GOVERNANCE
1. NHA INITIATIVE TO GRADE HOSPITALS
TAGS: GS-II- GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: The National Health Authority (NHA) in India is introducing a new system to measure and grade hospital performance under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) scheme, with the goal of shifting the focus of hospital performance measurement from the volume of services provided to the value of healthcare services.
THE EXPLANATION:
The new initiative will introduce the concept of “value-based care,” where payment will be outcome-based and providers will be rewarded based on the quality of treatment they deliver.
Shift from Quantity to Quality
- Traditionally, the healthcare model has been focused on the quantity of services delivered, with case-based bundled payments made on the basis of the number of services provided.
- Under the new value-based care model, providers will be rewarded for helping patients improve their health, which will ultimately reduce the effects of disease in the population in the long term.
- This shift promises significant increases in overall health gains and is expected to benefit all stakeholders, from patients to healthcare providers, payers, and suppliers.
Measures Taken by NHA to Ensure Quality Care
- To ensure that PM-JAY beneficiaries receive both cashless healthcare benefits and high-quality care at every empaneled hospital, the NHA has implemented various measures.
- These measures include standardizing the cost of treatment under the scheme and adding new and advanced treatment procedures. Additionally, the NHA has made provisions to incentivize the best performing hospitals that provide quality care to patients.
Performance Indicators and Public Dashboard
- Under the value-based care system, the performance of AB PM-JAY empaneled hospitals will be measured based on five performance indicators:
- Beneficiary Satisfaction;
- Hospital Readmission Rate;
- Out-of-Pocket Expenditure;
- Confirmed Grievances; and
- Improvement in Patient’s Health-Related Quality of Life.
- The performance of hospitals based on these indicators will also be made available on a public dashboard, allowing beneficiaries to make informed decisions about their healthcare. This will not only determine the financial incentives of hospitals, but also create a demand for quality treatment among PMJAY beneficiaries.
Connect the dots:
- Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- NATIONAL HEALTH MISSION
HEALTH ISSUES
2. AFRICAN SWINE FLU
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-II-HEALTH ISSUES
THE CONTEXT:Amid the outbreak of African swine fever in wild boars in Mudumalai (Tamil Nadu) and Bandipur (Karnataka) Tiger Reserves, the sale of pork has been banned in the picturesque Nilgiris, a hill district in western Tamil Nadu.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The authorities have imposed a ban on transportation of animals or meat outside the Nilgiris, which boasts scenic tourist destinations including Ooty (Udhagamandalam), Coonoor and Gudalur.
- The Mudumalai Tiger Reserve in the district is contiguous with the Bandipur Tiger Reserve in neighbouring Karnataka.
What is African swine fever?
- African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious viral disease of domestic and wild pigs, whose mortality rate can reach 100%.
- It is not a danger to human health, but it has devastating effects on pig populations and the farming economy. There is currently no effective vaccine against ASF.
- The virus is highly resistant in the environment, meaning that it can survive on clothes, boots, wheels, and other materials. It can also survive in various pork products, such as ham, sausages or bacon. Therefore, human behaviours can play an important role in spreading this pig disease across borders if adequate measures are not taken.
African swine fever: a socio-economic burden and a threat to food security and biodiversity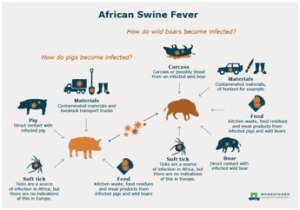
- Pigs are a primary source of household income in many countries. The spread of ASF across the world has devastated family-run pig farms, often the mainstay of people’s livelihoods and a driver of upward mobility. It has also reduced opportunities to access healthcare and education.
- Moreover, pork meat is one of the primary sources of animal proteins, accounting for more than 35% of the global meat intake. Hence, this disease poses a serious problem for food security worldwide.
- This disease is also a concern for biodiversity and the balance of ecosystems, as it affects not only domestic farmed pigs, but also wild boars, including native breeds.
ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
3. BHITARKANIKA NATIONAL PARK
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-III- ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT:According to the Odisha forest department, the Bhitarkanika National Park in Odisha has seen an increase in its bird population in 2023.
THE EXPLANATION:
- In a clear indication that the Bhitarkanika National Park is a congenial spot for attracting birds, the Odisha forest department informed that the number of birds in the national park has increased this year. The staff of the forest department counted 1,39,959 birds this year compared to 1,38,107 last year.
- While the number of bird count increased, the diversity of species has decreased compared to last year. This year the Bhitarkanika National Park saw 140 species of birds compared to 144 last year, however, many rare and endangered species were spotted this time.
- Bhitarkanika National Park is a prime location for birds of different species and is located 130 km from Odisha’s capital Bhubaneswar. The Chilka and Bhitarkanika wetland spots in Odisha are some of the favoured destinations for migratory birds during winter.
VALUE ADDITION:
Bhitarkanika Mangroves Conservation Area
- Bhitarkanika — a notified Ramsar wetland — is spread over 195 sq. km and is home to 62 mangrove species. Besides, 1,600 salt water crocodiles crawl on the mudflats of the Bhitarkanika mangrove forest.
- Bhitarkanika is a unique habitat of Mangrove Forests criss-crossed with numerous creeks and mud flats located in Kendrapara district of Orissa.
- It is one of the largest Mangrove Eco systems in India,Bhitarkanika is home to diverse flora and fauna.
- The Bhitarkanika mangrove conservation area comprises of Bhitarkanika National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary and Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary approximating around 3000 km2 area of which around 4.8% (145 km2 ) area has mangrove cover.
- Mangroves grow in brackish water. Proportionate fresh water flow from the Brahmani river basin and the Kharasrota river keep the salinity level of the water along the shore down. The brackish water becomes ideal for the mangroves to grow and stay healthy.
- The Bhitarkanika National Park, famous for the endangered saltwater crocodiles, has seen an increase of the rare species to 1,671, an annual census conducted by the Forest Department this year has found.

SECURITY AFFAIRS
4. GOVT DESIGNATES CANADA-BASED AARSHDEEP SINGH GILL AS TERRORIST
TAGS: GS-III-INTERNAL SECURITY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a 26-year old resident from Punjab, presently based in Canada has been designated as an “individual terrorist” by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) under the anti-terror law UAPA.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Arshdeep Singh Gill, a resident of Moga in Punjab is associated with Khalistan Tiger Force (KTF), is a banned terrorist organisation.
- MHA said that Gill alias ArshDala is very close to Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a designated terrorist under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) and runs terror modules on the matter’s behalf.
- In a notification, MHA said that Gill is involved in heinous crimes such as murder, extortion and targeted killings besides terror activities, terror financing, cross border smuggling of drugs or weapons in large scale. It added that Gill is accused in various cases registered and investigated by the National Investigation Agency including targeted killing, extorting money for terror funding, attempt to murder, disturbing communal harmony and creating terror among the people in the state of Punjab.
VALUE ADDITION:
The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act, 2019
The Act provides special procedures to deal with terrorist activities, among other things.
- Who may commit terrorism: Under the Act, the central government may designate an organisation as a terrorist organisation if it: (i) commits or participates in acts of terrorism, (ii) prepares for terrorism, (iii) promotes terrorism, or (iv) is otherwise involved in terrorism. The Act additionally empowers the government to designate individuals as terrorists on the same grounds.
- Approval for the seizure of property by NIA: Under the Act, an investigating officer is required to obtain the prior approval of the Director-General of Police to seize properties that may be connected with terrorism. The Act adds that if the investigation is conducted by an officer of the National Investigation Agency (NIA), the approval of the Director-General of NIA would be required for the seizure of such property.
- An investigation by NIA: Under the Act, investigation of cases may be conducted by officers of the rank of Deputy Superintendent or Assistant Commissioner of Police or above. The Act additionally empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases.
- Insertion to schedule of treaties: The Act defines terrorist acts to include acts committed within the scope of any of the treaties listed in a schedule to the Act. The Schedule lists nine treaties, including the Convention for the Suppression of Terrorist Bombings (1997), and the Convention against Taking of Hostages (1979). The Bill adds another treaty to the list. This is the International Convention for Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism (2005).
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. GLASS FROGS
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently scientists gleaned insight into how glassfrogs –a species known for this ability – are able to achieve such transparency.
THE CONTEXT:
THE EXPLANATION: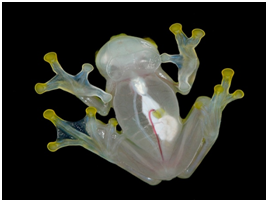
- Glass frogs live in the American tropics and are nocturnal amphibians that spend their days sleeping upside down on translucent leaves that match the colour of their backs — a common camouflage tactic.
- Their translucent skin and muscle allow their bones and organs to be visible – hence the name.
- Recent research has proposed that this adaptation masks the frogs’ outlines on their leafy perches, making them harder for predators to spot.
How do some animals become transparent?
- Transparency is a common form of camouflage among animals that live in water, but rare on land.
- In vertebrates, attaining transparency is difficult because their circulatory system is full of red blood cells that interact with light. Studies have shown that ice fish and larval eels achieve transparency by not producing haemoglobin and red blood cells.
- Glass frogs use an alternative strategy. Resting glass frogs increase transparency two- to threefold by removing nearly 90 percent of their red blood cells from circulation and packing them within their liver, which contains reflective guanine crystals.
- Whenever the frogs need to become active again, they bring the red blood cells back into the blood, which gives the frogs the ability to move around — at which point, light absorption from these cells breaks transparency.




