HEALTH ISSUES
1. WHAT ARE RARE DISEASES AND WHY IS THEIR TREATMENT SO EXPENSIVE?
TAGS: GS-II HEALTH ISSUES
THE CONTEXT: The central government recently exempted all foods and drugs for rare diseases imported by people for personal use from custom duty. With most therapy for rare diseases priced very high, this will make a significant difference to families of people living with the conditions.
THE EXPLANATION:
What are the drugs that have been exempted from customs duty?
- Medicines and foods needed for the management of 51 rare diseases have been exempt from custom duty, with the government notification stating, “drugs, medicines or food for special medical purposes used for treatment of rare diseases specified.”
- The specified conditions include lysosomal storage disorder (a group of metabolic disorders that lead to a buildup of toxic materials in the cells), maple syrup urine disease (a hereditary condition where the body cannot process the building blocks of proteins resulting in buildup of harmful substances in blood and urine), Severe food protein allergy, Wilson’s disease (a disorder that results in the body accumulating copper) among others.
- These medicines usually attract a basic custom duty of 10 per cent, with some vaccines or medicines attracting a lower 5 per cent or nil as previously notified. Medicines for the treatment of spinal muscular athrophy and duchenne muscular dystrophy were already exempt from customs.
What are rare diseases?
- Rare diseases as the name suggests are conditions that affect very few people. The World Health Organisation defines it as any debilitating lifelong disease or disorder with a prevalence of ten or less per 10,000 population; other countries follow standards ranging between 1 and 10 cases per 10,000 to define a condition as rare disease.
- There are about 7,000 to 8,000 conditions globally that have been defined as rare diseases. The landscape of rare diseases keeps changing, with newer conditions being identified and reported constantly.
Why are drugs for rare diseases so expensive?
- Even though there have been developments in the treatment of rare diseases in the recent year, almost 95 per cent of the conditions do not have specific treatment.
- With a very small number of people suffering each of the 7,000- 8,000 rare conditions, they do not make a good market for drugs. This is the reason most pharmaceutical companies are reluctant to spend on research for treatments of the disease. This is the reason the medicine for rare conditions that do exist are known as “orphan drugs” and are prohibitively priced to recoup the cost of research and development.
- As per the National Rare Disease Policy, treatment for some rare disease can vary from Rs 10 lakh to 1 crore per year for a child weighing 10 kgs. The treatment has to be continued lifelong, with the costs going up along with the age and weight of the person.
- “At present, very few pharmaceutical companies are manufacturing drugs for rare diseases globally and there are no domestic manufacturers in India”.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
2. DEEP SEA MINING
TAGS: GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY- PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT:The UN’s decision to take deep-sea mining applications comes when there is no mining code in place. Several countries have insisted that industrial undersea mining should require strict rules.
THE EXPLANATION:
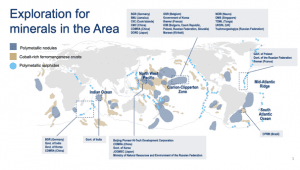
- Recently, the International Seabed Authority has decided that it will start taking permit applications in July from companies that want to mine the ocean’s floor.
- The undersea mining will be conducted to extract key battery materials — cobalt, copper, nickel, and manganese — from potato-sized rocks called “polymetallic nodules” found at depths of 4 kilometers to 6 kilometers (about 2.5 miles to 3.7 miles).
- The Jamaica-based ISA was established under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea. It holds authority over the ocean floors outside of its 167 member states’ Exclusive Economic Zones.
What is Deep Sea Mining?
- Deep-sea mining is the process of retrieving mineral deposits from the deep seabed – the ocean below 200m.
- Depleting terrestrial deposits and rising demand for metals mean deep-sea mining may begin soon, even though research suggests that it could destroy habitats and wipe out species.
- Deep-sea mining should be halted until the criteria specified by IUCN are met, including the introduction of assessments, effective regulation and mitigation strategies.
- Comprehensive studies are needed to improve our understanding of deep-sea ecosystems and the vital services they provide to people, such as food and carbon sequestration.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
3. WHAT IS MANUFACTURING PURCHASING MANAGERS’ INDEX (PMI)?
TAGS: GS-III- ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: According to S&P Global India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) New orders and output rose to a three-month high in March (2023) even as input cost inflation for manufacturing firms slipped to the second-lowest mark in two-and-a-half years.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The PMI reading rose to 56.4, from 55.3 in February, signalling the strongest improvement in operating conditions in 2023 so far. The PMI average for the January-March period was 55.7, lower than 56.3 in the previous quarter. New export orders grew at a faster pace in March than the previous month, but remained “slight and historically subdued.”
What is a PMI?
- PMI or a Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is an indicator of business activity — both in the manufacturing and services sectors. It is a survey-based measures that asks the respondents about changes in their perception of some key business variables from the month before. It is calculated separately for the manufacturing and services sectors and then a composite index is constructed.
How is the PMI derived?
- The PMI is derived from a series of qualitative questions. Executives from a reasonably big sample, running into hundreds of firms, are asked whether key indicators such as output, new orders, business expectations and employment were stronger than the month before and are asked to rate them.
How does one read the PMI?
- A figure above 50 denotes expansion in business activity. Anything below 50 denotes contraction. Higher the difference from this mid-point greater the expansion or contraction. The rate of expansion can also be judged by comparing the PMI with that of the previous month data.
- If the figure is higher than the previous month’s then the econ-omy is expanding at a faster rate. If the figure is higher than the previous month’s then the econ-omy is expanding at a faster rate. If it is lower than the previous month then it is growing at a lower rate.
What are its implications for the economy?
- The PMI is usually released at the start of the month, much before most of the official data on industrial output, manufacturing and GDP growth becomes available.
- It is, therefore, considered a good leading indicator of economic activity. Economists consider the manufacturing growth measured by the PMI as a good indicator of industrial output, for which official statistics are released later.
- Central banks of many countries also use the index to help make decisions on interest rates.
4. WHAT ARE ELECTORAL BONDS?
THE CONTEXT: The government recently announced the 26th tranche of electoral bond sales to be undertaken over a ten-day window at all authorized branches of the State Bank of India.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Electoral Bonds:
- The electoral bond scheme was launched by the Union government in 2018.
- It is a bearer instrument, like a promissory note that can be bought by any Indian citizen or company incorporated in India.
- The citizen or corporate can then donate the same to any eligible political party of his/her choice.
- The bonds are similar to bank notes that are payable to the bearer on demand and are free of interest.
- An individual or party is allowed to purchase these bonds digitally or through cheque.
Process:
- EBs are issued/purchased for any value, in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 1,00,000, Rs 10,00,000 and Rs 1,00,00,000.
- The electoral bonds are available for purchase for 10 days at the beginning of every quarter.
- SBI is the only bank authorized to sell these bonds.
- Anonymous cash donations were capped at Rs 2,000.
- EBs have a life of only 15 days during which it can be used for making donations to political parties.
Eligibility:
- Only political parties registered under Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 and which secured not less than 1% of votes polled in the last general election to the House of the People or the Legislative Assembly of the State, are eligible to receive electoral bonds.
- The bond can be encashed by an eligible political party only through a designated bank account with the authorized bank.
- The political parties have to disclose the amount to the Election Commission.
- The electoral bonds will not bear the name of the donor.
MISCELLANEOUS
5. WHAT IS SARBAT KHALSA?
TAGS: MISCELLANEOUS
THE CONTEXT: The Sarbat Khalsa, a term meaning “all congregation,” refers to a traditional assembly of all factions of Sikhs (Khalsa) to discuss political, social, and religious issues of great importance to the community. The idea of a deliberative assembly of Sikhs originated in the 18th century and was convened twice a year.
THE EXPLANATION:
Origins and Significance of Sarbat Khalsa
- The word “sarbat” means all, and the Sarbat Khalsa was an assembly where all members of the Khalsa were represented. It was a democratic institution where members could participate in decision-making. The assembly was called at times of crisis and was considered the supreme authority in the Sikh community.
- During the Mughal period, Zakarya Khan, the governor of Lahore, offered the title of Nawab to the Sikhs as a reward for their services. The Sikhs, however, refused to accept the title and instead called for a Sarbat Khalsa to discuss the issue. This marked the beginning of the tradition of calling the Sarbat Khalsa.
- The tradition continued during the period of the Sikh misls, which were essentially confederacies of Sikh chiefdoms. However, after the establishment of the Sikh kingdom by Maharaja Ranjit Singh in 1799, the need for an institution like the Sarbat Khalsa was reduced with the formation of the SGPC.
Sarbat Khalsa in Modern Times
- The Sarbat Khalsa was called in 1920 to discuss control over gurdwaras, and again in 1984 after the Indian Army’s Operation Blue Star in the Golden Temple. In 1986, a panthic committee was formed that gave a call for Khalistan.
- The Sarbat Khalsa was called again on November 10, 2015, by Sikh bodies opposed to the Shiromani Akali Dal (Badal). The gathering attracted a large number of Sikhs from all over the world, and its impact on Punjab politics was significant. It led to a demand for a separate Sikh state, the revival of the demand for the release of Sikh prisoners, and the establishment of a parallel committee to the SGPC




