Day-531
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Consider the following statements:
1. Flex-fuel vehicles can operate on maximum 85% ethanol.
2. Bioethanol is mainly derived from used cooking oil and animal fats.
3. Flex fuels have higher fuel efficiency than petrol.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Flex fuel vehicles (FFV) are capable of running on 100 per cent petrol or 100 per cent bio-ethanol or a combination of both. A flex-fuel or flexible fuel vehicle typically has an internal combustion engine (ICE), but unlike a regular petrol vehicle, it can run on more than one type of fuel, or a mixture of these fuels. The most common versions use a blend of petrol and ethanol or methanol.
Flex-fuel vehicles such as the prototype Hycross (by Toyota) can run on blends of ethanol that are far higher than the current standard 20% mix (E20). This is made possible by equipping the engine with a fuel mix sensor and an engine control module (ECM) programming those senses and automatically adjusts for any ratio of designated fuels.
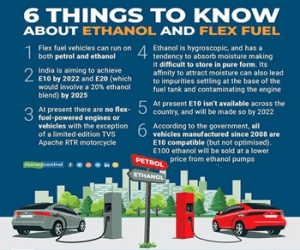
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Biodiesel is produced from used cooking oils or animal fats, the feedstock for first-generation bioethanol is mainly edible food crops such as rice, wheat, barley, potato, corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oil like soybean oil, sunflower oil, olive oil, canola oil, mustard oil, etc.
However, second-generation bioethanol production process exploits non-food crops, food crops residues, wastes of wood-based or food-based industries such as wood chips, skins or pulps from fruit pressing, etc.
Typically, bioethanol is produced from the fermentation of various feedstocks that contain mainly fermentable sugars or carbohydrates. Fermentation is the process of decomposing an organic substrate into products (e.g. bioethanol) by bacteria, yeast, fungi and other microorganisms usually present in gut.
According to a NITI Aayog report, in 2019-20, more than 90% of the ethanol produced in India came from sugarcane.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The fuel efficiency of flex fuels is lower than that of petrol. Flex-fuel cars typically take a 4-8% hit on fuel efficiency when using ethanol for motive power. Bio-ethanol contains less energy per litre than petrol. However, the calorific value (energy contained in the fuel) of bio-ethanol will become on par with petrol with use of advanced technology.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Flex fuel vehicles (FFV) are capable of running on 100 per cent petrol or 100 per cent bio-ethanol or a combination of both. A flex-fuel or flexible fuel vehicle typically has an internal combustion engine (ICE), but unlike a regular petrol vehicle, it can run on more than one type of fuel, or a mixture of these fuels. The most common versions use a blend of petrol and ethanol or methanol.
Flex-fuel vehicles such as the prototype Hycross (by Toyota) can run on blends of ethanol that are far higher than the current standard 20% mix (E20). This is made possible by equipping the engine with a fuel mix sensor and an engine control module (ECM) programming those senses and automatically adjusts for any ratio of designated fuels.

Statement 2 is incorrect: While Biodiesel is produced from used cooking oils or animal fats, the feedstock for first-generation bioethanol is mainly edible food crops such as rice, wheat, barley, potato, corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oil like soybean oil, sunflower oil, olive oil, canola oil, mustard oil, etc.
However, second-generation bioethanol production process exploits non-food crops, food crops residues, wastes of wood-based or food-based industries such as wood chips, skins or pulps from fruit pressing, etc.
Typically, bioethanol is produced from the fermentation of various feedstocks that contain mainly fermentable sugars or carbohydrates. Fermentation is the process of decomposing an organic substrate into products (e.g. bioethanol) by bacteria, yeast, fungi and other microorganisms usually present in gut.
According to a NITI Aayog report, in 2019-20, more than 90% of the ethanol produced in India came from sugarcane.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The fuel efficiency of flex fuels is lower than that of petrol. Flex-fuel cars typically take a 4-8% hit on fuel efficiency when using ethanol for motive power. Bio-ethanol contains less energy per litre than petrol. However, the calorific value (energy contained in the fuel) of bio-ethanol will become on par with petrol with use of advanced technology. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Belem declaration has been concluded successfully by the International Tropical Timber Organisation and Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Statement II: The Belem declaration has special emphasis on curbing deforestation in Amazon rainforest and recognises indigenous knowledge as a condition for biodiversity conservation.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Leaders from the eight countries across the Amazon, including Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela, failed to agree on the goal to protect the rainforest at the recently concluded Amazon Summit organised by the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) on 8-9 August,2023. This agreement is referred to as Belem declaration.
The declaration could not arrive at full consensus of all Amazon basin countries. Colombia had proposed that 80 per cent of the Amazon should be protected from deforestation and degradation by 2025 but did not find support from all the members.
The failure of consensus on protected areas could have implications on the overall goals and targets set under the Convention on Biological Diversity’s Global Biodiversity Framework set in December 2022. Under this, member countries had agreed to protect at least 30 per cent of land and sea by 2030.
Statement 2 is correct: The Belem Declaration released during the Amazon Summit recognises Indigenous knowledge as a condition for biodiversity conservation and calls for ensuring full and effective participation of Indigenous Peoples in decision-making and public policy formulation processes. The declaration contends that at least 80 per cent of forest needs to be protected to avoid an irreversible tipping point; thus, the need for cumulative action by all Amazon basin countries is required to curb the deforestation in the Amazon rainforests.
The declaration promotes sustainable use of biodiversity resources in the Amazon. At the moment, there is no indication of how much money members will invest to fund the declaration’s proposed objectives or support minimum conservation standards.
Additional information:
● The Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) is an intergovernmental organization formed by the eight Amazonian countries: Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, which signed the Amazon Cooperation Treaty (ACT), becoming the only socio-environmental block in Latin America.
● The Amazon Cooperation Treaty (ACT) signed on July 3, 1978 gave rise to the ACTO, that is oriented to promote the harmonious development of the Amazonian territories in such a way that the joint actions of the Amazonian countries produce equitable and mutually beneficial results in achieving the sustainable development of the Amazon Region.
● In 1995, the eight nations decided to create the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO), to strengthen and implement the objectives of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty.
● Permanent Secretariat of ACTO was established in Brasilia (Brazil) on December 13, 2002.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Leaders from the eight countries across the Amazon, including Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela, failed to agree on the goal to protect the rainforest at the recently concluded Amazon Summit organised by the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) on 8-9 August,2023. This agreement is referred to as Belem declaration.
The declaration could not arrive at full consensus of all Amazon basin countries. Colombia had proposed that 80 per cent of the Amazon should be protected from deforestation and degradation by 2025 but did not find support from all the members.
The failure of consensus on protected areas could have implications on the overall goals and targets set under the Convention on Biological Diversity’s Global Biodiversity Framework set in December 2022. Under this, member countries had agreed to protect at least 30 per cent of land and sea by 2030.
Statement 2 is correct: The Belem Declaration released during the Amazon Summit recognises Indigenous knowledge as a condition for biodiversity conservation and calls for ensuring full and effective participation of Indigenous Peoples in decision-making and public policy formulation processes. The declaration contends that at least 80 per cent of forest needs to be protected to avoid an irreversible tipping point; thus, the need for cumulative action by all Amazon basin countries is required to curb the deforestation in the Amazon rainforests.
The declaration promotes sustainable use of biodiversity resources in the Amazon. At the moment, there is no indication of how much money members will invest to fund the declaration’s proposed objectives or support minimum conservation standards.
Additional information:
● The Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) is an intergovernmental organization formed by the eight Amazonian countries: Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, which signed the Amazon Cooperation Treaty (ACT), becoming the only socio-environmental block in Latin America.
● The Amazon Cooperation Treaty (ACT) signed on July 3, 1978 gave rise to the ACTO, that is oriented to promote the harmonious development of the Amazonian territories in such a way that the joint actions of the Amazonian countries produce equitable and mutually beneficial results in achieving the sustainable development of the Amazon Region.
● In 1995, the eight nations decided to create the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO), to strengthen and implement the objectives of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty.
● Permanent Secretariat of ACTO was established in Brasilia (Brazil) on December 13, 2002. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. In the context of the International Blue Carbon Partnership (IBCP), consider the following statements:
1. It was launched at the UNFCCC COP27 in Sharm-el-Sheikh.
2. IUCN and WWF collaborated to launch the IBCP.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The International Partnership for Blue Carbon (IPBC) was launched at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties (COP21) in Paris in 2015.
It connects government agencies with non-governmental organisations, intergovernmental organisations and research institutions from around the world, with a joint vision to protect, sustainably manage and restore global coastal blue carbon ecosystems contributing to climate change mitigation, adaptation, biodiversity, ocean economies and livelihoods of coastal communities.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The International Partnership for Blue Carbon is the collaborative effort of:
● Australia, Indonesia, Costa Rica,
● the Blue Carbon Initiative (Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission – UNESCO, Conservation International, IUCN),
● GRID-Arendal,
● the Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Program (SPREP),
● the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat and Office of the Pacific Oceanscape Commissioner,
● the Centre for International Forestry Research; and the Global Change Institute.
Additional Information:
● The term ‘coastal blue carbon ecosystems’ refers to three main types of vegetated coastal habitats – mangroves, tidal marshes and seagrasses. When degraded or lost, coastal blue carbon ecosystems can become significant emission sources.
● Mangrove deforestation is estimated to be responsible for as much as 10 per cent of emissions from deforestation globally.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The International Partnership for Blue Carbon (IPBC) was launched at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties (COP21) in Paris in 2015.
It connects government agencies with non-governmental organisations, intergovernmental organisations and research institutions from around the world, with a joint vision to protect, sustainably manage and restore global coastal blue carbon ecosystems contributing to climate change mitigation, adaptation, biodiversity, ocean economies and livelihoods of coastal communities.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The International Partnership for Blue Carbon is the collaborative effort of:
● Australia, Indonesia, Costa Rica,
● the Blue Carbon Initiative (Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission – UNESCO, Conservation International, IUCN),
● GRID-Arendal,
● the Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Program (SPREP),
● the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat and Office of the Pacific Oceanscape Commissioner,
● the Centre for International Forestry Research; and the Global Change Institute.
Additional Information:
● The term ‘coastal blue carbon ecosystems’ refers to three main types of vegetated coastal habitats – mangroves, tidal marshes and seagrasses. When degraded or lost, coastal blue carbon ecosystems can become significant emission sources.
● Mangrove deforestation is estimated to be responsible for as much as 10 per cent of emissions from deforestation globally. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. In the context of Plastic Overshoot Day 2023, consider the following statements:
1. Plastic Overshoot Day Report is published by the Global Footprint Network.
2. Plastic Overshoot Day is determined based on a country’s Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI).
3. India ranks first in the Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI).
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: On July 28, 2023, the Earth saw its first Plastic Overshoot Day: The point at which the amount of plastics exceeds the global waste management capacity. The Report has been released by Swiss-based research consultancy Earth Action (EA). According to the Report, under current scenarios, despite pledges and increased waste management capacity, increased production of plastics will lead to global plastics pollution tripling by 2040.
Global Footprint Network brings out the Earth Overshoot Day report. Earth Overshoot Day marks the date when humanity has exhausted nature’s budget for the year. In 2023, Earth Overshoot Day fell on August 2, 2023.
Earth Overshoot Day is computed by dividing the planet’s biocapacity (the amount of ecological resources Earth is able to generate that year), by humanity’s Ecological Footprint (humanity’s demand for that year), and multiplying by 365, the number of days in a year.
Statement 2 is correct: Plastic Overshoot Day is determined based on a country’s Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI). The gap in waste management capacity and plastic consumption is called MWI.
Plastic Overshoot Day for India, or the date when the amount of plastic waste outweighed the country’s ability to manage it, was January 6 2023.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India ranks fourth in the MWI, with 98.55 per cent of generated waste being mismanaged and fares poorly in the management of plastics waste, according to the EA report.
Additional Information:
● India is among the 12 countries, along with China, Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, Russia, Mexico, the United States, Saudi Arabia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Iran and Kazakhstan, which are responsible for 52 per cent of the world’s mismanaged plastic waste.
● Iceland fares the worst when it comes to plastic consumption on a per-person basis, with annual consumption of 128.9 kg per person. This is 24.3 times higher than the yearly consumption per person of 5.3 kg in India.
● The global average consumption of plastic per person per year is 20.9 kg.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: On July 28, 2023, the Earth saw its first Plastic Overshoot Day: The point at which the amount of plastics exceeds the global waste management capacity. The Report has been released by Swiss-based research consultancy Earth Action (EA). According to the Report, under current scenarios, despite pledges and increased waste management capacity, increased production of plastics will lead to global plastics pollution tripling by 2040.
Global Footprint Network brings out the Earth Overshoot Day report. Earth Overshoot Day marks the date when humanity has exhausted nature’s budget for the year. In 2023, Earth Overshoot Day fell on August 2, 2023.
Earth Overshoot Day is computed by dividing the planet’s biocapacity (the amount of ecological resources Earth is able to generate that year), by humanity’s Ecological Footprint (humanity’s demand for that year), and multiplying by 365, the number of days in a year.
Statement 2 is correct: Plastic Overshoot Day is determined based on a country’s Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI). The gap in waste management capacity and plastic consumption is called MWI.
Plastic Overshoot Day for India, or the date when the amount of plastic waste outweighed the country’s ability to manage it, was January 6 2023.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India ranks fourth in the MWI, with 98.55 per cent of generated waste being mismanaged and fares poorly in the management of plastics waste, according to the EA report.
Additional Information:
● India is among the 12 countries, along with China, Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, Russia, Mexico, the United States, Saudi Arabia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Iran and Kazakhstan, which are responsible for 52 per cent of the world’s mismanaged plastic waste.
● Iceland fares the worst when it comes to plastic consumption on a per-person basis, with annual consumption of 128.9 kg per person. This is 24.3 times higher than the yearly consumption per person of 5.3 kg in India.
● The global average consumption of plastic per person per year is 20.9 kg. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following statements about African Lions and Asiatic Lions:
1. African lions are well-adapted to survive in open scrublands and deserts unlike Asiatic lions which are only found in the deciduous forests of India.
2. The longitudinal fold of skin under its belly distinguishes African lion from Asiatic lion which lacks such skin folds.
3. Both African lions and Asiatic lions are listed as ‘Endangered’ as per the IUCN Red List.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: African lions are highly adaptable big cats and can be found in a wide variety of habitats, including semi-arid desert areas and even very dry habitats such as the Kalahari desert. They prefer open woodland and thick bush, as well as scrub and grasslands, to help them stalk their prey and also find shade to rest during the hottest part of the day.
African lions used to be spread across most of the continent, but now are only found in sub-Saharan Africa, with 80% in eastern or southern Africa. Three of the five largest populations are in Tanzania.
On the other hand, Asiatic lions have an extremely restricted habitat. These lions can only be found in the Gir Forest National Park in the Indian state of Gujarat. This park is a protected area and is considered one of the last strongholds of the Asiatic lion. The park’s terrain is a mixture of dry deciduous forest and savanna grasslands providing an ideal habitat for these big cats.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The most striking morphological character, which is always seen in Asiatic lions, and rarely in African lions, is a longitudinal fold of skin running along its belly. African lions are larger in size than the Asiatic lions.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
IUCN status of Asiatic Lion: Endangered
IUCN status of African lion: Vulnerable. Three-quarters of their populations are in decline. The main threats to African lions are human-wildlife conflict and natural prey decline, as well as habitat loss, climate change and wildlife trade.
Differences between African lion and Asiatic lion in a nutshell-
PARAMETER – AFRICAN LION – ASIATIC LION
Size – Bigger in size than Asiatic counterparts.A male lion weighs about 500 pounds with females typically weighing about 345 pounds. – Relatively smaller in size. The males weigh about 35-450 pounds.
Mane (Only male lions have mane.) – Have a fuller and more prominent mane covering entire head and cascading down their shoulders. – Have much sparser, darker and less developed mane compared to that of African lions.It is also shorter due to which ears of Asiatic lion are more visible.
Skin folds – Do not have skin folds. Instead, they have a smooth belly, contributing to their regal and powerful look. – Impressive skin folds are another feature that sets Asiatic lions apart from their cousins.
Tail and elbow tufts – They have minimal tufts of hair on their elbows and tails, giving them a sleeker appearance. – Have a more pronounced and flamboyant style of tail hair and elbow hair.
Skull – They have only a single infraorbital foramen. – They have bifurcated infraorbital foramina. These tiny openings in the skull ensure the smooth flow of blood and protect the nerves of the eyes.Additional Information-
A recent study ‘Socio-political and ecological fragility of threatened, free-ranging African lion populations’, published in journal Nature Communications, observed that socio-political factors were threatening already fragile lion populations in Africa. Somalian and Malawian big cat populations were found to be the most threatened and Ethiopia’s Maze National Park had the most ecologically fragile geographic population.
● Threats to African lions: poaching for prey, indiscriminate killing due to human-lion conflict, bushmeat and others, prey depletion, livestock encroachment and small population size.
● The researchers found that bushmeat poaching with snares led to local extinction of lions in Nsumbu National Park in Zambia and Limpopo National Park in Mozambique, also driving lion populations to near extinction owing to poaching.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: African lions are highly adaptable big cats and can be found in a wide variety of habitats, including semi-arid desert areas and even very dry habitats such as the Kalahari desert. They prefer open woodland and thick bush, as well as scrub and grasslands, to help them stalk their prey and also find shade to rest during the hottest part of the day.
African lions used to be spread across most of the continent, but now are only found in sub-Saharan Africa, with 80% in eastern or southern Africa. Three of the five largest populations are in Tanzania.
On the other hand, Asiatic lions have an extremely restricted habitat. These lions can only be found in the Gir Forest National Park in the Indian state of Gujarat. This park is a protected area and is considered one of the last strongholds of the Asiatic lion. The park’s terrain is a mixture of dry deciduous forest and savanna grasslands providing an ideal habitat for these big cats.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The most striking morphological character, which is always seen in Asiatic lions, and rarely in African lions, is a longitudinal fold of skin running along its belly. African lions are larger in size than the Asiatic lions.
Statement 3 is incorrect:
IUCN status of Asiatic Lion: Endangered
IUCN status of African lion: Vulnerable. Three-quarters of their populations are in decline. The main threats to African lions are human-wildlife conflict and natural prey decline, as well as habitat loss, climate change and wildlife trade.
Differences between African lion and Asiatic lion in a nutshell-
PARAMETER – AFRICAN LION – ASIATIC LION
Size – Bigger in size than Asiatic counterparts.A male lion weighs about 500 pounds with females typically weighing about 345 pounds. – Relatively smaller in size. The males weigh about 35-450 pounds.
Mane (Only male lions have mane.) – Have a fuller and more prominent mane covering entire head and cascading down their shoulders. – Have much sparser, darker and less developed mane compared to that of African lions.It is also shorter due to which ears of Asiatic lion are more visible.
Skin folds – Do not have skin folds. Instead, they have a smooth belly, contributing to their regal and powerful look. – Impressive skin folds are another feature that sets Asiatic lions apart from their cousins.
Tail and elbow tufts – They have minimal tufts of hair on their elbows and tails, giving them a sleeker appearance. – Have a more pronounced and flamboyant style of tail hair and elbow hair.
Skull – They have only a single infraorbital foramen. – They have bifurcated infraorbital foramina. These tiny openings in the skull ensure the smooth flow of blood and protect the nerves of the eyes.Additional Information-
A recent study ‘Socio-political and ecological fragility of threatened, free-ranging African lion populations’, published in journal Nature Communications, observed that socio-political factors were threatening already fragile lion populations in Africa. Somalian and Malawian big cat populations were found to be the most threatened and Ethiopia’s Maze National Park had the most ecologically fragile geographic population.
● Threats to African lions: poaching for prey, indiscriminate killing due to human-lion conflict, bushmeat and others, prey depletion, livestock encroachment and small population size.
● The researchers found that bushmeat poaching with snares led to local extinction of lions in Nsumbu National Park in Zambia and Limpopo National Park in Mozambique, also driving lion populations to near extinction owing to poaching.




