1. LANDSLIDE IN UTTARAKHAND
TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY; GS 3: DISASTER MANAGEMENT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, landslide hit the state of Uttarakhand in the Langha Jakhan village of Vikasnagar tehsil in Dehradun district.
EXPLANATION:
- Incessant rain has been lashing various parts of the hill state, causing landslides that demolished buildings and flooding rivers and streams whose swirling waters swept away people in separate incidents.
- Landslide in Uttarakhand disrupted livelihoods, cause lossof human lives and damages to property and infrastructure.
- Meanwhile, State Disaster Response Force personnel have safely evacuated pilgrims stranded since Monday on the trek route to Madmaheshwar temple following a bridge collapse in rain-hit Uttarakhand’s Rudraprayag district.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecasted substantial rainfall in the mountainous regions of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand over the next four days.
What is a Landslide?
- A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope. Landslides are a type of “mass wasting,” which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
- The term “landslide” encompasses five modes of slope movement: falls, topples, slides, spreads, and flows.
- These are further subdivided by the type of geologic material (bedrock, debris, or earth). Debris flows (commonly referred to as mudflows or mudslides) and rock falls are examples of common landslide types.
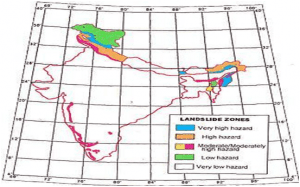
- A general landslide hazard map of India shown here marks the areas of different hazard zones in various states of India where Himalayas of Northwest and Northeast India and the Western Ghats are two regions of high vulnerability and are landslide prone.
- NDMA guidelines are being followed for Landslide Hazard Zonation (LHZ) maps at 1: 50,000 scale and progressively larger scales for specific areas.
Causes of landslides:
Landslides occur when masses of rock, earth, or debris move down a slope. Debris flows, also known as mudslides, are a common type of fast-moving landslide that tends to flow in channels. Landslides are caused by disturbances in the natural stability of a slope.
Natural causes:
- Earthquake: When earthquakes occur on areas with steep slopes, many times the soil slips causing landslides. Furthermore, ashes debris flows caused by earthquakes can also trigger mass movement of soil.
- Heavy rainfall: When sloped areas become completely saturated by heavy rainfall many times landslides can occur. Without the aid of mechanical root support the soil simply runs off when it contains too much water.
Human causes:
- Clear cutting of forest: Method of timber harvesting which completely removes all old growth timber from the area. This method is hazardous because it destroys the existing mechanical root structure in the area.
- Mining: Mining operations that use blasting techniques often cause other areas that are at the risk of sliding to slide due to vibrations under the soil.
Government Initiatives for landslide management:
- The Landslide Hazard Atlas of India containing small scale maps was published jointly by the Building Materials and Technology Promotion Council (BMTPC) and Anna University in 2004.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) was given the responsibility of nodal agency for LHZ and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Ministry of Environment and Forests and climate change (MoEFCC) were identified as nodal agencies for the remaining two task forces, respectively.
- In June 2009, the National Disaster Management Authority released the Guidelines on Management of Landslides and Snow Avalanches, laying down national policy for the management of landslides and related activities in the country.
2. COMPETITION COMMISSION OF INDIA (CCI)
TAG: GS 2: GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has slapped a fine of Rs 40 lakh on Axis Bank for failing to notify the regulator about its acquisition of a stake in CSC e-Governance.
EXPLANATION:
- The transaction under consideration comprised acquisition of a 9.91 per cent stake in CSC e-Governance by Axis Bank and got completed in November 2020.
- For the transaction, Axis Bank was required to give notice to the fair-trade regulator. However, it failed to do so.
- It is apparent that the acquisition of stake in CSC e-Governance by Axis Bank was neither solely as an investment nor can be considered to be in ordinary course of business.
- Therefore, the Axis-CSC e-Governance acquisition is not eligible for the benefit of the Item 1 of Schedule I (combination regulation) and accordingly, it is immaterial whether the transaction led to acquisition of control or not.
- To avail the benefit of combination rules, the acquirer should not be a member of the board of directors, does not have a right to nominate a director and should not participate in the affairs or management of the enterprise whose shares or voting right are being acquired.
- CSC e-Governance Services India Ltd is a special-purpose vehicle set up by the electronics and information technology ministry to oversee the implementation of the common services centre scheme.
Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- Competition Commission of India (CCI) is the chief national competition regulator in India.
- It is a statutory body within the Ministry of Corporate Affairs and is responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002.
- It aims to promote competition and prevent activities that have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in India. The CCI looks into cases and investigates them if the same has a negative impact on competition.
Objectives of CCI:
- Make the markets work for the benefit and welfare of consumers.
- Ensure fair and healthy competition in economic activities in the country for faster and inclusive growth and development of the economy.
- Implement competition policies with an aim to effectuate the most efficient utilization of economic resources.
- Develop and nurture effective relations and interactions with sectoral regulators to ensure smooth alignment of sectoral regulatory laws in tandem with competition law.
- Effectively carry out competition advocacy and spread the information on benefits of competition among all stakeholders to establish and nurture competition culture in Indian economy.
3. OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY
TAG: GS 3: ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: The Union ministry of new and renewable energy has sought bids to survey sites identified for offshore wind power projects in Tamil Nadu.
EXPLANATION:
- A notification released by the ministry showed that the government plans to bid out projects of 4GW capacity on 1 December. Further, in the next financial year, it plans to bid out projects with a total capacity of 3GW.
- The government will bid out sites for offshore wind power projects through two models.
- In one model, the government will provide viability gap funding, and in the other, identified offshore wind sites will be leased out under competitive bidding for carrying out studies and surveys and subsequent project development without any central financial assistance.
- The bids for the study of the sites have been called for the second model where financial support is not available.
- Under this model, sites are proposed to be allocated for a period of two years to carry out the survey.
- The government may also call for bids for procurement of power for distribution companies based on tariffs after two years.
- Although the government notified the national offshore wind energy policy in 2015, and efforts have been on to establish the sector in the country, the sector has not taken off as anticipated.
- To boost investments in this space, the Union power ministry in May announced a waiver of Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) charges on the transmission of electricity generated via offshore wind sources.
OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY IN INDIA
- India is blessed with a coastline of about 7600 km surrounded by water on three sides and has good prospects of harnessing offshore wind energy.
- The wind resources assessment carried out by the National Institute of Wind Energy shows India’s total wind energy potential at 302GW at 100m and 695.50GW at 120m hub height.
- Out of the total estimated potential, more than 95% of commercially exploitable wind resources are concentrated in seven states—Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
- Considering this, the Government had notified the “National offshore wind energy policy” as per the Gazette Notification dated 6th October 2015.
- As per the policy, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy will act as the nodal Ministry for development of Offshore Wind Energy in India.
- It will work in close coordination with other government entities for Development and Use of Maritime Space within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the country and shall be responsible for overall monitoring of offshore wind energy development in the country.
- National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE), Chennai will be the nodal agency to carryout resource assessment; surveys and studies in EEZ demarcate blocks and facilitate developers for setting up offshore wind energy farms.
- India has extensive experience with onshore wind turbines, with an installed capacity of more than 30 gigawatts. As part of its efforts to mitigate climate change, the country has decided to utilize offshore wind energy as well.
- India’s plan is a call for 5,000 megawatts of offshore wind by 2022, and 30,000 megawatts by 2030.
- Offshore wind is an important component of India’s plan to install 500GW of renewable capacity by 2030 and to achieve its target of reaching net zero by 2070.
4. BA.2.86: A NEW VARIANT OF THE CORONAVIRUS
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The World Health Organization (WHO) and the United States centre for Disease Control and Prevention are monitoring a new variant of the coronavirus, BA.2.86, also known as BA.X.
EXPLANATION:
- It has been detected in the U.S., the U.K., Denmark, and Israel.
- Over 1.4 million new COVID-19 cases and 2,300 deaths were reported from WHO’s six regions in the period of 28 days (July 17 to August 13, 2023).
- Reported cases do not accurately represent infection rates due to the reduction in testing and reporting globally.
- But the potential impacts of the BA.2.86 mutations are presently unknown and undergoing careful assessment.
- The United States federal agency Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is monitoring the lineage.
- WHO monitors the different COVID variants under three categories.
- variant under monitoring (VUM)
- variant of interest (VOI)
- variant of concern (VOC)
- WHO has classified BA.2.86 as a VUM.
- A “variant under monitoring” is a strain with genetic changes that could affect its characteristics like transmissibility, but that limited evidence makes its impact unclear, WHO has classified BA.2.86 as a VUM.
SOME NEW CORONAVIRUS VARIANTS
- 5:
- It is a descendent of the Omicron lineage of XBB.1.9.2.
- It was designated as VOI after risk evaluation by the World Health Organization. It was previously designated as VUM.
- 5 was first reported on February 17, 2023, and it has been reported from a total of 48 countries and in India, one EG.5.1 was detected in Maharashtra in May, 2023.
- 1.5:
- It is derived from the 2 Omicron subvariant and the most contagious variant of the virus causing COVID-19.
- The XBB.1.5 subvariant has a mutation that can become more transmissible.
- IT IS DESIGNATED AS variant of interest (VOI)
- It was reported in dec 2022, and it has been detected in 28 other countries worldwide.
5. 3D PRINTED BUILDINGS
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: India Inaugurated its first 3D-Printed Post Office in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
EXPLANATION:
- The post office building has been fully developed with the use of 3D printing technology.
- The company Larsen & Toubro Limited undertook the construction while IIT Madras provided technical guidance on the project.
- This new and unique building construction used 3D-concrete printing technology method.
3D Concrete Printing Technology
- It is a fully automated construction technology in which a robotic printer deposits the concrete layer after layer much like a human worker.
- It is also known as additive manufacturing.
- It carries out the construction in accordance with the approved design.
- Special-grade concrete is used in the project because it hardens quickly, ensuring easy and fast bonding between the layers to print the structure.
- Compared to the conventional methods, this technology has completed the construction of entire structure in just 45 days.
- Additive Manufacturing Society of India (AMSI) promotes 3D printing & Additive Manufacturing Technologies in India
- It is helping in the design, R&D organisations, manufacturing professionals and academics in 3D Printing.
- Its applications are Helmets, Dental meds, Jet Engine parts, Cars and Hearing aid and now even a house.
Benefits of 3D Printing Technology
- Contrasting to the traditional machines, it decreases waste and costs (through economy of scale).
- It is appropriate for products with challenging environmental conditions.
- It reduces capital, space required, and carbon footprint and improves customisation.
- Different materials can be mixed during the printing process to create a unique alloy.
- Prototypes can be made quicker allowing designers to check different iterations resulting in a quicker design cycle phase.
- Robust IT infrastructure and increased connectivity will support the Digital India Campaign.
SOURCE: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/everyday-explainers/how-does-3d-printing-work-8898689/
Spread the Word



