas.
● This is the reason that the enclosed seas of low latitudes have more salinity than the open seas in the same latitudes.
● Example – Red Sea, Dead Sea etc.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
Statement-I is correct:
Factors affecting Temperature Distribution in the oceans-
● The factors which affect the distribution of temperature of ocean water are:
⮚ Latitude
⮚ Prevailing wind
⮚ Ocean currents
⮚ Unequal distribution of land and water
⮚ Continentality
● All these factors influence the temperature of the ocean currents locally.
● The enclosed seas in the low latitudes record relatively higher temperatures than the open seas:
➢ The main reason for this phenomenon is the effect of continentality.
➢ Since the specific heat of continents is lower than that of oceans, the rate of cooling and heating of continents is higher than the water bodies. As the regions of lower latitudes receive a good amount of insolation, the enclosed seas are able to absorb more heat from the surrounding land. This makes the closed seas having higher temperature as compared to the open seas of the same latitudes.
➢ Moreover, enclosed seas are typically surrounded by land masses on most sides, which limits water exchange with the open ocean. This isolation can lead to reduced water movement, making it easier for heat to accumulate in the enclosed sea.
❖ Example – Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea
● whereas the enclosed seas in the high latitudes have lower temperatures than the open seas.
❖ The warming effect of the warm ocean currents seems to be the most pertinent reason for this effect in seas of higher latitudes.
➢ Enclosed seas in high latitudes often have limited exchange with warmer ocean currents. This geographical isolation can lead to slower heat transfer from other parts of the ocean, resulting in cooler temperatures.
➢ Example – Open seas at high latitudes, like the North Atlantic, can be influenced by warm ocean currents (e.g., the Gulf Stream), which carry warmer water from lower latitudes, raising their temperatures. Enclosed seas like the Baltic Sea due to their geographic barriers, don’t benefit from such warm currents.
Statement-II is correct but not an explanation for statement 1:
● Enclosed seas in low latitudes tend to experience more evaporation due to a combination of several factors like high temperatures, longer daylight hours, high humidity, limited freshwater input, and stable atmospheric conditions in low-latitude regions contribute to higher evaporation rates in enclosed seas located in these areas.
● This is the reason that the enclosed seas of low latitudes have more salinity than the open seas in the same latitudes.
● Example – Red Sea, Dead Sea etc. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements:
Statement – I: Andesitic lava is light in colour while basaltic lava is dark in colour.
Statement – II: Andesitic lava has more silica content than basaltic lava.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Lava:
● Magma is an extremely hot liquid and semi-liquid rock located under Earth’s surface. When magma flows onto Earth’s surface, it is called lava.
Types of lava:
● There are three basic types of magma: basaltic, andesitic, and rhyolitic, each of which has a different mineral composition.
The colour of lava is closely related to its composition, particularly the presence of silica (SiO2) content. The silica content influences the colour of lava as follows:
Andesitic Lava: There is a higher amount of silica in this type of lava.
● Color: Andesitic lava has a higher amount of silica content; it therefore appears light colored when solidified.
● These lavas are highly viscous with a high melting point.
● Andesitic lava is commonly associated with stratovolcanoes at convergent plate boundaries.
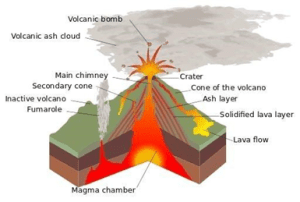
Basaltic Lava:
● Colour: Basaltic lava, which has a low silica content, typically appears dark gray to black when solidified. The dark colour of basaltic lava is primarily due to its high iron and magnesium content.
● Being highly fluid, they flow out of volcanic vents quietly and are not very explosive.
● Due to their high fluidity, they flow readily with a speed of 10 to 30 miles per hour.
● The resultant volcano is gently sloping with a wide diameter and forms a flattened shield or dome.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Lava:
● Magma is an extremely hot liquid and semi-liquid rock located under Earth’s surface. When magma flows onto Earth’s surface, it is called lava.
Types of lava:
● There are three basic types of magma: basaltic, andesitic, and rhyolitic, each of which has a different mineral composition.
The colour of lava is closely related to its composition, particularly the presence of silica (SiO2) content. The silica content influences the colour of lava as follows:
Andesitic Lava: There is a higher amount of silica in this type of lava.
● Color: Andesitic lava has a higher amount of silica content; it therefore appears light colored when solidified.
● These lavas are highly viscous with a high melting point.
● Andesitic lava is commonly associated with stratovolcanoes at convergent plate boundaries.

Basaltic Lava:
● Colour: Basaltic lava, which has a low silica content, typically appears dark gray to black when solidified. The dark colour of basaltic lava is primarily due to its high iron and magnesium content.
● Being highly fluid, they flow out of volcanic vents quietly and are not very explosive.
● Due to their high fluidity, they flow readily with a speed of 10 to 30 miles per hour.
● The resultant volcano is gently sloping with a wide diameter and forms a flattened shield or dome. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements:
1. Magnetic declination is the angle between the geomagnetic north pole and geographic north pole.
2. Ships using compass for navigation need to account for magnetic declination so that they reach their intended destination.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: Only Statement 2 is correct
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Magnetic Declination:
● Magnetic declination, also known as magnetic variation, is the angle between magnetic north (the direction a compass needle points) and true north (the direction towards the geographic North Pole).
⮚ Magnetic Poles: The magnetic poles refer to the points on the Earth’s surface where the magnetic field lines appear to converge and enter or emerge.
⮚ Geographical north: It is also known as true north, refers to the direction towards the geographic North Pole, which is the northernmost point on the Earth’s surface.
o It is aligned with the Earth’s axis of rotation, which extends from the geographic North Pole to the geographic South Pole.
o Unlike magnetic north, which is determined by the Earth’s magnetic field and can vary based on location and time, geographical north remains relatively constant and is the reference point for navigation and mapping purposes.
● In simpler terms, it’s the angular difference between the direction a compass points and the direction of the earth’s axis.
● Declination is positive when this angle is east of true north and negative when it is west.
● Magnetic declination changes over time, and with location.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Declination value is needed to determine true north, because compasses point toward magnetic north.
● By knowing the magnetic declination for their location, sailors can adjust their compass readings to compensate for the difference between magnetic north and true north.
⮚ Example – If the magnetic declination is known to be 10 degrees east, the sailors can correct their compass readings by subtracting 10 degrees from the indicated magnetic direction. With this correction, the ship can maintain a true north heading, aligning with the intended route.

● So, by accounting for magnetic declination, ships can navigate more accurately towards their destinations, reducing the risk of veering off course and ensuring they reach their intended ports or waypoints safely and efficiently.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: Only Statement 2 is correct
Statement 1 is incorrect:
Magnetic Declination:
● Magnetic declination, also known as magnetic variation, is the angle between magnetic north (the direction a compass needle points) and true north (the direction towards the geographic North Pole).
⮚ Magnetic Poles: The magnetic poles refer to the points on the Earth’s surface where the magnetic field lines appear to converge and enter or emerge.
⮚ Geographical north: It is also known as true north, refers to the direction towards the geographic North Pole, which is the northernmost point on the Earth’s surface.
o It is aligned with the Earth’s axis of rotation, which extends from the geographic North Pole to the geographic South Pole.
o Unlike magnetic north, which is determined by the Earth’s magnetic field and can vary based on location and time, geographical north remains relatively constant and is the reference point for navigation and mapping purposes.
● In simpler terms, it’s the angular difference between the direction a compass points and the direction of the earth’s axis.
● Declination is positive when this angle is east of true north and negative when it is west.
● Magnetic declination changes over time, and with location.
Statement 2 is correct:
● Declination value is needed to determine true north, because compasses point toward magnetic north.
● By knowing the magnetic declination for their location, sailors can adjust their compass readings to compensate for the difference between magnetic north and true north.
⮚ Example – If the magnetic declination is known to be 10 degrees east, the sailors can correct their compass readings by subtracting 10 degrees from the indicated magnetic direction. With this correction, the ship can maintain a true north heading, aligning with the intended route.


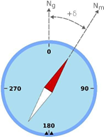
● So, by accounting for magnetic declination, ships can navigate more accurately towards their destinations, reducing the risk of veering off course and ensuring they reach their intended ports or waypoints safely and efficiently. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following rivers:
1. Kuno
2. Chambal
3. Kali Sindh
4. Sindh
5. Betwa
How many of the above are the tributaries of the Yamuna River?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: River Kali Sindh and River Kuno are the tributaries of the Chambal river.
Yamuna River:
The Yamuna is the largest and the most important tributary of the Ganga. It originates from the Yamunotri glacier on the Bandarpunch Peak in Garhwal in Uttarakhand.
The tributaries of the Yamuna:
● The main tributary of Yamuna in its upper reaches is the Tons which also rises from the Bandarpunch glacier and joins Yamuna at Kalsi near Dehradun.
● The Yamuna receives some important tributaries originating from the peninsular plateau which are-
⮚ The Chambal, the Sindh, the Betwa and the Ken.


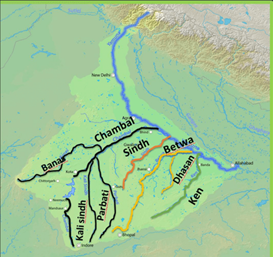
About Chambal River:
● The Chambal River is located in northern India and flows through three Indian states: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
● The Chambal also forms part of the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh boundary.
Tributaries of river Chambal:
● The main tributaries of Chambal include the Banas and Mej rivers on the left and the Parbati, Kali Sindh, Kuno and Shipra rivers on the right.


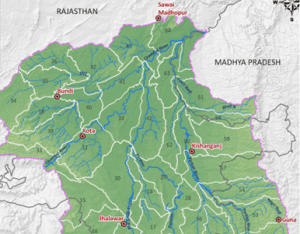
About Kuno river:
● The Kuno River is a prominent river that flows through the heart of the Kuno National Park from South to North in Madhya Pradesh.
● The river, which originates from the Vindhya mountain range, is a lifeline for the sanctuary’s diverse flora and fauna.
● The Kuno River originates In the Vindhya Range Of central India, from the plateau in Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh.
● Passing through districts like Guna, Shivpuri, Baran, Sheopur and Morena, it finally meets in the waters of the river Chambal in Morena (M.P.).Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: River Kali Sindh and River Kuno are the tributaries of the Chambal river.
Yamuna River:
The Yamuna is the largest and the most important tributary of the Ganga. It originates from the Yamunotri glacier on the Bandarpunch Peak in Garhwal in Uttarakhand.
The tributaries of the Yamuna:
● The main tributary of Yamuna in its upper reaches is the Tons which also rises from the Bandarpunch glacier and joins Yamuna at Kalsi near Dehradun.
● The Yamuna receives some important tributaries originating from the peninsular plateau which are-
⮚ The Chambal, the Sindh, the Betwa and the Ken.



About Chambal River:
● The Chambal River is located in northern India and flows through three Indian states: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
● The Chambal also forms part of the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh boundary.
Tributaries of river Chambal:
● The main tributaries of Chambal include the Banas and Mej rivers on the left and the Parbati, Kali Sindh, Kuno and Shipra rivers on the right.



About Kuno river:
● The Kuno River is a prominent river that flows through the heart of the Kuno National Park from South to North in Madhya Pradesh.
● The river, which originates from the Vindhya mountain range, is a lifeline for the sanctuary’s diverse flora and fauna.
● The Kuno River originates In the Vindhya Range Of central India, from the plateau in Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh.
● Passing through districts like Guna, Shivpuri, Baran, Sheopur and Morena, it finally meets in the waters of the river Chambal in Morena (M.P.). -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following:
1. Philippines islands
2. Indonesian islands
3. Hawaiian islands
4. Caribbean islands
How many of the above were formed due to the convergence of tectonic plates?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation: The Hawaiian Islands are more of a type of Volcanic islands.
Convergent Boundaries:
● A convergent boundary is an area on earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide with each other.
● Convergent boundaries are of three types, depending on the type of crust present on either side of the boundary — oceanic or continental.
⮚ The types are ocean-ocean, ocean-continent, and continent-continent.
● At convergent plate boundaries, oceanic crust is often forced down into the mantle where it begins to melt.
● Magma rises into and through the other plate, solidifying into granite, the rock that makes up the continents.
● Thus, at convergent boundaries, continental crust is created and oceanic crust is destroyed.
● This can give rise to large land masses like in the case of the formation of island masses of the Philippines, the Indonesian islands and the Caribbean islands.
The formation of the Philippines Islands:
● The Philippine Island system is formed due to subduction of the Philippine Sea plate under the Sunda Plate.


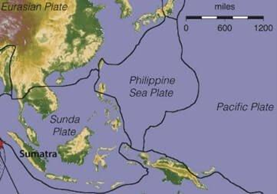
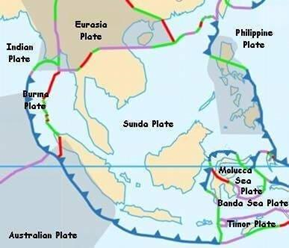
The formation of the Indonesian Island:
● In the case of the Indonesian Archipelago, the Indo-Australian plate is subducting below the Sunda Plate.


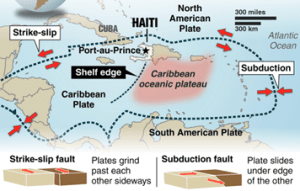
The formation of the Caribbean Islands:
● The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate.
● The northern boundary with the North American plate is a transform or strike-slip boundary.
● The Caribbean Plate is moving to the east while the North American Plate is moving to the west.
● The boundary between the two plates in the past has been convergent, and most of the Greater Antilles group of islands are formed due to the complex interaction between the two plates.


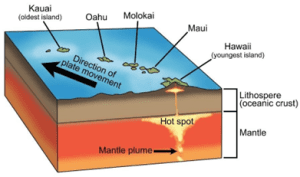
Hawaiian Islands: The formation of the Hawaiian Islands is primarily attributed to volcanic activity associated with a hotspot in the earth’s mantle beneath the Pacific plate. This hotspot, known as the Hawaiian hotspot, has remained relatively stationary over millions of years while the Pacific Plate has moved northwestward over it.


central deputations are concerned. There is consultation process between DOPT and state governments and union generally gives consent to the choice of the state government.
The State High Court does not have any role in the administrative appointment of the Chief Secretary. Its functions are judicial, not administrative or executive. The High Court does not involve itself in the administrative decisions of the state unless there is a legal challenge or a judicial review prompted by issues of legality or constitutional violation.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation: The Hawaiian Islands are more of a type of Volcanic islands.
Convergent Boundaries:
● A convergent boundary is an area on earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide with each other.
● Convergent boundaries are of three types, depending on the type of crust present on either side of the boundary — oceanic or continental.
⮚ The types are ocean-ocean, ocean-continent, and continent-continent.
● At convergent plate boundaries, oceanic crust is often forced down into the mantle where it begins to melt.
● Magma rises into and through the other plate, solidifying into granite, the rock that makes up the continents.
● Thus, at convergent boundaries, continental crust is created and oceanic crust is destroyed.
● This can give rise to large land masses like in the case of the formation of island masses of the Philippines, the Indonesian islands and the Caribbean islands.
The formation of the Philippines Islands:
● The Philippine Island system is formed due to subduction of the Philippine Sea plate under the Sunda Plate.



The formation of the Indonesian Island:
● In the case of the Indonesian Archipelago, the Indo-Australian plate is subducting below the Sunda Plate.



The formation of the Caribbean Islands:
● The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate.
● The northern boundary with the North American plate is a transform or strike-slip boundary.
● The Caribbean Plate is moving to the east while the North American Plate is moving to the west.
● The boundary between the two plates in the past has been convergent, and most of the Greater Antilles group of islands are formed due to the complex interaction between the two plates.



Hawaiian Islands: The formation of the Hawaiian Islands is primarily attributed to volcanic activity associated with a hotspot in the earth’s mantle beneath the Pacific plate. This hotspot, known as the Hawaiian hotspot, has remained relatively stationary over millions of years while the Pacific Plate has moved northwestward over it.



central deputations are concerned. There is consultation process between DOPT and state governments and union generally gives consent to the choice of the state government.
The State High Court does not have any role in the administrative appointment of the Chief Secretary. Its functions are judicial, not administrative or executive. The High Court does not involve itself in the administrative decisions of the state unless there is a legal challenge or a judicial review prompted by issues of legality or constitutional violation.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.




