Day-650
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. “The wetland supports traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production. Farmers grow a salt-tolerant rice called “kagga”, which is one of the specialities of the region. The mangroves found here provide it the much-needed protection from cyclones.” The Ramsar site being described here is:
Correct
Answer. B
Explanation: Aghanashini Estuary, spread over an area of 4801 ha, is formed at the confluence of Aghanashini River with the Arabian sea. The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
● The wetland also provides livelihoods to 6000-7500 families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
● Additionally, the mangroves bordering the estuary help to protect the shores against storms and cyclones.
● The estuary regularly supports over 43,000 counts of over 66 waterbird species and over 1% of the biogeographic population of 15 waterbird species (which includes river tern, oriental darter, lesser black-backed gull, woolly- necked stork, Eurasian oystercatcher and others).Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation: Aghanashini Estuary, spread over an area of 4801 ha, is formed at the confluence of Aghanashini River with the Arabian sea. The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
● The wetland also provides livelihoods to 6000-7500 families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
● Additionally, the mangroves bordering the estuary help to protect the shores against storms and cyclones.
● The estuary regularly supports over 43,000 counts of over 66 waterbird species and over 1% of the biogeographic population of 15 waterbird species (which includes river tern, oriental darter, lesser black-backed gull, woolly- necked stork, Eurasian oystercatcher and others). -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Aardvarks (Orycteropus afer) are endemic to Africa only.
Statement II: Aardvarks are naturally found only in the arid and semi-arid regions.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. C
Explanation:
Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect: Aardvarks (Orycteropus afer) are a unique mammal species that are found exclusively in Africa, and their home range extends from the southern tip of the continent to as far north as Sudan. They are found in most of sub-Saharan Africa (the part of the continent south of the Sahara Desert).

● Aardvarks are found in a variety of different habitats throughout sub-Saharan Africa, including grasslands, savannas, and forests.
● They are most commonly found in regions with sandy or loamy soils, which they use to create their burrows.
● Aardvarks are well adapted to life in arid environments, where water is scarce and temperatures can be extreme.
● The nocturnal animals use their long noses and keen sense of smell to sniff out ants and termites, which they lap up with an anteater-like tongue covered in sticky saliva. These insects make up most of the aardvark’s diet, although they’ll occasionally eat beetle larvae.
● Aardvarks use their long, powerful claws to tear open termite mounds, as well as dig underground burrows in which they sleep and care for their young.
● The International Union for the Conservation of Species considers the aardvark a species of “least concern”.Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation:
Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect: Aardvarks (Orycteropus afer) are a unique mammal species that are found exclusively in Africa, and their home range extends from the southern tip of the continent to as far north as Sudan. They are found in most of sub-Saharan Africa (the part of the continent south of the Sahara Desert).

● Aardvarks are found in a variety of different habitats throughout sub-Saharan Africa, including grasslands, savannas, and forests.
● They are most commonly found in regions with sandy or loamy soils, which they use to create their burrows.
● Aardvarks are well adapted to life in arid environments, where water is scarce and temperatures can be extreme.
● The nocturnal animals use their long noses and keen sense of smell to sniff out ants and termites, which they lap up with an anteater-like tongue covered in sticky saliva. These insects make up most of the aardvark’s diet, although they’ll occasionally eat beetle larvae.
● Aardvarks use their long, powerful claws to tear open termite mounds, as well as dig underground burrows in which they sleep and care for their young.
● The International Union for the Conservation of Species considers the aardvark a species of “least concern”. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the nitrate limit in potable water should be 50 mg/l or less.
Statement II: The excessive nitrate content in drinking water causes blue-baby syndrome.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation:
Statements I and II are correct and statement II explains statement I: As per the Drinking Water Standards prescribed by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the nitrate limit in potable water should be 50 mg/l or less.
This is to prevent the adverse effects on the health of people exposed to excessive nitrate concentration in drinking water/groundwater. It has been established that increased nitrate in drinking water may be associated with an increased risk of preterm birth and some specific congenital anomalies. It also causes blue baby syndrome as a result of low oxygen levels in the blood.
Reverse osmosis is considered as one of the most effective methods that can remove about 80% of nitrate from water.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation:
Statements I and II are correct and statement II explains statement I: As per the Drinking Water Standards prescribed by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the nitrate limit in potable water should be 50 mg/l or less.
This is to prevent the adverse effects on the health of people exposed to excessive nitrate concentration in drinking water/groundwater. It has been established that increased nitrate in drinking water may be associated with an increased risk of preterm birth and some specific congenital anomalies. It also causes blue baby syndrome as a result of low oxygen levels in the blood.
Reverse osmosis is considered as one of the most effective methods that can remove about 80% of nitrate from water. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following kinds of organisms:
1. Foraminifera
2. Copepods
3. Cephalopods
4. Diatoms
5. Rotifers
How many of the above are examples of zooplanktons in the aquatic food chain?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation: Options 1, 2 and 5 are correct.
There are two main types of plankton: phytoplankton and zooplankton. Phytoplankton make their energy through photosynthesis, the process of using chlorophyll and sunlight to create energy. Zooplankton and other small marine creatures eat phytoplankton and then become food for fish, crustaceans, and other larger species.
Examples of Zooplankton include:
● Copepods
● Rotifers
● Foraminifera
Diatom is an example of phytoplankton. (Hence, option 4 is incorrect).
Cephalopods are invertebrate marine organisms. A highly intelligent group of ocean dwelling creatures, the living cephalopods include the eight-armed octopuses, the ten-armed squids and cuttlefishes, and the shelled chambered nautiluses.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation: Options 1, 2 and 5 are correct.
There are two main types of plankton: phytoplankton and zooplankton. Phytoplankton make their energy through photosynthesis, the process of using chlorophyll and sunlight to create energy. Zooplankton and other small marine creatures eat phytoplankton and then become food for fish, crustaceans, and other larger species.
Examples of Zooplankton include:
● Copepods
● Rotifers
● Foraminifera
Diatom is an example of phytoplankton. (Hence, option 4 is incorrect).
Cephalopods are invertebrate marine organisms. A highly intelligent group of ocean dwelling creatures, the living cephalopods include the eight-armed octopuses, the ten-armed squids and cuttlefishes, and the shelled chambered nautiluses. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following statements:
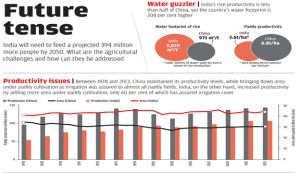
Statement I: The water footprint of China exceeds that of India.
Statement II: The rice productivity of China is almost double as compared to India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. D
Explanation:
Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct: Although the rice productivity of India is less than half of that of China, India’s water footprint is about 208 % higher than that of China.
● The water footprint of a country is the sum of water footprints of all members (people, industry, agriculture).
● India has the largest population in the world, putting excessive strain on the limited water resources of the country.
● Groundwater is the main source of domestic water supply for rural and urban India as more than 80% of the supply is sourced through it, making the country the largest user of groundwater in the world. The agriculture sector uses 89% of the groundwater for irrigation while 11% is used in the domestic and industrial sectors.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation:
Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct: Although the rice productivity of India is less than half of that of China, India’s water footprint is about 208 % higher than that of China.
● The water footprint of a country is the sum of water footprints of all members (people, industry, agriculture).
● India has the largest population in the world, putting excessive strain on the limited water resources of the country.
● Groundwater is the main source of domestic water supply for rural and urban India as more than 80% of the supply is sourced through it, making the country the largest user of groundwater in the world. The agriculture sector uses 89% of the groundwater for irrigation while 11% is used in the domestic and industrial sectors.