POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. SPECIAL CATEGORY STATUS
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-II- POLITY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Union Finance Minister announced that the Centre will not consider the demands for “special category status “ for any states.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Special Category Status :
- It is a classification given by the Centre to assist development of states that face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages.
- Under this, the Central government extends financial assistance to states that are at a comparative disadvantage against others.
- There is no provision of SCS in the Constitution of India.
- The concept emerged in 1969 with the approval of the Gadgil formula in the Fifth Finance Commission in 1969.
The parameters required for Special Category Status:
- Must be economically backward with poor infrastructure.
- The states must be located in hilly and challenging terrain.
- They should have low population density and significant tribal population.
- Should be strategically situated along the borders of neighboring countries.
- First SCS was accorded in 1969 to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland.
- The 14th Finance Commission has done away with the ‘special category status’ for states, except for the North-eastern and three hill states.
- Presently, eleven states have the Special Category Status in the country including Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Uttarakhand, and Telangana.
Benefits to States with SCS:
- The Centre pays 90% of the funds required in a centrally-sponsored scheme to special category status states as against 60% or 75% in case of other states, while the remaining funds are provided by the state governments.
- Preferential treatment in getting central funds.
- 30 percent of the Centre’s gross budget also goes to special category states.
- Unspent money does not lapse and is carried forward.
- Significant concessions are provided to these states in excise and customs duties, income tax and corporate tax.
- These states can avail the benefit of debt-swapping and debt relief schemes.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
2. INVESTOR EDUCATION AND PROTECTION FUND AUTHORITY (IEPFA)
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-I
THE CONTEXT: The IEPFA is seeking applications from young students and scholars for its short-term internship programme which began recently.
THE EXPLANATION:
About IEPFA:
- IEPF is a statutory body under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, established under the Companies Act 2013.
- It administers the Investor Education and Protection Fund.
- IEPF Authority has undertaken a proactive approach to achieve its mandate of promoting investor education, awareness and protection.
- Its objective is to promote Investor Education, Awareness, and Protection.
- The Amounts credited to IEPF are maintained under the Consolidated Fund of India (Article 266 of the Constitution).
Composition:
- Secretary Ministry of Corporate Affairs is the Chairperson of the Authority.
- The Joint Secretary Ministry of Corporate Affairs is the Chief Executive Officer of the Authority.
- The Authority is entrusted with the responsibility of administration of the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF), make refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc. to investors and to promote awareness among investors.
- The Authority has taken a 360 degree approach to sensitize stakeholders to include household investors, housewives, professionals, etc. across the country in rural and urban areas through direct investor awareness programmes, media campaign and engaging with other stakeholders with the common goal.
- In the urban and semi-urban areas the Authority organizes investor awareness programmes in association with the Institute of charted Accountants of India, Institute of Cost Accountants of India and Institute of Company Secretaries of India.
- In the rural areas the programmes are organised in collaboration with CSC e-governance Services Private Limited through the Common Service Centre (CSC’s) located in villages.
- Multilingual Information, Education and Communication booklets and films have been developed for creating awareness.
- A Joint Awareness campaign has been launched in association with Reserve Bank of India, Securities and Exchange Board of India & Department of Consumer Affairs.
The IEPF is to be utilized for :
• The refund of unclaimed dividends , matured deposits, debentures , application money due for refund and interest thereon.
• Promotion of investor’s education, awareness and protection.
• Distribution of any disgorged amount among eligible and identifiable applicants for shares or debentures , shareholders, debenture-holders or depositors who have suffered loss due to wrong actions by any one person , in accordance with the ordered made by the court which had ordered disgorgement.
3. SPECIAL RUPEE VOSTRO ACCOUNTS
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, government of India informed that Russian banks have opened Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVA) with partner banks in India.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVA):
- The SRVA is an additional arrangement to the existing system that uses freely convertible currencies.
- It works as a complimentary system to facilitate transactions that cannot be executed through the existing banking setup.
About Vostro Accounts: - A Vostro account is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency.
- In this, a foreign bank acts as an agent providing financial services on behalf of a domestic bank.
- It enables domestic banks to provide international banking services to their clients who have global banking needs.
- Domestic banks use Vostro accounts to facilitate transfers, conduct business transactions, accept deposits, and gather documents on behalf of the foreign bank.
Significance:
- The system could reduce the “net demand for foreign exchange, the U.S. dollar in particular, for the settlement of trade flows”
- It will reduce the dependence on foreign currencies.
- It can make the country less vulnerable to external shocks.
- Ensure timely payments.
- This helps domestic banks to gain wider access to foreign financial markets and serve international clients without having to be physically present abroad.
- Vostro accounts are not restricted to banks, they can be used by other entities such as insurance companies and business entities to keep funds with another entity.
- When Vostro accounts are used by corresponding banks, the domestic bank can execute transfers, deposits, and withdrawals on behalf of the corresponding bank.
Functioning :
- The framework entails three important components, namely, invoicing, exchange rate and settlement.
- Invoicing entails that all exports and imports must be denominated and invoiced in INR.
- The exchange rate between the currencies of the trading partner countries would be market-determined.
- The final settlement also takes place in Indian National Rupee (INR).
- Domestic importers are required to make payment in INR into the SRVA account of the correspondent bank against the invoices.
- Domestic exporters are to be paid the export proceeds in INR from the balances in the designated account of the correspondent bank of the partner country.
Legal framework:
- All reporting of cross-border transactions are to be done in accordance with the extant guidelines under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
Eligibility criteria of banks:
- Banks from partner countries are required to approach an authorised domestic dealer bank for opening the SRVA.
- The domestic bank would then seek approval from the apex banking regulator providing details of the arrangement.
- Domestic banks should ensure that the correspondent bank is not from a country mentioned in the updated Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Public Statement on High Risk & Non-Co-operative jurisdictions.
- Authorised banks can open multiple SRV accounts for different banks from the same country.
- Balances in the account can be repatriated in freely convertible currency and/or currency of the beneficiary partner country depending on the underlying transaction, that is, for which the account was credited.
There are 3 types of accounts : Vostro, Nostro and Loro Accounts
1. Vostro accounts -are maintained in the domestic currency.
2. Nostro accounts- are maintained in foreign currency.
3. A Loro account -is a current account that is maintained by one domestic bank for another domestic bank in the form of a third-party account, unlike nostro and vostro which is bilateral correspondence.
The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA):
- It is a civil law dealing with foreign exchange market in India.
- Under it the Central Government can regulate the flow of payments to and from a person situated outside the country.
- Financial transactions concerning foreign securities or exchange cannot be carried out without the approval of FEMA.
- The Act empowers RBI to place restrictions on transactions from capital Account even if it is carried out via an authorized individual.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
4. GLOBAL ASSESSMENT OF SOIL CARBON IN GRASSLANDS
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III- ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the FAO(Food and Agricultural Organization) published its first Global Assessment of Soil Carbon in Grasslands.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The study found that if the SOC content in the 0–30 cm depth layer of available grasslands increased by 0.3 percent after 20 years of the application of management practices that enhance soil organic carbon sequestration, 0.3 tonnes C/ha per year could be sequestered.
- Grasslands contain approximately 20 percent of the world’s SOC
- Grasslands have suffered losses because of human activities such as intensive livestock grazing, agricultural activities, and other land-use activities.
- Most of the world’s grasslands have a positive carbon balance, meaning the land is stable or well-maintained.
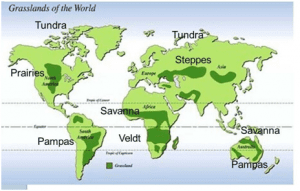
About Grasslands:
- Grasslands are areas dominated by grasses.
- Distribution: Grasslands are found in areas having well-defined hot and dry, warm and rainy seasons.
- Grasslands can majorly be divided into two parts:
- Tropical Grasslands – Savannah, Campos, and Llanos
- Temperate Grasslands- Pampas, Prairie, Veld, Steppe, and Down.
Significance of Grasslands :
- Farmers who keep cattle or goats, as well as shepherds who keep sheep, are highly dependent on grasslands.
- Domestic animals are grazed in the ‘common’ land of the village.
- Fodder is collected and stored to feed cattle when there is no grass left for them to graze in summer.
- The grass is also used to thatch houses and farm sheds.
- The thorny bushes and branches of the few trees that are seen in grasslands are used as a major source of fuelwood.
- Nutrient cycling (biogeochemical cycles)
- Ecological succession or ecosystem development
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. SURVEY OF INDIA
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Centre officially released the National Geospatial Policy of India which allows any private agency to make high-resolution maps.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Survey of India:
- Survey of India, The National Survey and Mapping Organization of the country under the Department of Science & Technology.
- It is the oldest scientific department of the Indian government.
- It was established in 1767 to help consolidate the Indian territories of the British East India Company.
- Its assigned role as the nation’s Principal Mapping Agency.
- It is headquartered in Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- It is India’s principal mapping agency and functions under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India.
- It provides base maps for expeditious and integrated development of the country by ensuring that all resources contribute to the progress, security, and prosperity of the nation for the present and the future.
- It is headed by the Surveyor-General of India.


