Day-503
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To attempt the Quiz, simply click on START Button.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
2 points1. With reference to the cell metabolism process, consider the following statements:
1. Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria of the cell and is present in all living organisms.
2. Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
The term glycolysis has originated from the Greek words, glycos for sugar, and lysis for splitting.
The scheme of glycolysis was given by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and J. Parnas, and is often referred to as the EMP pathway. In anaerobic organisms, it is the only process in respiration.
● Statement 1 is incorrect: Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms. In this process, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose, which is the end product of photosynthesis, or from storage carbohydrates.
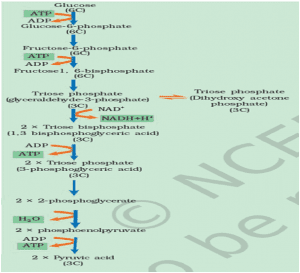
● Sucrose is converted into glucose and fructose by the enzyme, invertase, and these two monosaccharides readily enter the glycolytic pathway. Glucose and fructose are phosphorylated to give rise to glucose-6-phosphate by the activity of the enzyme hexokinase. This phosphorylated form of glucose then isomerises to produce fructose-6-phosphate. Subsequent steps of metabolism of glucose and fructose are the same. The various steps of glycolysis are depicted in Figure attached alongside.
● In glycolysis, a chain of ten reactions, under the control of different enzymes, takes place to produce pyruvate from glucose. While studying the steps of glycolysis, please note the steps at which utilisation or synthesis of ATP or (in this case) NADH + H+ take place.
● ATP is utilised at two steps: first in the conversion of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate and second in the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate.
● The fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is split into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL). We find that there is one step where NADH + H+ is formed from NAD+; this is when 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) is converted to 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPGA). Two redox-equivalents are removed (in the form of two hydrogen atoms) from PGAL and transferred to a molecule of NAD+. PGAL is oxidised and with inorganic phosphate to get converted into BPGA. The conversion of BPGA to 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), is also an energy yielding process; this energy is trapped by the formation of ATP. Another ATP is synthesised during the conversion of PEP to pyruvic acid.
● Statement 2 is correct: Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule.
Hence, option B is correct.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
The term glycolysis has originated from the Greek words, glycos for sugar, and lysis for splitting.
The scheme of glycolysis was given by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and J. Parnas, and is often referred to as the EMP pathway. In anaerobic organisms, it is the only process in respiration.
● Statement 1 is incorrect: Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms. In this process, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose, which is the end product of photosynthesis, or from storage carbohydrates.
● Sucrose is converted into glucose and fructose by the enzyme, invertase, and these two monosaccharides readily enter the glycolytic pathway. Glucose and fructose are phosphorylated to give rise to glucose-6-phosphate by the activity of the enzyme hexokinase. This phosphorylated form of glucose then isomerises to produce fructose-6-phosphate. Subsequent steps of metabolism of glucose and fructose are the same. The various steps of glycolysis are depicted in Figure attached alongside.
● In glycolysis, a chain of ten reactions, under the control of different enzymes, takes place to produce pyruvate from glucose. While studying the steps of glycolysis, please note the steps at which utilisation or synthesis of ATP or (in this case) NADH + H+ take place.
● ATP is utilised at two steps: first in the conversion of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate and second in the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate.
● The fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is split into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL). We find that there is one step where NADH + H+ is formed from NAD+; this is when 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) is converted to 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPGA). Two redox-equivalents are removed (in the form of two hydrogen atoms) from PGAL and transferred to a molecule of NAD+. PGAL is oxidised and with inorganic phosphate to get converted into BPGA. The conversion of BPGA to 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), is also an energy yielding process; this energy is trapped by the formation of ATP. Another ATP is synthesised during the conversion of PEP to pyruvic acid.
● Statement 2 is correct: Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule.
Hence, option B is correct.

-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2 points2. Consider the following pairs:
Protein – Functions
1. Collagen – Intercellular ground substance
2. Trypsin – Enzyme
3. Insulin – Hormone
4. Antibody – Fights infectious agents
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
Proteins are polypeptides. They are linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Each protein is a polymer of amino acids. As there are 20 types of amino acids (e.g., alanine, cysteine, proline, tryptophan, lysine, etc.), a protein is a heteropolymer and not a homopolymer.
A homopolymer has only one type of monomer repeating ‘n’ number of times. This information about the amino acid content is important as later in your nutrition lessons, you will learn that certain amino acids are essential for our health and they have to be supplied through our diet.
Hence, dietary proteins are the source of essential amino acids. Therefore, amino acids can be essential or non-essential. The latter are those which our body can make, while we get essential amino acids through our diet/food. Proteins carry out many functions in living organisms, some transport nutrients across cell membranes, some fight infectious organisms, some are hormones, some are enzymes.
Hence, option D is correct.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
Proteins are polypeptides. They are linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Each protein is a polymer of amino acids. As there are 20 types of amino acids (e.g., alanine, cysteine, proline, tryptophan, lysine, etc.), a protein is a heteropolymer and not a homopolymer.
A homopolymer has only one type of monomer repeating ‘n’ number of times. This information about the amino acid content is important as later in your nutrition lessons, you will learn that certain amino acids are essential for our health and they have to be supplied through our diet.
Hence, dietary proteins are the source of essential amino acids. Therefore, amino acids can be essential or non-essential. The latter are those which our body can make, while we get essential amino acids through our diet/food. Proteins carry out many functions in living organisms, some transport nutrients across cell membranes, some fight infectious organisms, some are hormones, some are enzymes.
Hence, option D is correct.



-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
2 points3. Which of the following is/are not an example of electromagnetic waves?
1. Ultrasonic waves
2. Light waves
3. X-rays
4. Infra-red waves
Select the correct answer using the code given below:Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
● Electromagnetic waves are waves that can travel through vacuum. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of radiant energy released by certain electromagnetic processes.
o Visible light is one type of electromagnetic radiation;
o Other familiar forms are invisible electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays and infrared radiation etc.
● A sound is a form of a mechanical wave that needs a physical medium for its propagation. Therefore, ultrasonic waves (high-frequency sound waves) are not examples of electromagnetic waves.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
● Electromagnetic waves are waves that can travel through vacuum. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of radiant energy released by certain electromagnetic processes.
o Visible light is one type of electromagnetic radiation;
o Other familiar forms are invisible electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays and infrared radiation etc.
● A sound is a form of a mechanical wave that needs a physical medium for its propagation. Therefore, ultrasonic waves (high-frequency sound waves) are not examples of electromagnetic waves. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
2 points4. Recently, India signed a bilateral Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), aimed at deepening military and techno-economic cooperation with which of the following countries?
Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
● The talks between India’s National Security Advisor and his American counterpart in Washington in January 2023, have concluded with the announcement of a new road map for deeper military and techno-economic cooperation between the two countries. If implemented with speed and purpose, the bilateral Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) could lend a new strategic depth and breadth to the expanding engagement between India and the United States.
● The iCET involves collaboration in a range of areas including quantum computing, semiconductors, 5G and 6G wireless infrastructure, and civilian space projects such as lunar exploration. The two sides are also focused on cooperation in defence production.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
● The talks between India’s National Security Advisor and his American counterpart in Washington in January 2023, have concluded with the announcement of a new road map for deeper military and techno-economic cooperation between the two countries. If implemented with speed and purpose, the bilateral Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) could lend a new strategic depth and breadth to the expanding engagement between India and the United States.
● The iCET involves collaboration in a range of areas including quantum computing, semiconductors, 5G and 6G wireless infrastructure, and civilian space projects such as lunar exploration. The two sides are also focused on cooperation in defence production. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
2 points5. Which of the following parts of the brain is responsible for controlling body temperature and the release of hormones by the pituitary gland?
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Scientists have recently identified neurons responsible for regulating the body temperature of mammals, paving the way for technological development which can artificially adjust it to help treat heat stroke, hypothermia, and even obesity, according to a new study. A research group at Nagoya University, Japan, has reported that a group of neurons, called EP3 neurons, in the preoptic area of the brain play a key role in regulating body temperature in mammals. The preoptic area is a part of the hypothalamus that controls the body’s vital functions.
● The Central Nervous System includes the brain and the spinal cord and is the site of information processing and control. The Peripheral Nervous System comprises all the nerves of the body associated with the CNS (brain and spinal cord). The brain is the central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the ‘command and control system’. It controls the voluntary movements, balance of the body, functioning of vital involuntary organs (e.g., lungs, heart, kidneys, etc.), thermoregulation, hunger and thirst, circadian (24-hour) rhythms of our body, activities of several endocrine glands and human behaviour. It is also the site for processing of vision, hearing, speech, memory, intelligence, emotions and thoughts.
● The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain. It’s located at the base of the brain, near the pituitary gland. It synthesizes and secretes neurohormones, often called hypothalamic releasing hormones. These hypothalamic releasing hormones control and regulate the secretion of pituitary hormones.
● Functions of the hypothalamus can be listed as:
o controls the release of 8 major hormones by the pituitary gland
o controls body temperature
o control of food and water intake, hunger and thirst
o control of sexual behavior and reproduction
o control of daily cycles in physiological state and behaviour also known as circadian rhythm
o mediation of emotional responses
Hence, option B is correct.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
Scientists have recently identified neurons responsible for regulating the body temperature of mammals, paving the way for technological development which can artificially adjust it to help treat heat stroke, hypothermia, and even obesity, according to a new study. A research group at Nagoya University, Japan, has reported that a group of neurons, called EP3 neurons, in the preoptic area of the brain play a key role in regulating body temperature in mammals. The preoptic area is a part of the hypothalamus that controls the body’s vital functions.
● The Central Nervous System includes the brain and the spinal cord and is the site of information processing and control. The Peripheral Nervous System comprises all the nerves of the body associated with the CNS (brain and spinal cord). The brain is the central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the ‘command and control system’. It controls the voluntary movements, balance of the body, functioning of vital involuntary organs (e.g., lungs, heart, kidneys, etc.), thermoregulation, hunger and thirst, circadian (24-hour) rhythms of our body, activities of several endocrine glands and human behaviour. It is also the site for processing of vision, hearing, speech, memory, intelligence, emotions and thoughts.
● The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain. It’s located at the base of the brain, near the pituitary gland. It synthesizes and secretes neurohormones, often called hypothalamic releasing hormones. These hypothalamic releasing hormones control and regulate the secretion of pituitary hormones.
● Functions of the hypothalamus can be listed as:
o controls the release of 8 major hormones by the pituitary gland
o controls body temperature
o control of food and water intake, hunger and thirst
o control of sexual behavior and reproduction
o control of daily cycles in physiological state and behaviour also known as circadian rhythm
o mediation of emotional responses
Hence, option B is correct.




