INDIAN POLITY
1. THE KARNATAKA-MAHARASHTRA BORDER ROW
TAGS:GS-II & III-INTER STATE BORDER DISPUTES
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Karnataka Legislative Assembly, unanimously passed a resolution to protect its interests and called the dispute a “closed chapter”. For that the Maharashtra government retaliated by passing a unanimous resolution in its Assembly to legally pursue the inclusion of 865 Marathi-speaking villages from Belagavi, Karwar, Nipani, Bidar, Bhalki and others in Karnataka into the State.
THE EXPLANATION:
What are the claims of the two States?
- The raging boundary dispute between the two States dates back to the reorganisation of States along linguistic
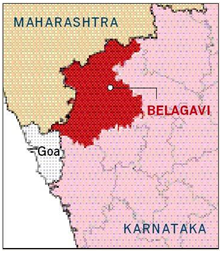 lines. In 1957, unhappy with the demarcation of boundaries, Maharashtra demanded realignment of its border with Karnataka.
lines. In 1957, unhappy with the demarcation of boundaries, Maharashtra demanded realignment of its border with Karnataka. - It invoked Section 21 (2)(b) of the Act, submitting a memorandum to the Union Ministry of Home Affairs stating its objection to Marathi-speaking areas being included in Karnataka. It filed a petition in the Supreme Court staking a claim over Belagavi.
- Karnataka has argued that the inclusion of Belagavi as part of its territory is beyond dispute. It has cited the demarcation done on linguistic lines as per the Act and the 1967 Mahajan Commission Report to substantiate its position.
- Karnataka has argued for the inclusion of areas in Kolhapur, Sholapur and Sangli districts (falling under Maharashtra) in its territory. From 2006, Karnataka started holding the winter session of the Legislature in Belagavi, building the massive Suvarna Vidhana Soudha in the district headquarters to reassert its claim.
What were the terms of the Mahajan Commission?
- In 1966, at Maharashtra’s insistence, the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi established a one-man commission led by Mehr Chand Mahajan, which recommended that 264 villages be transferred to Maharashtra and that Belagavi (Belgaum) and 247 villages remain with Karnataka.
- Maharashtra rejected the report, while Karnataka welcomed it. Karnataka argued that either the Mahajan Commission Report should be accepted fully, or the status quo maintained.
Connect the dots: States Reorganisation Act 1956
2. WHAT IS TRIPLE TEST SURVEY?
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS -II-POLITY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Allahabad High Court ordered the Uttar Pradesh government to hold urban local body elections without reservation for Other Backward Classes (OBCs) because the ‘triple test’ requirement for the quota had not been fulfilled, the state set up a commission for this purpose.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The five-member commission will conduct a survey to ensure that the OBCs are provided reservation on the basis of the triple test, as mandated by the Supreme Court.
- This is the first time that the triple test exercise will be carried out in Uttar Pradesh. Sources said the law department and the urban development department will lay down the guidelines to be adopted for the process.
a) To set up a dedicated commission to conduct a rigorous empirical inquiry into the nature and implications of the backwardness in local bodies;
b) To specify the proportion of reservation required in local bodies in light of recommendations of the commission, so as not to fall foul of overbreadth;
c) To ensure reservation for SCs/STs/OBCs taken together does not exceed an aggregate of 50 per cent of the total seats.
d) These triple test/conditions were outlined by the Supreme Court in the case of Vikas KishanraoGawali vs. State of Maharashtra and others, decided on March 4, 2021.
Why triple test instead of rapid survey?
The Lucknow Bench of the Allahabad High Court on said that any inquiry or study into the nature and implications of the backwardness with respect to local bodies involves ascertainment of representation in such bodies. The court said such an exercise cannot be confined to counting of heads alone, as is being done through the rapid survey.
SOCIAL ISSUES AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
3. PROPOSAL TO SHIFT FROM “MINIMUM” TO “LIVING” WAGES
TAGS:GS-II & III- SOCIAL ISSUES-ECONOMY
THE CONTEXT: The Union Labour Ministry is currently mulling to shift from the “minimum wages” to “living wages” in a bid to bring more people from poverty in the country.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is a living wage?
- The term “living wage” is the theoretical income level that enables an individual or a family to afford adequate shelter, food, healthcare and other basic necessities. It is the minimum income of that helps support a satisfactory standard of living and prevents individuals from falling into poverty.
How is the living wage different from minimum wage?
- A living wage is defined as the minimum income necessary for workers to meet their basic necessities. It is different from the minimum wage, which is based on labor productivity and skill sets.
- Minimum wage is the lowest amount of money a laborer can earn as mandated by the law. It does not change based on inflation. It can increase only with the government intervention. This is not true for the living wage.
- The living wage is determined by the average cost to live comfortably, while the minimum wage is the fixed amount set by the government.
- The difference between the minimum wage and the living wage can range between 10 and 25 percent based on the cost of living in a specific place.
About India’s decision
- The Indian government is considering to shift from the minimum wage to the living wage to eliminate poverty in the country. If such a shift happens, it would have significant financial implications for India and the government. It will make Sustainable Development Goal commitments easily achievable.
- India is planning to receive assistance from the International Labour Organization (ILO) to understand what constitutes a living wage since it is highly subjective. The ILO member states, including India, have recently requested the ILO to contribute to the improved understanding of living wages by undertaking a peer-reviewed research on the theoretical concepts and theoretical estimations.
Connect the Dots: ILO
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
4. OMEGA CENTAURI
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE- GS-III-SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Astronomers and scientists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), while studying the Omega Centauri found that hot stars and white dwarfs emitted less ultraviolet radiation than expected.
THE EXPLANATION:
- A team of Scientists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics detected strange hot stars in the Globular clusters using the Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (UVIT) images on AstroSat (India’s first dedicated space observatory, which has been operating since 2015).
What are Globular clusters?
- Globular clusters are spherical aggregates of several thousand to millions of stars bound by gravity. These systems are thought to have formed early on in the Universe and can serve as perfect astrophysical laboratories for astronomers to understand how stars evolve through various phases.
- Omega Centauri is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677.
- Located at a distance of 17,090 light-years, it is the largest-known globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150 light-years.
What is Galaxy?
- A galaxy is a huge collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems bound together by gravity.
- Milky Way, is stuffed with between 100 billion and 400 billion other stars, many of them with planets of their own. The Milky Way got its name from the way it looks from the ground: like a streak of spilt milk across the sky.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. GARRARNAWUN BUSH TOMATO
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: A new species of bush tomato, christened Garrarnawun bush tomato (Solanum scalarium), was discovered in Australia recently.
THE EXPLANATION:
About the genus Solanum
- Genus Solanum has around 1,400 accepted species that are distributed across the world. The species belonging to this genus are found in all continents except Antarctica. It is the most species-rich genus in the Solanaceae family and is among the largest in the angiosperms (flowering plants).
- The genus includes 3 food crops having high economic value. These are the potato, tomato and eggplant (brinjal).
- Much of the species belonging to the Solanum are concentrated in circum-Amazonian tropical South America. However, its hotspots are also found in Africa and Australia.
- This genus is often recognized by its two-chambered superior ovary, fused sepals and petals, 5 stamens, poricidal anthers, and sometimes branched hairs and/or prickles.
About the new species
- The Garrarnawun bush tomato (Solanum scalarium) is currently found only in one site in world i.e., the Judbarra/Gregory National Park in the Australia’s Northern Territory.
- It is a perennial pale green shrub that is around 30 cm tall.
- This species belongs to the taxonomically challenging group called Kimberley dioecious clade in Australia. It is distinguished from other members of this group by its spreading decumbent habit and conspicuously prickly male floral rachis.
- Its common name recognizes the lookout point in the Judbarra/Gregory National Park. This point is the traditional meeting place of the Wardaman and Nungali-Ngaliwurru peoples, whose lands intersect in this region.
- This species is currently known from a single population of around 50 to 100 individuals. Hence, scientists are proposing to include in the “data deficit” category of the IUCN Red List.
- It is found on skeletal pink soil, dissected rocks and exposed sandstone pavements.
- It is expected to be found in more locations due to the prevalence of a similar and less accessible outcrops in the immediate region.




