1. G20 AND TRADE MEASURES
TAG: GS 2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS; GS 3: ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: The G20 members took major trade measures and reiterated their commitment to reforming the World Trade Organization (WTO).
EXPLANATION:
- The New Delhi declaration has the trade and investment agenda under the title “unlocking trade for growth”.
- G20 Members emphasized the need to avoid discriminatory green economic policies and promote fair competition. The G20 also expressed support for positive outcomes at the WTO’s Thirteenth Ministerial Conference (MC13).
- G20 leaders have committed to reforming the World Trade Organization’s dispute settlement system, which has been dysfunctional since 2019, leading to protectionism in global trade by 2024.
- They affirm that a rule based, non discriminatory, fair, open, inclusive, equitable, sustainable and transparent multilateral trading system with WTO at its core is indispensable.
- They agreed to mobilise necessary resources to WTO’s ‘Aid for Trade’ initiative to enable developing countries, notably LDCs to effectively participate in global trade, including through enhances local value creation.
- The five outcomes of G20 Trade and Investment of G20 Trade and Investment Ministers Meeting which culminated into Jaipur Call for Action are:
- Digitilisation of trade documents
- Enhancing information access to MSMEs
- Framework to map global value chains
- Best practices on mutual recognition agreements for professional services
- A standards dialogue
- In the declaration, the G20 referred to this Jaipur call for Action for enhancing micro, small, and medium enterprise (MSME) access to information to promote their integration into international trade.
- As per the New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration, the G20 Generic Framework for Mapping Global Value Chains (GVCs) will help members identify risks and build resilience.
- The members said that trade and environment policies should be mutually supportive, consistent with WTO and multilateral environmental agreements.
For more information on WTO refer to 19th July DNA.
2. G20 ON TAX EVASIONS AND CRYPTO AND FOREIGN ASSETS
TAG: GS 2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS; GS 3: ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: In their joint declaration, the G20 leaders agreed to continue cooperation towards a globally fair, sustainable and modern international tax system appropriate to the needs of the 21st century.
EXPLANATION:
- The leaders of G20 met and deliberated upon various socio-economic and geo-political policy decisions including ‘tax’, which is seen as being progressive.
- The G20 has reaffirmed its commitment to the swift implementation of the ‘Two-Pillar’ international tax package.
- ‘Pillar One’ allocates certain portion of the taxing right to market jurisdictions, from residential jurisdictions.
- For instance, under ‘Pillar ‘One, India will be able to impose certain portion of income tax on the sales generated in the Indian marketplace by giant e-commerce digital platforms like Amazon, Google, Facebook, ChatGPT etc,. These digital platform otherwise claim non-applicability of any Indian tax liability in the absence of any permanent establishment (PE) of these companies in the country.
- ‘Pillar Two’ provides for the levy of a global minimum corporate tax rate of 15% on big MNCs, whereby any shortfall between such global minimum tax rate and the tax rate in the low tax jurisdiction will have to be paid by such MNCs as a top-up tax.
- The big US-based multinational companies (MNCs) such as Apple, Amazon, Google and Facebook have consistently used complex networks of international subsidiaries incorporated in low tax jurisdictions or tax havens with multiple routes to minimise their tax incidences by moving their bases or profits from higher tax jurisdictions to lower tax jurisdictions or tax havens.
- One of the major highlights of the joint declaration is the G20’s call for the swift implementation of the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) and amendments to the Common Reporting Standard (CRS).
- CARF is developed in light of the rapid growth of the crypto-asset market and for the reporting of tax information on transactions in crypto assets in a standardized manner. It automatically exchange such information with the jurisdictions of residence of taxpayers on an annual basis.
- So, now crypto transactions undertaken by Indians on foreign-domiciled crypto exchanges will also come under the purview of automatic exchange of information protocol under CARF, and as such it will no longer be possible to hide such crypto transactions.
- Similarly, the amended CRS, requires more tax transparency with respect to financial accounts held abroad, that will make it impossible for Indians not to disclose their foreign bank accounts and assets holdings abroad to the tax authorities.
- So, from now, non-disclosure of any crypto transaction, foreign bank account, or real estate holding abroad by an Indian resident to Indian tax authorities may prove to be a very costly affair in terms of regulatory fines and penalties.
3. MEGALITH CULTURE
TAG: GS 1: ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Ancient terracotta figurines found during archaeological explorations at megalithic dolmen site near Moodbidri.
EXPLANATION:
- Unique terracotta figurines in different states of preservation, with bone and iron pieces have been found in recent archaeological explorations conducted in the megalithic dolmen site at Mudu Konaje, near Moodbidri, in Dakshina Kannada.
- According to historian these ancient terracotta figurines were datable to 800-700 B.C and provide solid ground for the study of Bhoota cult or Daiva Aradhane of coastal Karnataka.
- Cow bovine or Cow goddess had its parallels in Malampuzha megalithic terracotta figurines of Kerala and Egypt.
- Of the eight figurines found, there are two cow bovines, one mother goddess, two peacocks, a horse, a hand of a mother goddess, and an unknown object.
- The megalithic site at Mudu Konaje is located near Moodbidri. It was the biggest megalithic dolmen site which consisted nine dolmens on the slope of a stone hill.
- The terracotta figurines found at Mudu Konaje in a megalithic context are a rare find of India as they were found inside the surface of dolmens.
- Under a dolmen, huge stone slabs known as orthostats were erected in clockwise order, which created a square room. This square chamber was closed by an another huge stone slab as a cap stone. Generally, on the Eastern slab, a round or U-shaped entrance known as port-hole was created.
- Dolmen is known by different names in South India like Kalmane, Pandavara Mane, Moriyara Mane, Moriyara Betta, Panara Arekallu, Madmal Gunda, Kandi Kone, Kottya, Toonth Kal, Pandavara Kal and so on which reveals its popularity among the common people.
Megalith :
- Megalith refer to monuments built of large stones. But all monuments constructed of big stones are not megaliths. The megalithic usually refer to burials made of large stones in graveyards away from the habitation area.
- Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Some types of Megalith structures are given below:
- Menhir: Menhir is the name used in Western Europe for a single upright stone erected in prehistoric times which is sometimes called a “standing stone”.

- Stone circles: A stone circle is a ring of standing stones. They are usually grouped in terms of the shape and size of the stones, the span of their radius, and their population within the local area’s

- Dolmen: A Dolmen is a megalithic form created by placing a large capstone on two or more support stones creating a chamber below, sometimes closed in on one or more sides. It is often used as a tomb or burial chamber.

- Cist: A Cist is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Burials are megalithic forms very similar to dolmens in structure. These type of burials were completely underground. There were single- and multiple-chambered cists.

4. GOLD AND COPPER SULPHIDE HYBRID NANOPARTICLES
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed hybrid nanoparticles, a new approach to potentially detect and kill cancer cells, especially those which form a solid tumour mass as per a study published in ACS Applied Nano Materials.
GOLD AND COPPER SULPHIDE HYBRID NANOPARTICLES:
- Scientists have created hybrid nanoparticles made of gold and copper sulphide, which can kill cancer cells using heat, and enable their detection using sound waves.
- Copper sulphide nanoparticles have previously received attention for their application in cancer diagnosis.
- Gold nanoparticles can be chemically modified to target cancer cells which have shown anticancer effects.
- In the current study, the IISc team decided to combine these two into hybrid nanoparticles.
- These particles have photothermal, oxidative stress, and photoacoustic properties.
HOW IT WORKS?
- When light is shined on these hybrid nanoparticles, they absorb the light and generate heat, which can kill cancer cells.
- These nanoparticles also produce singlet oxygen atoms that are toxic for the cancer cells.
- Both these mechanisms are needed to kill the cancer cells.
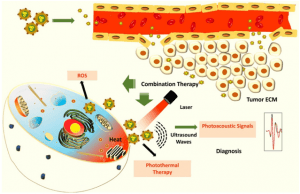
HOW CAN IT HELP OTHER EXISTING TECHNOLOGIES?
- Nanoparticles can also help diagnose certain cancers. Existing methods such as standalone CT and MRI scans require trained radiology professionals to decipher the images.
- The photoacoustic property of the nanoparticles allows them to absorb light and generate ultrasound waves, which can be used to detect cancer cells with high contrast once the particles reach them.
- The ultrasound waves generated from the particles allow for a more accurate image resolution as sound waves scatter less when they pass through tissues compared to light.
- Scans created from the generated ultrasound waves can also provide better clarity and can be used to measure the oxygen saturation in the tumour, boosting their detection.
- Nanoparticles can integrate with existing systems of detection or treatment.
- For example, the nanoparticles can be triggered to produce heat by shining a light on them using an endoscope that is typically used for cancer screening.
5. DROUGHT
TAG: GS 3: DISASTER MANAGEMENT; GS 3: AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: As per the Drought Early Warning System (DEWS), 30 per cent land area in India was under different degrees of drought in the first week of September 2023, worsening crop failure troubles for farmers and increasing food security concerns.
EXPLANATION:
- According to the data by DEWS, 11.5 per cent area was under ‘severe’, ‘extreme’ and ‘exceptional’ dry conditions, while 18.9 per cent was under ‘abnormal’ to ‘moderate’ dry conditions.
- DEWS is India’s first real-time drought-monitoring platform run by IIT Gandhinagar’s Water and Climate Lab.
- August 2023 was the driest August since 1901.
- The country received only about 162 millimetres of rainfall in the month of the August, instead of the expected 255 mm — a deficiency of 36 per cent.
- The drought has increased troubles for farmers:
- It delayed sowing in June and July because of low rainfall.
- Farmers have to face crop failures and a decrease in crop output because of increase in the evapotranspiration rates.
Standardised Soil Moisture Index (SSI):
- The Standardised Soil Moisture Index (SSI) showed that many districts are facing extreme stress of which maximum districts lie in the states of Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
- SSI represents soil moisture drought.
- SSI is an indication of the water that is available to plants.
- Some of the worst affected districts experiencing soil moisture stress are Satara, Raigad, Nashik, and Kohlapur in Maharashtra, West Nimar in Madhya Pradesh, Balangir in Odisha, Korba and Raigarh in Chhattisgarh, Hazaribagh in Jharkhand, Chandauli and Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, Murshidabad and Hugli in West Bengal, Udupi and Chikkamagaluru in Karnataka, Ernakulam and Thrissur in Kerala.
Standardised soil moisture index (as on September 6, 2023)
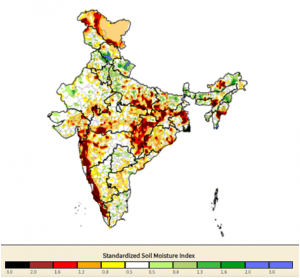
The yellow to red colours on the map show the degree of deviations from the historic mean soil moisture.
Standardised Precipitation Index (SPI):
- It is used to show meteorological drought, based on rainfall data.
- It highlighted a substantial increase in rainfall deficit in the northern, western and central parts of the country in the month of August.
Standardised precipitation index (as on September 6, 2023)
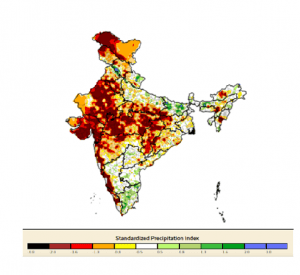
- The overall drought condition has been worsening in the last three months.
- While 22.1 per cent land area was under drought in June, it increased to 24.4 per cent on August 7, 28.8 per cent on August 30 and 30.4 per cent on September 6, 2023.




