1. NILGIRI TAHR
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Tamil Nadu and Kerala governments may join hands to count endangered Nilgiri tahr.
EXPLANATION:
- Tamil Nadu is working on a standardised technique to count the endangered population of southern India’s only mountain ungulate.
- The Tamil Nadu Forest Department will also propose to its Kerala counterpart to conduct a synchronised census, as the animal is only found in select habitats in the two States.
About Nilgiri Tahr:
- The Nilgiri Tahr is the only mountain ungulate in southern India amongst the 12 species present in India.
- It is the state animal of Tamil Nadu.
- The Nilgiri Tahr, which used to be found along the entire stretch of Western Ghats, is presently found only in small fragmented pockets.
- The Eravikulam National Park has the highest density and largest surviving population of Nilgiri tahr.
- October 7 is celebrated as ‘Niligiri Tahr Day’ in honour of E.R.C. Davidar, who was responsible for pioneering one of the first studies of the species in 1975.
Conservation status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered.
- WPA: Schedule-1.
Reproduction:
- A grown-up male is known as ‘saddle back’. The male would be bigger and darker than the female and has a silvery saddle like patch on its back. Mating takes place during the monsoon season and calving is during January-February.
- The female gestates for about 180 days and usually gives birth to one kid per pregnancy. Sexual maturity is achieved at around three years of age.
- The average life expectancy for Nilgiri tahr in the wild is estimated to be only three or 3.5 years although the potential life span is at least 9 years.
Threats to Nilgiri Tahr: The Nilgiri tahr faces a multitude of threats such as:
- Habitat loss due to rampant deforestation, competition with domestic livestock, hydroelectric projects in Nilgiri tahr habitat, and monoculture plantations.
- Occasional hunting for its meat and skin
- Nilgiri tahr habitats face threats in the form of the spread of invasive plants such as wattles, pines, and eucalyptus in the grasslands.
Nilgiri Tahr project:
- The Tamil Nadu government launched a project for the conservation of the Nilgiri Tahr.
- Under The Nilgiri Tahr project, the government of Tamil nadu plans to develop a better understanding of the Nilgiri Tahr population through surveys and radio telemetry studies.
- Tamil Nadu government plans to reintroduce the Tahrs to their historical habitat.
- It will address the proximate threats to Nilgiri Tahr.
- It will increase public awareness of the species.
- The project is to be implemented from 2022 to 2027.
2. OSIRIS-REX
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: NASA capsule carrying first asteroid samples landed on Earth.
EXPLANATION:
- NASA’s first asteroid samples fetched from deep space landed into the Utah desert.
- Initially, the Genesis spacecraft dropped off bits of solar wind in 2004, but the samples were compromised when the parachute failed and the capsule slammed into the ground. Secondly ,the Stardust spacecraft successfully delivered comet dust in 2006. OSIRIS-REx was NASA’s third sample return from a deep-space robotic mission.
- Japan is the only other country to bring back asteroid samples.
About OSIRIS-REx:
- It was launched in 2016.
- A NASA spacecraft mission called OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer) is designed to investigate the near-Earth asteroid Bennu.
- The project is going to improve the knowledge of asteroids and assist scientists in their investigations into the origins of life, planet formation and development of our solar system.
About Asteroid Bennu:
- Bennu was formed in the first 10 million years of the solar system’s history- over 4.5 billion years ago.
- Asteroid Bennu, which is rich in carbon, is thought to be a piece of the early solar system.
- It could also be dangerous because there is a remote risk that it will collide with Earth in the late 22nd century.
- Bennu is a B-type asteroid with a ~500 meter diameter. It completes an orbit around the Sun every 436.604 days (1.2 years) and every 6 years comes very close to Earth, within 0.002 AU.
What is an asteroid?
Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun. Although asteroids orbit the Sun like planets, they are much smaller than planets.
3. AIRCRAFT CARRIER INS VIKRANT.
TAG: GS 3: DEFENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Defence Procurement Board discussed Navy’s proposal for a second Vikrant-like aircraft carrier.
EXPLANATION:
- India’s first indigenously built aircraft carrier INS Vikrant was commissioned in 2022, now Defence Procurement Board discussing for second of its type as demanded by the Indian Navy for security reasons.
About INS Vikrant:
- Under Project 71 Air Defence Ship (ADS), the Indian Navy is currently using the aircraft carrier INS Vikrant. It is India’s first indigenously designed and built aircraft carrier.
- The Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) in Kerala built the carrier.
- The INS Vikrant, India’s first aircraft carrier, was given the name Vikrant in 1961. In Sanskrit vikrant means courageous.
- The ship’s name was changed from Air Defence Ship (ADS) to Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC) in 2022.
- The design of the ship was created starting in 1999, and it was finally commissioned in 2022.
- It supports a prominent ski jump and a STOBAR (Short Take-Off But Arrested Recovery) design.
- It has capability to carry MiG-29K fighter jets and airborne early warning control helicopter Kamov-31 helicopters, US origin MH-60R multi-role helicopters, in addition to homegrown Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH) and Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) (Navy).
Significance of Aircraft Carriers:
- Aircraft carriers are extremely strong and have powerful weapons.
- Their military capabilities, which include carrier borne aircraft, have completely changed the marine domain.
- An aircraft carrier offers a wide range of strategic benefits and it offers incredibly flexible operational options. For example, Surveillance, air defence, airborne early warning, protection of Sea Lines of Communication (SLOC), and anti-submarine warfare are some of its principal functions.
- For India, the carrier battle group, with its inherent combat elements and firepower, becomes a key capability to establish effective air dominance and efficient sea control.
Defence Procurement Board:
- The Defence Procurement Board (DPB) is the highest decision-making body on defence procurement in India. It is chaired by the Raksha Mantri (Defence Minister) and includes senior members of the Ministry of Defence (MoD), the armed forces, and the bureaucracy.
- The DPB is responsible for approving all major defence procurement proposals, including those for the acquisition of new weapons systems, platforms, and ammunition. It also oversees the implementation of defence procurement policies and procedures.
- The DPB plays a vital role in ensuring that the Indian military has the equipment and capabilities it needs to defend the country. It also promotes the development of a domestic defence industry.
The functions of the DPB:
- To approve all major defence procurement proposals, including those for the acquisition of new weapons systems, platforms, and ammunition.
- To oversee the implementation of defence procurement policies and procedures.
- To ensure that the Indian military has the equipment and capabilities it needs to defend the country.
- To promote the development of a domestic defence industry.
4. SHORE TEMPLE
TAG: GS 1: ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: The Shore Temple in Tamil Nadu has achieved a significant milestone by becoming India’s first-ever green energy archaeological site.
SHORE TEMPLE:
- The Shore Temple in Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu, is over 1300 years old.
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the most popular tourist destinations in India.
- It is one of the few temples in India that is dedicated to both Lord Shiva and Lord Vishnu.
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style of architecture.
- The temple is carved out of a single rock face. It is one of the oldest structural excellences (rock-cut) stone temples of the South India.
- The temple is surrounded by a number of other historical monuments, including the Five Rathas and the Arjuna’s Penance.
- The Shore Temple is a must-visit for anyone interested in Indian history and culture. It is also a great place to learn about the country’s commitment to sustainability.
- The Shore Temple is a beautiful and historic site, and the green energy project is a great example of how we can preserve our heritage while also protecting the environment.

THE GREEN HERITAGE PROJECT:
- The Green Heritage Project, which made it possible for the Shore Temple to become a green energy site, was a collaborative initiative between Renault Nissan Technology & Business Centre India and Hand in Hand India.
- The project was launched in 2022 and the project aims to promote sustainability at archaeological sites in India.
- The project involved the installation of three solar plants, each with a capacity of 10 kilowatts.
- Solar panels were installed on the temple grounds to provide clean energy for the site.
- The project also installed a solar-operated reverse osmosis plant to provide clean drinking water to tourists.
- In addition to the solar panels and water purification plant, the project also aims to promote clean transportation by providing electric vehicle charging stations.
- These solar plants will now provide all of the energy needed to illuminate the Shore Temple.
Benefits of the Green Heritage Project:
- The Green Heritage Project is a positive development for both India’s cultural heritage and its environment.
- The project is helping to create jobs and boost the local economy.
- It shows that India is committed to protecting its cultural heritage while also reducing its environmental impact.
- It is also a good example of how public-private partnerships can be used to achieve important goals.
- The Green Heritage Project is a model that can be replicated at other archaeological sites in India and around the world. It is a way to protect our cultural heritage while also reducing our environmental impact.
- India is making efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and promote renewable energy.
5. VIBRIO VULNIFICUS
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Vibrio vulnificus will proliferate due to the ideal conditions resulting from warmer oceans and high rainfall.
EXPLANATION:
- Vibrio vulnificus is underreported in India, but experts believe that the number of cases could increase significantly in coming years due to climate change.
VIBRIO VULNIFICUS:
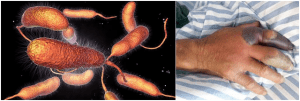
- Vibrio vulnificus is a marine bacterium that can cause serious infections in humans, including a flesh-eating disease.
- It is found in warm coastal waters and is typically associated with eating raw or undercooked seafood.
- Climate change is causing sea levels to rise and water temperatures to increase, as well as increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as cyclones, rain, and flooding.
- These changes are creating a more favourable environment for Vibrio vulnificus to thrive, which could lead to an increase in the number of infections in coastal populations.
- The mortality rate for Vibrio vulnificus infection is 15-50% despite prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- The incidence of V vulnificus in marine fish ranges from 13 per cent to 16 per cent; in molluscan shellfish, it is 38.5 per cent; and in oysters, it is 43 per cent to 75 per cent, as per a study in Microorganisms in 2020.
- Experts recommend that doctors consider testing for this pathogen when patients exhibiting signs of flesh-eating disease live close to a marine environment.
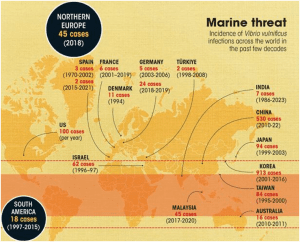
CASES OF VIBRIO VULNIFICUS ALL OVER THE WORLD:
HOW DOES CLIMATE CHANGE INCREASES THE RISK OF VIBRIO VULNIFICUS?
- Vibrio vulnificus prefers warm, brackish waters with low salinity.
- Climate change is causing sea surface temperatures to rise and salinity levels to decrease, creating more ideal conditions for the bacterium to grow and reproduce.
- Extreme weather events such as cyclones, rain, and flooding can cause storm surge and inundation, which can introduce Vibrio vulnificus into new areas and increase people’s exposure to the bacterium.
- Vibrio vulnificus can infect people through open wounds or by ingesting contaminated seafood.
- As more people live and work in coastal areas, and as seafood consumption continues to rise, the number of people at risk of infection is increasing.
IMPACTS:
- Vibrio vulnificus infections can cause a range of illnesses, from mild diarrhoea to severe sepsis and death.
- The bacterium is especially dangerous for people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, and people with chronic diseases.
- An increase in the number of Vibrio vulnificus infections could have a significant impact on coastal communities.
- It could lead to an increase in hospitalizations and deaths, as well as a decrease in tourism and economic activity.
- It is important to raise awareness of this risk and to implement measures to reduce people’s exposure to the bacterium.
- This could include public education campaigns, seafood safety measures, and improved sanitation and drainage systems.
What can be done to reduce the risk of Vibrio vulnificus infection?
- Avoid eating raw or undercooked seafood, especially shellfish.
- Cook seafood thoroughly to an internal temperature of at least 145 degrees Fahrenheit (63 degrees Celsius).
- Avoid swimming in warm coastal waters with open wounds.
- Washing hands thoroughly after handling seafood and after using the bathroom.
- Clean all surfaces and utensils that come into contact with seafood with hot soapy water.
- If one develops any signs of illness after eating seafood, such as diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, or chills, seek medical attention immediately.




