1. PADMA AWARDS
TAG: GS 1: ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: The last date for online nominations for the Padma Awards 2024 is 15th September, 2023. Padma Awards will later be announced on the occasion of Republic Day in 2024.
EXPLANATION:
- The Padma Awards nominations and recommendations will be received online on the Rashtriya Puraskar Portal (https://awards.gov.in). Online nominations were opened on 1st May 2023.
About Padma Awars:
- The Padma Awards are one of the highest civilian honours of India. It is instituted in 1954 and these awards are announced on the occasion of the Republic Day every year.
- The Awards are given in three categories: Padma Vibhushan (for exceptional and distinguished service), Padma Bhushan (distinguished service of higher order) and Padma Shri (distinguished service).
- The Padma Awards are conferred on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee, which is constituted by the Prime Minister every year.
- The Padma Awards Committee is headed by the Cabinet Secretary and includes Home Secretary, Secretary to the President and four to six eminent persons as members.
- The award seeks to recognize ‘work of distinction’ and is given for distinguished and exceptional achievements in various fields where an element of public service is involved.
- All persons without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex are eligible for these Awards. Every citizens can make nominations and recommendations, including self nomination.
- Government servants including those working with PSUs, except doctors and scientists, are not eligible for Padma Awards.

- The award is normally not conferred posthumously. However, in highly deserving cases, the Government could consider giving an award posthumously.
- A higher category of Padma award can be conferred on a person only where a period of at least five years has elapsed since conferment of the earlier Padma award. However, in highly deserving cases, a relaxation can be made by the Awards Committee.
- The awards are presented by the President of India where the awardees are presented a Sanad (certificate) signed by the President and a medallion.
- The recipients are also given a small replica of the medallion, which they can wear during any ceremonial/State functions etc.
- The names of the awardees are published in the Gazette of India on the day of the presentation ceremony.
- The total number of awards to be given in a year (excluding posthumous awards and to NRI/foreigners/OCIs) should not be more than 120.
- The award does not amount to a title and cannot be used as a suffix or prefix to the awardees’ name.
- The Padma Awards has been briefly suspended twice, from July 1977 to January 1980 and from August 1992 to December 1995.
History and Relevance
- The Government of India instituted two civilian awards-Bharat Ratna & Padma Vibhushan in 1954.
- The latter had three classes namely Pahela Varg, Dusra Varg and Tisra Varg. These were subsequently renamed as Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri vide Presidential Notification issued on January 8, 1955.
List of Fields:
The award seeks to recognize works of distinction and is given for distinguished and exceptional achievements/service in all fields of activities/disciplines. An illustrative list of the fields is as under:
- Art (includes Music, Painting, Sculpture, Photography, Cinema, Theatre etc.)
- Social work (includes social service, charitable service, contribution in community projects etc.)
- Public Affairs (includes Law, Public Life, Politics etc.)
- Science & Engineering (includes Space Engineering, Nuclear Science, Information Technology, Research & Development in Science & its allied subjects etc.)
- Trade & Industry (includes Banking, Economic Activities, Management, Promotion of Tourism, Business etc.)
- Medicine (includes medical research, distinction/specialization in Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Sidhha, Allopathy, Naturopathy etc.)
- Literature & Education (includes Journalism, Teaching, Book composing, Literature, Poetry, Promotion of education, Promotion of literacy, Education Reforms etc.)
- Civil Service (includes distinction/excellence in administration etc. by Government Servants)
- Sports (includes popular Sports, Athletics, Adventure, Mountaineering, promotion of sports, Yoga etc.)
- Others (fields not covered above and may include propagation of Indian Culture, protection of Human Rights, Wild Life protection/conservation etc.)
2. WHITE SAMBAR DEER SPOTTED IN CAUVERY WILDLIFE SANCTUARY
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: The presence of a leucistic sambar has been documented in the Sangama range of Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary during studies carried out on leopards by researchers.
EXPLANATION:
- This is the first time a leucistic sambar deer has been spotted in this forest area. A similar deer was spotted at Bandipur Tiger Reserve earlier in 2014.
- This condition is identified as leucistic which is caused due to lack of melanin in body parts. In the condition of albinism, the eyes become pink or red. But in leucistic animals, the eye colour is normal.
- This condition can occur naturally from birth due to a phenotype (a trait of any living being) that may have formed from a defect in the animal’s development.
Sambar deer
- The sambar (Rusa unicolor) is a large deer native to the Indian subcontinent, South China and Southeast Asia.
- It is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 2008.
- Populations have declined substantially due to severe hunting, local insurgency, and industrial exploitation of habitat.

Habitat
- The sambar is distributed in much of South Asia in the slopes of the Himalayas in Nepal, Bhutan and India and in mainland Southeast Asia including Burma, Thailand, Indochina, the Malay Peninsula, Indonesia (Sumatra and Borneo), Taiwan, and South China.
- It inhabits tropical dry forests, tropical seasonal forests, subtropical mixed forests with stands of conifers and montane grasslands, broadleaved deciduous and broadleaved evergreen trees, to tropical rainforests.
Behaviour
- Sambar are nocturnal species and they often congregate near water, and are good swimmers.
- The males live alone for much of the year, and the females live in small herds of up to 16 individuals.
- Like most deer, sambar are generally quiet, although all adults can scream or make short, high-pitched sounds when alarmed. However, they commonly communicate by scent marking and foot stamping.
Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary
- Cauvery wildlife division is spread over three districts, namely, Chamarajanagar, Mandya and Ramanagara.
- The wildlife sanctuary was originally notified in 1987 with an area of about 510 Km². Subsequently it was expanded by adding more forest areas in stages, and its present extent is 1,027 Km².
- Cauvery wildlife division has two sub-divisions, namely, Hanur and Kanakapura sub-divisions, and consists of seven ranges, namely, Kothnur, Hanur, Cowdally, Gopinatham, Halagur, Sangam and Muggur ranges.
- The sanctuary provides a vital link between Bannerghatta National Park in the north and Biligiri Ranganatha Swamy Temple Tiger Reserve and Malai Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary in the south.
- The area is drained by three rivers, namely, Cauvery, Arkavathi and Shimsha, along with their numerous rivulets.
- The forest is primarily of dry deciduous and scrub types, but a wide range of forest types including moist deciduous, semi-evergreen, evergreen, shola, riverine, Hardwickia forest, etc. are encountered at different altitudes.
- Important animals found in the sanctuary are tiger, elephant, leopard, bison, wild dog, sambar, spotted deer, barking deer, sloth bear, wild boar, common langur, bonnet macaque, giant squirrel, honey badger (ratel), chevrotain, kollegal ground gecko, varieties of reptiles and birds, etc.
3. UPI ENABLED ATM
TAG: GS 3: ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: Hitachi Payment Services, a subsidiary of Japan’s Hitachi, has introduced a new UPI enabled ATM in collaboration with the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
EXPLANATION:
- The launch of the ‘UPI ATM’ will mark a significant milestone in banking services by seamlessly integrating the convenience and security of UPI into traditional ATMs.
- This innovative concept is designed to provide quick access to cash even in remote areas of India without the use of debit or credit cards.
- These ATMs will allow customers to make cash withdrawals from bank accounts through the UPI apps. Anyone with a registered UPI app will be eligible for UPI ATM transactions. Both Android and iPhone users will be able these ATMs.
- These UPI-ATMs are also expected to improve security by eliminating the risk of card smikking by scammers and fraudersters.
Features of UPI-ATM
- Compatible with various systems.
- Transactions without the need for a physical card.
- Transaction limit of up to ₹10,000 per transaction is aligned with existing UPI daily limits and issuer bank’s UPI-ATM transaction limits.
- Offers convenience by eliminating the necessity to carry an ATM card for cash withdrawals
How does this work?
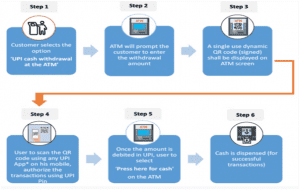
- The UPI-ATM service, also known as Interoperable Cardless Cash Withdrawal (ICCW), offers a convenient way for customers of participating banks who are using UPI to withdraw cash from any ATM that supports UPI-ATM functionality.
- When a customer selects the ‘UPI cash withdrawal’ option at the ATM, they will be prompted to enter the desired withdrawal amount.
- Once the amount is entered, a unique and secure dynamic QR code will appear on the ATM screen.
- To complete the transaction and obtain cash from the ATM, the customer simply needs to scan this QR code using any UPI app and authorize the transaction with their UPI PIN on their mobile device.
How is it different from cardless cash withdrawals offered by banks?
- The current card-less cash withdrawals depend on mobile numbers and OTPs, whereas UPI-ATM functions through QR-based UPI cash withdrawals.
- UPI-ATM is available to individuals using UPI who have installed a UPI application on their Android or iOS smartphones.
- To conduct transactions, users need to have a UPI application installed on their Android or iOS mobile devices.
National Payments Corporations of India (NPCI)
- It is an umbrella organisation launched in 2008 by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- The NPCI, owned by a consortium of banks, is aimed at creating robust payments and settlement systems.
- NPCI is promoted by ten major banks, including the State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Citibank, Bank of Baroda, and HSBC. In 2016 the shareholding was broad-based to 56 member banks to include more banks representing all sectors.
- The regulatory board of the NPCI, headquartered in Mumbai, includes nominees from the RBI along with nominees from ten core promoter banks.
- Payment systems that the NPCI can operate include National Financial Switch (NFS), Immediate Payment System (IMPS), Aadhaar-enabled Payments System (AEPS) and National Automated Clearing House (NACH).
- NPCI has also launched products including RuPay, Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
4. HEAT INDEX
TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Iran recorded a scorching heat index of 70 degrees Celsius (°C) in the coastal part of the country.
EXPLANATION:
- This is not the first time that Iran is dealing with extreme heat. In July as well, U.S.-based weather observer reported that the Persian Gulf Airport reported a heat index of 66.7 °C.
What is heat index?
- Heat index, also known as apparent temperature, is a measure of how the temperature feels to humans. Relative humidity is an important factor that determines heat index, along with air temperature.
- Heat index is an important indicator for how atmospheric temperatures and humidity impact populations during heat waves.
Heat index calculation
- Hot air can hold more moisture than cold air. Therefore, when temperature rises, the air’s capacity to hold moisture also increases, thus affecting the apparent temperature or heat index.
- Dew point, which is the temperature at which gas is transformed into liquid state, is an important factor in the calculation of heat index.
- In terms of atmospheric moisture, dew point is the temperature at which air cannot hold any more water vapour, and droplets of water begin to form. In heat index 14 °C is taken as the dew point.
- In 2024, India is scheduled to launch its own heat index to quantify the impact of heat on its population and generate impact-based heat wave alerts for specific locations.
Why is it important to measure heat index?
- High humidity can lead to heat stress, meaning the body is unable to get rid of excess heat. Humans usually maintain a core temperature in the range of 36.1 to 37.2 °C.
- When the body is unable to get rid of excess heat, the heart rate increases due to a rise in core temperature, leading to heat-related exhaustion and rashes, among other symptoms.
- This is why a measure of heat index is more useful than just the temperature to gauge the impact of heat on humans.
5. ASEAN AND THE EAST ASIA SUMMIT
TAG: GS 2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: Prime Minister attended the ASEAN-India and the East Asia summit in Indonesia to discuss the future contours of India’s partnership with the countries in the strategically important region.
EXPLANATION:
- The comprehensive strategic partnership between India and the ASEAN has injected new dynamism into the group’s ties with India. Engagement with ASEAN is an important pillar of India’s ‘Act East’ policy’.
- This year’s theme of ASEAN is ‘’ASEAN Matters: Epicentrum of Growth’’.
- PM emphasised the importance of establishing “a rule-based post-COVID world order and collective particpation towards human welfare and spoke about “free and open Indo-pacific” and amplifying the voice of the global south.
- East Asia Summit forum provides a useful opportunity to deliberate on issues of importance to the region including food and energy security, environment, health, and digital transformation.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- ASEAN is a regional grouping that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- The group has played a central role in Asian economic integration, joining negotiations to form the world’s largest free trade agreement and signing six free trade deals with other regional economies.
- ASEAN Secretariat is located in Indonesia, Jakarta.
- The ASEAN Declaration states that the aims and purposes of the Association are:
(1) to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region (2) to promote regional peace and stability through abiding respect for justice and the rule of law in the relationship among countries in the region and adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter.
Fundamental principles
ASEAN Member Countries have adopted the following fundamental principles in their
relations with one another, as contained in the Treaty of Amity and Cooperation in Southeast
Asia (TAC):
- mutual respect for the independence, sovereignty, equality, territorial integrity, and
- national identity of all nations;
- the right of every State to lead its national existence free from external interference,
- subversion or coercion;
- non-interference in the internal affairs of one another;
- settlement of differences or disputes by peaceful manner;
- renunciation of the threat or use of force; and
- effective cooperation among themselves.
Working of the ASEAN:
- ASEAN is headed by a chair a position that rotates annually among member states and is assisted by a secretariat based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Important decisions are usually reached through consultation and consensus guided by the principles of noninterference in internal affairs and peaceful resolution of conflicts.
History of ASEAN
- It was formed in 1967, by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand, who sought to create a common front against the spread of communism.
- In 1976, the members signed the Treaty of Amity and Cooperation in Southeast Asia which emphasizes mutual respect and noninterference in other countries’ affairs.
- Membership doubled by the end of the 1990s. With the addition of Brunei (1984), Vietnam (1995), Laos and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999), the group started to launch initiatives to boost regional cooperation.
- In 2007, the ten members adopted the ASEAN Charter, a constitutional document that provided the grouping with legal status and an institutional framework. The charter enshrines core principles and delineates requirements for membership.
- The charter laid out a blueprint for a community made up of three branches: the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), the ASEAN Political-Security Community, and the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community.
East Asia Summit (EAS)
- The EAS was established in 2005 as an Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)-led initiative.
- The East Asia Summit (EAS) is a regional forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian, Southeast Asian, South Asian and Oceanian regions, based on the ASEAN Plus Six mechanism. Membership expanded to 18 countries including Russia and the United States at the Sixth EAS in 2011.
- The EAS comprises 18 members: the 10 ASEAN countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) and eight dialogue partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia and the United States)
- The EAS is the only leader-led forum in the Indo-Pacific that brings together all key partners to discuss political, security and economic issues of strategic importance.
- Since its establishment, ASEAN has held the central role and leadership in the forum. EAS meetings are held after the annual ASEAN leaders’ meetings, and plays an important role in the regional architecture of Asia-Pacific.
- The EAS has six priority areas of cooperation: environment and energy; education; finance; global health issues and pandemic diseases; natural disaster management; and ASEAN connectivity.




