TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: Kodagu, a district in Southern Karnataka known for its lush landscapes and coffee estates, is grappling with an unprecedented drought crisis.
EXPLANATION:
- The iconic Cauvery River, originating from Talakaveri has dwindled to a trickle, posing threats to wildlife, livelihoods, and the environment.
- Groundwater levels have witnessed a notable decrease over the past decade. Data spanning from 2014 to 2023 indicates a consistent decline in the static water levels of both dug wells and borewells.
- According to records from the district groundwater office, borewell groundwater levels plummeted to 15.7 metres (m) in 2023, from 13.4 m in 2014. A minor improvement was noted at 12.9 m in 2018.
- Similarly, the groundwater level in dug wells exhibited a downward trajectory, decreasing to 6.7 m from 6 m during the same period, with a temporary upturn observed at 5.8 m in 2021.
Causes of the Drought Crisis:
- Altered Rainfall Patterns: Kodagu, once characterized by abundant rainfall, is now experiencing erratic precipitation patterns attributed to climate change.
- Water Extraction: Increased extraction of water during drought exacerbates the decline in groundwater levels, worsening the crisis.
- Rapid Urbanization: Uncontrolled urban expansion and land conversion for commercial purposes contribute to environmental degradation and water scarcity.
- Land Conversion: Conversion of coffee estates into housing layouts for tourism development further diminishes green cover and exacerbates ecological challenges.
Impacts on Environment and Economy:
- Wildlife Deprivation: Diminished water sources adversely affect wildlife, particularly elephants reliant on the Cauvery for sustenance, leading to conflicts and endangerment of species.
- Loss of Livelihoods: The drought disrupts livelihoods dependent on the river’s vitality, including tourism, agriculture, and related industries, leading to economic losses and social upheaval.
- Coffee Crop Failure: The backbone of Kodagu’s economy, coffee farming, faces a dual threat of accelerated blossoms due to the sun and crop failure due to rain scarcity, causing distress among growers and impacting India’s coffee production.
Community Concerns and Activism:
- Local Activism: Concerned locals and environmental activists advocate for stringent measures to mitigate the crisis, including catchment area conservation policies and regulations on land use and tourism activities.
- Political Advocacy: Organizations like the Kodava National Council (CNC) highlight the ecological and cultural significance of Kodagu, urging authorities to halt large-scale land conversions and hold accountable those responsible for environmental degradation.
Proposed Solutions and Mitigation Strategies:
- Catchment Area Conservation: Implementation of policies to protect essential river catchments, including limitations on land conversion and controls on urban expansion, to safeguard Kodagu’s delicate ecology.
- Regulation of Tourism: Stringent regulations on tourism activities to prevent further degradation of natural habitats and mitigate human-wildlife conflicts.
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Promotion of sustainable farming practices to conserve water resources and mitigate the impact of climate change on agriculture.
- Community Engagement: Involvement of local communities in conservation efforts and sustainable resource management to ensure long-term resilience against drought and environmental degradation.
| Drought
|
|
| Definition
|
A period of drier-than-normal conditions that can last for days, months, or years, affecting ecosystems, agriculture, and local economies.
|
| Causes
|
Droughts are caused by reduced precipitation and can be exacerbated by periods of heat that increase evaporation, making conditions drier.
|
| Consequences
|
Environmental (loss of biodiversity, more wildfires), economic (disruption of water supplies, higher food-production costs), and social impacts (health issues, mass migrations).
|
| Climate Change Link
|
Droughts are becoming more extreme and less predictable due to climate change, with impacts worsening over time.
|
| Adaptations
|
Some plant species have adaptations like reduced leaf area and waxy cuticles to enhance drought tolerance.
|
| Historical Impact
|
The most prolonged drought recorded is in the Atacama Desert, Chile, lasting 400 years. |
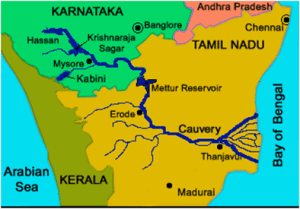
Cauvery River:
- The Kaveri is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- The Kaveri River rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu district of the state of Karnataka, at an elevation of 1,341 m above mean sea level and flows for about 800 km before its outfall into the Bay of Bengal.
- It reaches the sea in Poompuhar, in Mayiladuthurai district.
- It is the third largest river – after Godavari and Krishna – in southern India, and the largest in the state of Tamil Nadu, which, on its course, bisects the state into north and south.
- In ancient Tamil literature, the river was also called Ponni (the golden mother, in reference to the fine silt it deposits).
- The Kaveri is a sacred river to the people of southern India and is worshipped as the Goddess Kaveramme (Mother Cauvery).
- It is considered to be among the seven holy rivers of India. It is extensively used for agriculture in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.