1. REPORT ON ELDERLY POPULATION OF INDIA
TAG: GS 2: SOCIAL JUSTICE
THE CONTEXT: Elderly population of India will make up 20% of the total population by 2050.
EXPLANATION:
Growth rate of the elderly population:
- The decadal growth rate of the elderly population of India is estimated to be at 41 percent.
- The percentage of elderly population in the India is projected to double to over 20% of total population by 2050.
- According to the India Ageing Report by the United Nations Population Fund, India (UNFPA), elderly population of India will surpass the population of children (aged 0 to 15 years) by 2046.
Life expectancy of women as compared to men:
- The life expectancy of women at the age of 60 and at the 80 is higher as compared to men.
- For example, in Himachal Pradesh and Kerala, women at 60 years have a life expectancy of 23 and 22 years, respectively, which is four years greater than men at 60 years.
Economic Problem:
- According to the India Ageing Report, poverty may affect their quality of life and healthcare utilization because more than 40% of the elderly in India are in the poorest wealth quintile and out of 40%, about 18.7% are living without an income.
Regional Differences:
- The absolute numbers and growth of the aged population vary significantly by location.
- The proportion of the old population in southern states and a few northern states, including Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, is higher than the national average.
- States like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, which have greater fertility rates and slower demographic shifts, will experience an increase in the proportion of the senior population, although at a lesser rate than the national average.
Elderly Population Feminization and Ruralization:
- According to the report, two key issues affecting India’s aging population are the country’s feminization (with a higher proportion of old women) and ruralization (with a concentration of the elderly in rural areas).
- This necessitates the development of policies that are specifically geared toward the requirements of older women, who are more likely to be widowed, live alone, and rely on family support.
Sex Ratio Among the Elderly:
- The sex ratio (females per 1,000 males) among the elderly population has been growing steadily since 1991, with the ratio in the general population stagnating.
- In central India, where the sex ratio went from 973 in 2011 to 1,053 in 2021, implying that the women caught up with and outperformed the men in survival after 60 years over the decade.
- However, In the northeast and the east, while the sex ratio of the elderly increased, it remained below 1,000 in both years, indicating that men still outnumber the women in these regions even at 60-plus years.
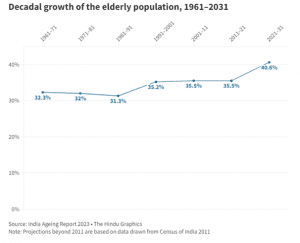
Future prospect: The report projected that the population of people aged 80+ years will grow at a rate of around 279% between 2022 and 2050 with a predominance of widowed and highly dependent very old women.
2. ARMED FORCES (SPECIAL POWERS) ACT (AFSPA)
TAG: GS 3: INTERNAL SECURITY
THE CONTEXT: Manipur government extends AFSPA in hill districts for 6 months.
EXPLANATION:
- The “disturbed area” status under the Act will remain applicable in all the hill districts, which are dominated by tribal communities.
Article 355 of the Indian Constitution provides that the Central Government is under an obligation to protect the States from “external aggression and internal disturbance“. The AFSPA enables the Central Government to discharge its Constitutional obligation.
AFSPA:
- The AFSPA grants unrestricted authority to the armed forces and the Central Armed Police forces stationed in “disturbed areas” to kill anyone acting against the law, to arrest and search any location without a warrant, and to do so while being shielded from legal action and prosecution.
- In order to address the Naga revolt, the law was originally implemented in 1958.
- When the Act was revised in 1972, the Central government and the States got the authority to designate a region as “disturbed” at the same time.
- Meghalaya was subject to the AFSPA for 27 years before the MHA abolished it on April 1st, 2018, after Tripura had revoked the Act in 2015.
- Parts of Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, and Arunachal Pradesh currently have AFSFA.
Criticism of AFSPA:
- The Act gives unfettered powers to the armed forces and the Central armed police forces deployed in “disturbed areas” to kill anyone who is acting in a way to create disharmony in the society.
- It empowers armed forces to search any place without a warrant and also gives them insulation from prosecution and legal rights.
- The use of these extraordinary powers by the armed forces has frequently sparked accusations of fake encounters and other human rights abuses by security forces in unrest areas, raising concerns about the permanent installation of the AFSPA in some states, including Nagaland, Manipur and J&K.
AFSPA withdrawal:
- Since 1981, AFSPA has been applicable in Manipur, a former Union Territory which attained Statehood in 1972. AFSPA also existed in the Naga-dominated areas of the erstwhile UT of Manipur since 1958.
- However, the provisions of the Act were withdrawn from the Imphal Municipality area in 2004.
- In April 2022, AFSPA was removed from 15 police station areas in six districts, and from April 1, 2023, the disturbed area notification was withdrawn from four other police stations.
3. RISE AND FALL OF INSECT
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Climate change influences rise and fall of insect populations.
EXPLANATION:
- It is observed that numbers of insects decrease during unfavorable conditions and a spike in normal periods.
- The weather in 2022 was consistently favorable for insects, as was the summer of 2021.
- Temperatures and precipitation affect insect populations at various stages of their life cycle.
- For example, the insect’s survival depends on winter conditions and the last weather conditions such as spring or summer.
About Climate change influences the rise and fall of insect populations:
- Insects are cold-blooded animals, meaning that their body temperature is regulated by the environment.
- This makes them particularly vulnerable to changes in temperature.
- Insect populations are widely influenced by weather anomalies. Climate change is causing global temperatures to rise, and this is having a negative impact on many insect populations.
- Some insects are able to tolerate a wider range of temperatures than others, but many species are struggling to adapt to the rapid warming that is happening now.
- Climate change is causing other changes to the environment, such as changes in precipitation patterns, more extreme weather events, and the spread of invasive species.
- The decline of insect populations is a serious problem because insects play a vital role in ecosystems. They are pollinators, predators, and decomposers. Without insects, many plants and animals would not be able to survive.
Some specific things that help protect insect populations:
- Plant native plants in your yard or garden.
- Provide water and shelter for insects.
- Avoid using pesticides and other chemicals in your yard or garden.
- Support organizations that are working to protect insects and their habitats.
4. CABOMBA FURCUTA
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Cabomba furcuta, an invasive alien species has spread in the water canals and threatening the Kole fields of Kerala.

EXPLANATION:
- Many parts of the water canals, crisscrossing the vast Kole fields, have turned pink now because of its Pink Bloom.
- It is repeating its presence for the third year in a row in the Kole fields.
- It is a native of central and south America and it was brought to Kerala as an aquarium plant.
- But it has posed major threat to the biodiversity both in the terrestrial system as well as the aquatic landscape.
- The Pink bloom had emerged as a tourist attraction a few years ago during the COVID period near Perambra in Kozhikode.
- It attracted people due to the massive flowering, which turns the entire water body pink.
CABOMBA FURCUTA:
- It is a red stem plant with finely divided leaves.
- It is popularly called as Pink Bloom due its massive flowering.
- It can be found in nature in Central and South America.
- It has attractive reddish foliage when grown well but isn’t a popular plant due to its high demands.
- In sub-optimal conditions the plant is greenish rather than red, with more elongated internodes.
- The plant needs an aggressive amount of light to show good coloration and shorter internodes. Greening of the top leaves coupled with elongated internodes are a sign lighting is insufficient.
- Though this plant is known to originate from soft-water, it seems to tolerate some hardness and can grow well.

Key factors for the growth:
- Aggressively high light levels.
- Regular, all-round fertilization.
- CO2 injection brings out coloration.
- Cooler temperatures, higher light levels give shorter internodes.
KOLE WETLANDS:
- It is an internationally important Ramsar site of high value biodiversity.
- They are a large brackish wetland ecosystem located in the Thrissur and Malappuram districts of Kerala, India.
- They cover an area of about 13,632 hectares (33,690 acres) and are fed by 10 rivers.
- The wetlands are home to a variety of plants and animals, including over 250 species of birds.
Here are some of the ways that the Kole wetlands are important:
- They provide food and livelihoods for thousands of people, through agriculture, fishing, and tourism.
- They help to control flooding and protect coastal areas from erosion.
- They are home to a variety of plants and animals.
- They are a popular tourist destination, known for their scenic beauty and unique biodiversity.
5. BENNU
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Bennu asteroid sample has been dropped off by the NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft which contains a lot for the scientists to study.
EXPLANATION:
- Study of Bennu include significant commercial components such as opportunities for space-mining and impact mitigation technologies.
- They also participate in a more timeless quest to find out where life came from and what its fate could be.
- With OSIRIS’s capsule, humankind virtually gets to hold infinity in the palm of the hand.
BENNU:
- Bennu – discovered in 1999 – is a small, near-Earth asteroid that passes close to Earth about every six years.
- Bennu is an asteroid orbiting the sun (with a period of 436 days) such that it comes relatively close to the earth once every six years or so.
- It is a carbonaceous asteroid with characteristics that suggest it settled into its present form and composition within 10 million years after the solar system’s formation, surviving the last 4.5 billion years nearly intact.
- Such ‘leftover’ pieces of debris are expected to reveal the system’s ingredients and the signatures of the processes that combined them in different ways.
- Many scientists also believe that when rocks such as Bennu crashed into the earth, they delivered the compounds required for the formation of life.
- Also, as Bennu could smash into the earth between 2178 and 2290, studying it could inform ways to prevent this collision.

OSIRIS-Rex MISSION:
- The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is a NASA mission to study and collect a sample from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu.
- In 2016, NASA launched the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft to study Bennu.
- The spacecraft arrived at Bennu in 2018 and began to study the asteroid.
- In 2020, the spacecraft collected a sample of Bennu’s surface material.
- The sample is scheduled to return to Earth in 2023.
- It is equipped with a variety of instruments to study Bennu, including cameras, spectrometers, and a laser altimeter.
- The spacecraft has also been equipped with a robotic arm that will be used to collect the sample from Bennu’s surface.
- The OSIRIS-REx mission is expected to provide scientists with valuable insights into the formation and evolution of asteroids.
- The sample of Bennu’s surface material is expected to contain organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life.

Here are some of the key objectives of the OSIRIS-REx mission:
- To study the global and local characteristics of Bennu.
- To collect a sample of Bennu’s surface material and return it to Earth.
- To investigate Bennu’s potential hazard to Earth.
- To contribute to our understanding of the origins and evolution of the solar system.
- The OSIRIS-REx mission is a complex and challenging undertaking, but it has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of asteroids and their role in the formation of the solar system.




