Day-595
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Which of the following statements describes the term ‘de minimis’, which is often heard in the news in context to economy?
Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
The World Trade Organisation (WTO) defines de minimis as the “minimal amounts of domestic support that are allowed even though they distort trade — up to 5% of the value of production for developed countries, 10% for developing”.
The present rules and commitments on agriculture are often called the “Uruguay Round reform programme” — they were negotiated in the Uruguay Round and they include reductions in subsidies and protection as well as other disciplines on the trade.
The main conceptual consideration is that there are basically two categories of domestic support —
● Green Box: Support with no, or minimal, distortive effect on trade.
● Amber Box: Trade-distorting support
Other than that, there is:
Blue Box: Direct payments under production limiting programmes (often referred to as “Blue Box” measures) are exempt from commitments if such payments are made on fixed areas and yield or a fixed number of livestock.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
The World Trade Organisation (WTO) defines de minimis as the “minimal amounts of domestic support that are allowed even though they distort trade — up to 5% of the value of production for developed countries, 10% for developing”.
The present rules and commitments on agriculture are often called the “Uruguay Round reform programme” — they were negotiated in the Uruguay Round and they include reductions in subsidies and protection as well as other disciplines on the trade.
The main conceptual consideration is that there are basically two categories of domestic support —
● Green Box: Support with no, or minimal, distortive effect on trade.
● Amber Box: Trade-distorting support
Other than that, there is:
Blue Box: Direct payments under production limiting programmes (often referred to as “Blue Box” measures) are exempt from commitments if such payments are made on fixed areas and yield or a fixed number of livestock. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following conditions:
1. Increase in expenditure by the government.
2. Reduction in the interest rates on loans.
3. Increase in crude oil prices.
4. Increase in income tax.
How many of the above-mentioned conditions may result in demand-pull inflation?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Demand-pull inflation’ is caused by developments on the demand side of the economy, while ‘cost-push inflation’ is caused by the effect of higher input costs on the supply side of the economy.
As demand for a particular good or service increases, the available supply decreases. When fewer items are available, consumers are willing to pay more to obtain the item—as outlined in the economic principle of supply and demand. The result is higher prices due to demand-pull inflation.
On the other hand, the cost-push inflation occurs when prices increase due to increases in production costs, such as raw materials and wages. The demand for goods is unchanged while the supply of goods declines due to the higher costs of production. As a result, the added costs of production are passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices for the finished goods.
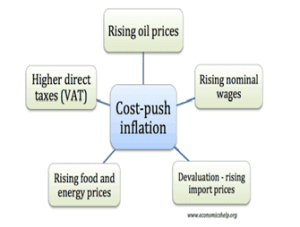
● Increase in government expenditure may result in stimulating the aggregate demand in the economy and that can drive up the prices of the goods.
● Reduction in the interest rate on loan, a form of expansionary monetary policy, would also create demand-pull inflation in the economy due to increased demand for goods and services.
● Increase in crude oil price would increase the raw material cost. Thus, it is a form of cost-push inflation that indicates supply-side bottlenecks.
● An increase in income tax is likely to result in decrease in the aggregate demand as it would reduce the disposable income available with an individual. Thus, it would not lead to demand-pull inflation.
Factors leading to cost-push inflation:
Thus, while demand-pull inflation influences the demand-side dynamics, resulting in price increase, cost-push inflation influences the supply-side dynamics.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Demand-pull inflation’ is caused by developments on the demand side of the economy, while ‘cost-push inflation’ is caused by the effect of higher input costs on the supply side of the economy.
As demand for a particular good or service increases, the available supply decreases. When fewer items are available, consumers are willing to pay more to obtain the item—as outlined in the economic principle of supply and demand. The result is higher prices due to demand-pull inflation.
On the other hand, the cost-push inflation occurs when prices increase due to increases in production costs, such as raw materials and wages. The demand for goods is unchanged while the supply of goods declines due to the higher costs of production. As a result, the added costs of production are passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices for the finished goods.

● Increase in government expenditure may result in stimulating the aggregate demand in the economy and that can drive up the prices of the goods.
● Reduction in the interest rate on loan, a form of expansionary monetary policy, would also create demand-pull inflation in the economy due to increased demand for goods and services.
● Increase in crude oil price would increase the raw material cost. Thus, it is a form of cost-push inflation that indicates supply-side bottlenecks.
● An increase in income tax is likely to result in decrease in the aggregate demand as it would reduce the disposable income available with an individual. Thus, it would not lead to demand-pull inflation.
Factors leading to cost-push inflation:
Thus, while demand-pull inflation influences the demand-side dynamics, resulting in price increase, cost-push inflation influences the supply-side dynamics. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements about the types of unemployment:
1. In Structural unemployment, the marginal productivity of labour becomes zero.
2. Disguised unemployment is majorly found in the agricultural sector.
3. Frictional unemployment is a temporary period of joblessness resulting from voluntary employment transitions.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Structural unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the jobs that are available and the people looking for work. This mismatch could be because jobseekers don’t have the skills required to do the available jobs, or because the available jobs are a long way from the jobseekers.
Disguised unemployment” or “hidden unemployment” describes a section of the labour force engaged in duplicate activity with little to no production. In disguised unemployment, people appear to be employed but are actually not making a meaningful contribution to the economy. Thus, the marginal productivity of labour is zero. Disguised unemployment does not affect an economy’s aggregate economic output.
Statement 2 is correct: In developing economies, the disguised unemployment is majorly found in the agricultural sector, where a greater number of workers are employed than required.
Statement 3 is correct: Frictional unemployment occurs when people move between jobs in the labour market, as well as when people transition into and out of the labour force.
Movement of workers is necessary for a flexible labour market and helps achieve an efficient allocation of labour across the economy. However, people may not find jobs immediately and need to invest time and effort in searching for the right job. Businesses also spend time searching for suitable candidates to fill job vacancies. As a result, people looking for jobs are not matched immediately with vacancies and may experience a period of temporary unemployment.
This type of unemployment is generally for a shorter term (less than one month). Frictional unemployment is likely to occur at all points of the business cycle and, like structural unemployment, may not influence wages or inflation.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Structural unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the jobs that are available and the people looking for work. This mismatch could be because jobseekers don’t have the skills required to do the available jobs, or because the available jobs are a long way from the jobseekers.
Disguised unemployment” or “hidden unemployment” describes a section of the labour force engaged in duplicate activity with little to no production. In disguised unemployment, people appear to be employed but are actually not making a meaningful contribution to the economy. Thus, the marginal productivity of labour is zero. Disguised unemployment does not affect an economy’s aggregate economic output.
Statement 2 is correct: In developing economies, the disguised unemployment is majorly found in the agricultural sector, where a greater number of workers are employed than required.
Statement 3 is correct: Frictional unemployment occurs when people move between jobs in the labour market, as well as when people transition into and out of the labour force.
Movement of workers is necessary for a flexible labour market and helps achieve an efficient allocation of labour across the economy. However, people may not find jobs immediately and need to invest time and effort in searching for the right job. Businesses also spend time searching for suitable candidates to fill job vacancies. As a result, people looking for jobs are not matched immediately with vacancies and may experience a period of temporary unemployment.
This type of unemployment is generally for a shorter term (less than one month). Frictional unemployment is likely to occur at all points of the business cycle and, like structural unemployment, may not influence wages or inflation. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. With reference to the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), consider the following statements:
1. The IBC architecture is built on the principle of “debtors in possession”, as opposed to the previous position of “creditors in control’.
2. The loan recovery rate of large corporates has substantially increased under this system.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC) is the umbrella legislation for insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms and individuals.
The IBC architecture is built on the principle of “creditors in control” as opposed to the previous position of “debtors in possession,”, and as a result, management control is transferred from the hands of the current owners to a new management headed by interim resolution professional (IRP) who practically acts under the supervision and control of Committee of Creditors (CoC) for all purposes.
The CoC is formed by the Interim Resolution Professional once the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) is initiated against a Corporate Debtor. The CoC is a committee consisting of financial creditors of the corporate debtor.
A time-bound resolution of insolvency was the main objective. It aimed to resolve insolvency proceedings within 180 days (extendable by 90 days).
Statement 2 is incorrect: Contrary to the objective of the resolution, the recovery rate of loans has been quite low.
● The Financial Stability Report (FSR) released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on December 28, 2023 summarises the Corporate Insolvency Process (CIRP): “Since the inception of the IBC, a total of 2,808 corporate debtors (CDs) have been rescued and 2,249 CDs have been referred for liquidation till September 2023. The total admitted claims till September 23 are 7,058. As many as 2,001 are pending, of which 36 (out of 37) for seven years, 502 for six years. During the resolution plan approval, only about 15% is paid by the purchaser and the repayment takes years without any further interest collected by the banks.”
● The FSR report mentions that realizable value to the creditors is only 16.9% in 2020-21, 22.4% in 2021-22 and 37.1% in 2022-23.
● Banks or financial creditors are recovering an average of just 10-15% in NCLT-settled cases of large corporates.
● As of September 2023, 67% of ongoing CIRP cases have crossed the timeline of 270 days. The average time taken for admission during FY21 and FY22 was 468 days and 650 days, respectively.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC) is the umbrella legislation for insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms and individuals.
The IBC architecture is built on the principle of “creditors in control” as opposed to the previous position of “debtors in possession,”, and as a result, management control is transferred from the hands of the current owners to a new management headed by interim resolution professional (IRP) who practically acts under the supervision and control of Committee of Creditors (CoC) for all purposes.
The CoC is formed by the Interim Resolution Professional once the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) is initiated against a Corporate Debtor. The CoC is a committee consisting of financial creditors of the corporate debtor.
A time-bound resolution of insolvency was the main objective. It aimed to resolve insolvency proceedings within 180 days (extendable by 90 days).
Statement 2 is incorrect: Contrary to the objective of the resolution, the recovery rate of loans has been quite low.
● The Financial Stability Report (FSR) released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on December 28, 2023 summarises the Corporate Insolvency Process (CIRP): “Since the inception of the IBC, a total of 2,808 corporate debtors (CDs) have been rescued and 2,249 CDs have been referred for liquidation till September 2023. The total admitted claims till September 23 are 7,058. As many as 2,001 are pending, of which 36 (out of 37) for seven years, 502 for six years. During the resolution plan approval, only about 15% is paid by the purchaser and the repayment takes years without any further interest collected by the banks.”
● The FSR report mentions that realizable value to the creditors is only 16.9% in 2020-21, 22.4% in 2021-22 and 37.1% in 2022-23.
● Banks or financial creditors are recovering an average of just 10-15% in NCLT-settled cases of large corporates.
● As of September 2023, 67% of ongoing CIRP cases have crossed the timeline of 270 days. The average time taken for admission during FY21 and FY22 was 468 days and 650 days, respectively. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Under the ‘fiscal drag’, government revenue increases without an explicit increase in tax rates.
Statement-II: Inflation and earnings growth may push more taxpayers into higher tax brackets, thus undermining spending.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Fiscal Drag occurs when earnings growth and inflation push more earners into higher tax brackets. Consequently, the government’s tax revenue rises without any increases in tax rates. If earners pay a higher percentage of income in tax, their spending declines.
This fiscal drag has the effect of reducing (or limiting increase) the aggregate demand. The greater tax burden on incomes dampens spending, i.e., it undermines demand. This is a drag on the economy caused by taxation, i.e., it is a fiscal drag.
It works as automatic brakes that a progressive tax system applies to aggregate demand. Fiscal drag slows down or tames a rapidly expanding economy.
Progressive tax is a system that taxes higher earners more than lower earners. In other words, higher earners pay a greater percentage of their income in tax than lower earners.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Fiscal Drag occurs when earnings growth and inflation push more earners into higher tax brackets. Consequently, the government’s tax revenue rises without any increases in tax rates. If earners pay a higher percentage of income in tax, their spending declines.
This fiscal drag has the effect of reducing (or limiting increase) the aggregate demand. The greater tax burden on incomes dampens spending, i.e., it undermines demand. This is a drag on the economy caused by taxation, i.e., it is a fiscal drag.
It works as automatic brakes that a progressive tax system applies to aggregate demand. Fiscal drag slows down or tames a rapidly expanding economy.
Progressive tax is a system that taxes higher earners more than lower earners. In other words, higher earners pay a greater percentage of their income in tax than lower earners.




