Day-594
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. In the context of cloud seeding, consider the following statements:
1. Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that guarantees a cloud’s ability to produce rain or snow by introducing tiny ice nuclei into certain types of subfreezing clouds.
2. Table salt, silver iodide, calcium chloride and potassium nitrate are the chemicals commonly used for seeding the clouds.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?Correct
Answer. C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that improves (not guarantees) a cloud’s ability to produce rain or snow by introducing tiny ice nuclei into certain types of subfreezing clouds. The effectiveness and success of cloud seeding is often a topic of hot debate. There is no evidence so far that cloud seeding will be successful in non-monsoon months; also, ‘not all clouds are seedable, not all clouds will make rain’.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The chemicals commonly used in seeding the clouds include table salt, silver iodide, calcium chloride, propane and potassium iodide (not potassium nitrate).Incorrect
Answer. C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that improves (not guarantees) a cloud’s ability to produce rain or snow by introducing tiny ice nuclei into certain types of subfreezing clouds. The effectiveness and success of cloud seeding is often a topic of hot debate. There is no evidence so far that cloud seeding will be successful in non-monsoon months; also, ‘not all clouds are seedable, not all clouds will make rain’.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The chemicals commonly used in seeding the clouds include table salt, silver iodide, calcium chloride, propane and potassium iodide (not potassium nitrate). -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Global Warming Potential* (GWP*) is a better means of determining if the world is on track to temperature targets, compared to GWP100.
Statement II: Global Warming Potential * (GWP*) takes into account the removal of short-lived gases from the atmosphere.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. A
Explanation: Both statements are correct and statement 2 explains statement 1.
Essentially, Global Warming Potential (GWP) measures how potent a gas is as a contributor to climate change. The most commonly used metric to quantify greenhouse gas emissions is known as GWP100. This metric looks at the GWP of the greenhouse gases over 100 years. For example, methane has a GWP of 34. This means 1 ton of methane is equal to 34 tons of CO2 and therefore captures more heat per molecule compared to CO2.
However, a flaw in GWP100 measurements was assessed a few years ago by researchers based at the University of Oxford. GWP100 assumed that all greenhouse gases were stagnant in the atmosphere, meaning they remained there for centuries. What GWP100 did not account for was that methane, as a short-lived gas, was actively removed from the atmosphere relatively soon after being emitted.
While GWP100 does consider short-lived gases like methane, it does not account for removal from the atmosphere. Since methane is removed in about 12 years through a natural process, stable emissions do not increase warming after those 12 years.
Today, GWP* represents a new means of measuring carbon in the atmosphere, taking short-lived gas removal from the atmosphere into consideration. GWP* is a better means of determining if the world is on track to temperature targets, compared to GWP100. Methane should be treated a temporary pulse, rather than a constant agent of warming.
Additional information
The established metric under the 2015 Paris Agreement for measuring the global warming potential of a gas over a 100-year period is GWP100, which is the global warming potential evaluated over a 100-year timeline. It focuses on the absolute level of emissions.
GWP* was developed in 2016 by a team of researchers from Oxford University, led by two academics who argued it was more accurate than the current systems used to report national methane emissions at the international level. It was then introduced in 2018 at 24th Conference of Parties (COP24) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (held at Katowice, Poland).
GWP100 measures the warming effect of a quantity of a non-carbon dioxide (CO2) GHG, emitted at a given point in time, relative to an equal amount of CO2. On the other hand, GWP* focuses on changes in emissions over decadal timescales rather than absolute levels.Incorrect
Answer. A
Explanation: Both statements are correct and statement 2 explains statement 1.
Essentially, Global Warming Potential (GWP) measures how potent a gas is as a contributor to climate change. The most commonly used metric to quantify greenhouse gas emissions is known as GWP100. This metric looks at the GWP of the greenhouse gases over 100 years. For example, methane has a GWP of 34. This means 1 ton of methane is equal to 34 tons of CO2 and therefore captures more heat per molecule compared to CO2.
However, a flaw in GWP100 measurements was assessed a few years ago by researchers based at the University of Oxford. GWP100 assumed that all greenhouse gases were stagnant in the atmosphere, meaning they remained there for centuries. What GWP100 did not account for was that methane, as a short-lived gas, was actively removed from the atmosphere relatively soon after being emitted.
While GWP100 does consider short-lived gases like methane, it does not account for removal from the atmosphere. Since methane is removed in about 12 years through a natural process, stable emissions do not increase warming after those 12 years.
Today, GWP* represents a new means of measuring carbon in the atmosphere, taking short-lived gas removal from the atmosphere into consideration. GWP* is a better means of determining if the world is on track to temperature targets, compared to GWP100. Methane should be treated a temporary pulse, rather than a constant agent of warming.
Additional information
The established metric under the 2015 Paris Agreement for measuring the global warming potential of a gas over a 100-year period is GWP100, which is the global warming potential evaluated over a 100-year timeline. It focuses on the absolute level of emissions.
GWP* was developed in 2016 by a team of researchers from Oxford University, led by two academics who argued it was more accurate than the current systems used to report national methane emissions at the international level. It was then introduced in 2018 at 24th Conference of Parties (COP24) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (held at Katowice, Poland).
GWP100 measures the warming effect of a quantity of a non-carbon dioxide (CO2) GHG, emitted at a given point in time, relative to an equal amount of CO2. On the other hand, GWP* focuses on changes in emissions over decadal timescales rather than absolute levels. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Recently, there was a growing concern in our country about the use of Monocroptophos, Dicofol, and Dinocap. These are widely used as:
Correct
Answer. D
Explanation: The Central government has prohibited the use of four insecticides from the initial list of 27. This list includes the controversial monocrotophos (MCP). It is a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide with applications in agricultural crops like rice, maize, sugarcane, cotton, soybeans, groundnut and vegetables. MCP solubilizes in water readily and thus reduced sorption occurs in soil. This leads to MCP leaching into the groundwater and poses a significant threat of contamination.
Due to its toxicology and ill-effects on the health of humans, it has been banned by the European Union as well as India.
Along with monocrotophos, three other insecticides—Dicofol, Dinocap, and Methomyl—have also been banned in India recently.
Monocrotophos causes abnormality, ranging from mild to severe confusion, agitation, hypersalivation, convulsion, pulmonary failure, senescence in mammals and insects. MCP affects humans by inhibiting the activity of the acetylcholine esterase enzyme. MCP is accountable for the catalytic degradation of acetylcholine and affects the neurotransmission between neurons. In India, monocrotophos continues to be produced, used and exported. The perception that monocrotophos is cheap and necessary, have prevented the product from being taken off the market. Another cause of concern is the use of MCP for suicide attempts in the country.
Additional information:
The government of India regulates the manufacture, registration, sale, transport, distribution, use, import and export of pesticides through the Insecticides Act 1968 and the Insecticides Rules 1971.Incorrect
Answer. D
Explanation: The Central government has prohibited the use of four insecticides from the initial list of 27. This list includes the controversial monocrotophos (MCP). It is a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide with applications in agricultural crops like rice, maize, sugarcane, cotton, soybeans, groundnut and vegetables. MCP solubilizes in water readily and thus reduced sorption occurs in soil. This leads to MCP leaching into the groundwater and poses a significant threat of contamination.
Due to its toxicology and ill-effects on the health of humans, it has been banned by the European Union as well as India.
Along with monocrotophos, three other insecticides—Dicofol, Dinocap, and Methomyl—have also been banned in India recently.
Monocrotophos causes abnormality, ranging from mild to severe confusion, agitation, hypersalivation, convulsion, pulmonary failure, senescence in mammals and insects. MCP affects humans by inhibiting the activity of the acetylcholine esterase enzyme. MCP is accountable for the catalytic degradation of acetylcholine and affects the neurotransmission between neurons. In India, monocrotophos continues to be produced, used and exported. The perception that monocrotophos is cheap and necessary, have prevented the product from being taken off the market. Another cause of concern is the use of MCP for suicide attempts in the country.
Additional information:
The government of India regulates the manufacture, registration, sale, transport, distribution, use, import and export of pesticides through the Insecticides Act 1968 and the Insecticides Rules 1971. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Net primary productivity is a measure of the biomass available for the consumption from the primary producers.
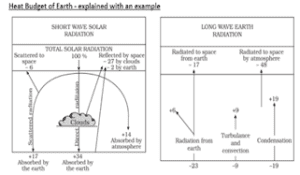
Statement II: A large part of the sunlight gets absorbed, reflected and scattered through the layers of the atmosphere, leaving roughly 2% of sunlight to be captured by plants for photosynthesis.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis (i.e. biomass generated from primary producers through photosynthesis). But it must be noted that a considerable amount of GPP is utilised by plants in respiration. Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses (R), is the net primary productivity (NPP).
GPP – R = NPP
Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs (herbivores and decomposers).
Statement 2 is correct but does not explain statement 1: 50% of light from the sunlight supports the process of photosynthesis. Out of which 2-10% is captured by plants, which is absorbed through chlorophyll and utilised in photosynthesis.
The atmosphere of the earth comprises different layers having varying density and composition. The sunlight, therefore, gets either absorbed or reflected or scattered through the atmosphere.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis (i.e. biomass generated from primary producers through photosynthesis). But it must be noted that a considerable amount of GPP is utilised by plants in respiration. Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses (R), is the net primary productivity (NPP).
GPP – R = NPP
Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs (herbivores and decomposers).
Statement 2 is correct but does not explain statement 1: 50% of light from the sunlight supports the process of photosynthesis. Out of which 2-10% is captured by plants, which is absorbed through chlorophyll and utilised in photosynthesis.
The atmosphere of the earth comprises different layers having varying density and composition. The sunlight, therefore, gets either absorbed or reflected or scattered through the atmosphere.

-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following statements:
1. Megaherbivores have a direct bearing on the spread of invasive species.
2. Some tribals in India use invasive plants to make sculptures.
3. While mangroves can be affected by invasive species, they can never turn invasive themselves.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Megaherbivores unwittingly promote the spread of invasive species by dispersing their seeds.
By virtue of their size and varied diets, the megaherbivores such as Indian bison, sambar deer, elephant, rhinoceros etc. can clear swathes of vegetation, including invasive plants, creating opportunities for new growth. In places like Kaziranga and Manas, this “gardening” has led to a reduction in invasive species. However, in drier regions, invasive trees like Lantana camara and Prosopis juliflora have established an impenetrable fortress. Unable to break through these thorny thickets, megaherbivores turn to native plants, adding pressure on already struggling population. Even worse, some, like elephants, unwittingly promote the spread of invasive species by eating on their fruits and dispersing their seeds.
Statement 2 is correct: The sculptures of elephants were skillfully crafted by tribal artisans hailing from Gudalur in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve from lantana camara, an invasive species. These elephant sculptures were brought to Chennai for display at the Tamil Nadu Global Investors Meet 2024.

Statement 3 is incorrect: Many salt-tolerant aquatic and terrestrial plants as well as epiphytes can colonize and persist in mangrove forests. Many opportunistic invaders can also invade mangrove forests during periodic reduced soil and water salinity.
The rising temperatures and sea level due to climate change are allowing mangroves to expand their ranges farther away from the equator and encroach on temperate wetlands, like salt marshes. Also, on some isolated tropical islands, such as Hawaii and Tahiti, mangroves are not native and are sometimes considered invasive species.Incorrect
Answer. B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Megaherbivores unwittingly promote the spread of invasive species by dispersing their seeds.
By virtue of their size and varied diets, the megaherbivores such as Indian bison, sambar deer, elephant, rhinoceros etc. can clear swathes of vegetation, including invasive plants, creating opportunities for new growth. In places like Kaziranga and Manas, this “gardening” has led to a reduction in invasive species. However, in drier regions, invasive trees like Lantana camara and Prosopis juliflora have established an impenetrable fortress. Unable to break through these thorny thickets, megaherbivores turn to native plants, adding pressure on already struggling population. Even worse, some, like elephants, unwittingly promote the spread of invasive species by eating on their fruits and dispersing their seeds.
Statement 2 is correct: The sculptures of elephants were skillfully crafted by tribal artisans hailing from Gudalur in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve from lantana camara, an invasive species. These elephant sculptures were brought to Chennai for display at the Tamil Nadu Global Investors Meet 2024.



Statement 3 is incorrect: Many salt-tolerant aquatic and terrestrial plants as well as epiphytes can colonize and persist in mangrove forests. Many opportunistic invaders can also invade mangrove forests during periodic reduced soil and water salinity.
The rising temperatures and sea level due to climate change are allowing mangroves to expand their ranges farther away from the equator and encroach on temperate wetlands, like salt marshes. Also, on some isolated tropical islands, such as Hawaii and Tahiti, mangroves are not native and are sometimes considered invasive species.




