1. ANGIOSTRONGYLUS CANTONENSIS
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Dangerous rat-borne disease threatens the southeastern US.
EXPLANATION:
- In southeastern America, a parasitic worm is spreading. The worm can cause coma or even death in humans and can also infect pets.
Angiostrongylus Cantonensis:
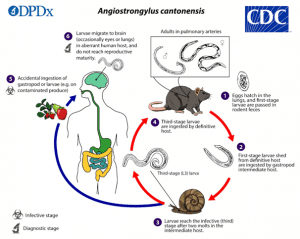
- Angiostrongylus cantonensis is also known as the rat lungworm, causes eosinophilic meningitis and is prevalent in Southeast Asia and tropical Pacific islands.
- However, recently it has been identified in Texas, Louisiana, Alabama, Florida and most recently in Georgia.
- It is a parasitic worm typically found in rats.
- It is spread through rat faeces and can infect humans and other animals through produce or other food items.
- Inside the human body, the parasitic worm migrates to the brain, eyes or lungs, and in severe cases can lead to coma and death.
Symptoms:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Neck stiffness
- Headaches
- Sometimes arm and leg tingling
Precaution:
- Washing your hands.
- Washing vegetables, fruits and other produce.
- Not eating raw or undercooked snails or slugs, crabs,etc.
- Wear gloves if handling snails or slugs etc.
2. INTERNET COOKIES
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Inside the digital world of cookies.
EXPLANATION:
- The digital world of cookies plays a significant role in any online experience.
- In the digital world, cookies help in personalisation and user convenience.
- These unassuming bits of code, stored on a device when one visits websites, play a pivotal role in shaping any online experience.
What are cookies and how do they work?
- Cookies are text files with small pieces of data like a username and password, that are used to identify your computer as you use a network.
- Cookies remember your login information on websites. This means you do not have to repeatedly enter your credentials every time you revisit a site, making it convenient for use.
- For example, websites like Amazon, cookies remember your previous interactions; from products you have browsed to purchases you have made, on the basis of that they recommend you tailored products.
- Platforms like Facebook and Google use cookies to track online behaviour, ensuring the ads you encounter align with your preferences.
Types of cookies:
- Session cookie: It is temporary cookies like post-it notes for websites. They are stored in your computer’s memory only during your browsing session. Once you close your browser, they vanish.
- Persistent cookies: Persistent cookies are the digital equivalent of bookmarks. They stay on your device after your browsing session ends. It remembers your login information, language preferences, and even the ads you have interacted with. They are handy for a more personalised web experience.
- Secure cookies: They are only sent over encrypted connections, making them safer from prying eyes. Secure cookies are often used for sensitive data like login credentials.
- Third-party cookies: They come from a domain other than the one you are visiting. They are often used for tracking and advertising purposes, which can be both useful and, at times, intrusive.
Significance of cookies:
- They act as digital ID cards, aiding in user authentication by allowing websites to recognise and keep you logged in during your visit.
- They foster a sense of personalisation, recalling your preferences such as language choice or website theme.
- They function as the digital equivalent of a persistent shopping cart, ensuring that items you have added online remain there when you return.
- Cookies play a pivotal role in targeted advertising, as advertisers use them to display ads that align with your interests and browsing history, making online shopping more enticing.
Challenges:
- Privacy concerns arise as cookies could track your online behaviour, which can sometimes encroach upon your digital privacy.
- Security risks loom when cookies are inadequately secured, opening doors for cybercriminals to steal your personal information.
- Third-party cookies have sparked debates, prompting many web browsers to curb their usage to safeguard user privacy.
- The data deluge generated by the multitude of cookies can potentially clog your browser, leading to a sluggish web experience.
Way forward:
- The era of user consent has dawned, due to privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation and The California Consumer Privacy Act, necessitating websites to seek your approval before deploying certain cookie types, resulting in those somewhat irksome pop-ups and prompts.
- India’s newly enacted Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 now necessitates websites to acquire explicit consent from users prior to collecting or processing their personal data via cookies.
Source:(https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/inside-the-digital-world-of-cookies/article67357119.ece)
3. CURRENT ACCOUNT DEFICIT
TAG: GS 3: ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: Current account deficit (CAD) of India has widened to $9.2 billion (1.1% of GDP) from $1.3 billion (0.2% of GDP).
EXPLANATION:
- According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Current account deficit (CAD) of India has widened to $9.2 billion (1.1% of GDP) from $1.3 billion (0.2% of GDP).
- The reasons for the CAD are lower surplus in net services and decline in private transfer receipts.
Current Account Deficit:
- Current Account Deficit (CAD) is the shortfall between the money received by selling products to other countries and the money spent to buy goods and services from other nations. If the value of goods and services we import exceeds the value of those we export, the country is said to be in a deficit.
- A lower CAD can improve investor confidence and make the country’s currency more appealing to investors.
- A surplus in the current account can increase foreign exchange reserves and the value of the local currency.
Impact of increase in CAD:
- Rupee depreciation: As a result of the growing current account deficit, there will be a greater demand for foreign currency, which will cause the domestic currency to lose value.
- Depleted foreign currency reserves: As the powerful dollar rises, the Reserve Bank of India will continue to defend against the rupee’s decline, which depletes the forex reserves.
- Imported inflation: An additional effect of the weakening rupee is the increase in imported inflation, which in turn causes broad-based inflation in India to increase.
- Costlier Imports: Since India imports expensive goods and commodities like crude oil, the falling rupee has made imports more expensive.
4. FIVE EYES INTELLIGENCE ALLIANCE
TAG: GS:2 INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: The Five Eyes intelligence-sharing agreement, which is thought to have provided the information that “helped” Canada, has come been in spotlight following recent charges made by the Canadian Prime Minister tying the execution of Khalistani leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar to the Indian government.
WHAT IS FIVE EYES INTELLIGENCE ALLIANCE?
- The Five Eyes Alliance is characterised by a unique multilateral arrangement.
- Its partner countries share a wide range of intelligence, united by common principles of rule of law, robust human rights, etc according to the the National Counter intelligence and Security Center.
- This alliance plays a crucial role in safeguarding their shared national interests by facilitating information exchange.
- The Five Eyes, often referred to as FVEY, constitutes a coalition consisting of five intelligence agencies:
-
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Canada
- It is both surveillance-based and signals intelligence (SIGINT).
HOW DID THE ALLIANCE COME INTO BEING?
- The alliance between the U.S. and the U.K. evolved around the Second World War to counter the Cold War Soviet threat.
- The two countries had successfully deciphered German and Japanese codes during the World War.
- They forged a collaboration to share intelligence related to signals such as radio, satellite and internet communications.
- In the aftermath of the war in 1946, the alliance was formalised through an agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence.
- The treaty was called the British-U.S. Communication Intelligence Agreement, or BRUSA (now known as the UKUSA Agreement),
- Scope of the agreement was limited to “communication intelligence matters only” related to “unrestricted” exchange of intelligence products in six areas:
- collection of traffic;
- acquisition of communication documents and equipment;
- traffic analysis;
- cryptanalysis;
- decryption and translation; and
- acquisition of information regarding communication organisations, practices, procedures, and equipment.
- The arrangement was later extended to ‘second party’ countries Canada joined in 1948, while Australia and New Zealand became part of the alliance in 1956.
FUNCTIONING OF THE FIVE EYES ALLIANCE:
- The Five Eyes countries engage in intelligence gathering and security cooperation, aligning closely in recent years due to shared interests, such as addressing the rise of China.
- They maintain this closeness through the Five Eyes Intelligence Oversight and Review Council.
- It is an entity that facilitates the exchange of views, best practices, and annual in-person meetings among non-political intelligence oversight and review agencies of the member countries.
- Despite their proximity, the Five Eyes countries do not always align in their foreign policies.
- For stance, New Zealand’s stance on certain Chinese actions differs from that of the other four countries due to its deep trade ties with China.
- The US has also sought to exert its influence through other groupings like the Quad and AUKUS, involving like-minded countries on security matters.
WHAT ARE THE CONCERNS?
- Lack of transparency and accountability:
- The FVEY is a highly secretive alliance, and its members have often been reluctant to disclose information about their intelligence-sharing activities.
- This lack of transparency makes it difficult to hold the FVEY accountable for its actions.
- Invading privacy:
- The FVEY’s mass surveillance programs have been criticized for violating the privacy rights of individuals.
- For example, the Edward Snowden leaks revealed that the US National Security Agency (NSA) was collecting the phone records of millions of Americans without a warrant.
- Abuse of the power:
- There have been concerns that the FVEY has abused its power by spying on foreign leaders and businesses.
- For example, in 2013, it was revealed that the NSA had been spying on German Chancellor Angela Merkel’s phone.
- Discrimination:
- Some critics have argued that the FVEY’s intelligence-sharing practices discriminate against countries that are not members of the alliance.
- For example, the NSA’s PRISM program allowed the US government to collect data from major internet companies, including Google and Facebook.
- This data could then be shared with other FVEY members, even if the target countries were not members of the alliance.
- In addition to these general concerns, there have also been specific concerns raised about the FVEY’s role in certain countries and regions.
5. ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
TAG: GS:3 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The Antimicrobial Resistance Research and Surveillance Network of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) released its annual report for 2022.
EXPLANATION:
- This is the sixth report which sheds light on the evolving landscape of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the country.
- The report showed a trend of declining susceptibility towards critically important antimicrobials (CIA).
- The report is based on data collected from 107,053 culture-positive isolates from 50 medical institutions across India.
- The data was collected from patients with a variety of infections, including bloodstream infections, urinary tract infections, and lower respiratory tract infections.
- The report found that the most common pathogens isolated were Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Resistance to a variety of antibiotics was observed, including carbapenems, cephalosporins, and fluoroquinolones.
- The report also found that resistance to carbapenems, a last-resort class of antibiotics, is increasing in India.
- This is a serious concern, as carbapenems are often the only effective treatment for infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria.
The report makes a number of recommendations to address the growing threat of AMR in India. These recommendations include:
- Strengthening antimicrobial stewardship programs in hospitals and other healthcare settings
- Increasing public awareness about AMR
- Promoting the use of alternative therapies to antibiotics, such as vaccines and phage therapy
- Investing in research on AMR
ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR):
- It is also known as drug resistance.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), it occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change in ways that render the medications used to cure the infections they cause ineffective.
- When the microorganisms become resistant to most antimicrobials they are often referred to as “superbugs”.
- This is a major concern because a resistant infection may kill, can spread to others, and imposes huge costs to individuals and society.
CIA AND HPCIA:
- Critically important antimicrobials (CIA) and Highest Priority Critically Important Antimicrobials (HPCIA) are the categories of antimicrobial agents identified by the World Health Organization (WHO) based on their importance in human medicine and the urgency to preserve their effectiveness.




