INDIAN POLITY
1. EXPLAINED: THE AMENDMENTS TO THE IT RULES, 2021
THE CONTEXT: Recently the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) has notified amendments to the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 (IT Rules, 2021) .In June 2022, MeitY had put out a draft of the amendments and solicited feedback from the relevant stakeholders.
THE EXPLANATION:
What are the key features of the IT Rules, 2021?
Grievance Appellate Committees (GACs):
- The new rules pave the way for the establishment of one or more Grievance Appellate Committees (GACs) within 3 months.
- These committees will enable users of social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter to get recourse to settle complaints without depending on the judiciary.
- The committee will have three members. One of them will be a government officer and the other two will be independent representatives.
SMIs obligations:
- SMIs (social media intermediaries) are mandated to ensure that their users comply with the relevant rules of the social platform. Earlier, the rules only mandated SMIs to inform their users of the “rules and regulation, privacy policy and user agreement”.
- The SMIs are required to make “reasonable” efforts to prevent prohibited content from being hosted in their platforms. They will be responsible for policing and moderating the content on their platform. This rule has been met with scepticism due to the subjectivity of the content’s nature and magnitude of information.
- SMIs are required to remove information or communication links that belong to 6 prohibited categories of content within 72 hours after the complaint is raised. This will help stop the content from becoming viral and spreading across the world.
- The SMIs are required to take reasonable measures to increase accessibility to their services to make them more inclusive. This is to strengthen inclusivity of the SMI ecosystem, making it accessible to persons with disabilities and those with diverse linguistic backgrounds. The new IT rules require the platforms to make available the “rules and regulations, privacy policy and user agreement” in all languages listed in the 8th schedule of the Indian constitution.
What is the criticism of the rules?
High cost
- Rights provided under the Indian Constitution, which the SMIs are mandated to protect, are subject to wide range of interpretations.
- Thus, compliance cost for the SMIs is expected to increase significantly.
- It could also lead to regulatory uncertainties as well.
Uncertainties regarding GAC
- It is uncertain whether the user needs to approach GAC before accessing the court. This confusion arises since the press note mentions that the user is not prohibited from approaching the court directly against the order of the grievance officer. However, the final amendments of the IT rules do not have provisions related to it.
- Due to this uncertainty, if the user approached the GAC and courts parallelly, it could result in conflicting decisions. This will undermine the impartiality and merit of one institution or the other.
- GAC’s members are appointed by the Central Government. This creates apprehension of bias in content moderation.
- Furthermore, the IT rules, 2021 do not provide any explicit power to GAC to enforce its rulings.
What is IT Rules, 2021?
Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 or IT Rules, 2021 was notified by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY). It replaces decade-old rules regulating social media intermediaries (SMI) to make them more accountable towards providing open, safe and trusted internet.
ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
2. GEAC PLANNING TO RECOMMEND ‘ENVIRONMENTAL RELEASE’ OF BAYER’S GM COTTON
THE CONTEXT: Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is currently planning to recommend environmental release of a genetically modified (GM) herbicide tolerant cotton of German multinational company Bayer AG.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is BG-II RRF?
- Bollgard II Roundup Ready Flex (BG-II RRF) is a transgenic cotton having three alien genes.
- Two of the alien genes – cry1Ac and cry2Ab – were isolated from a soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. These genes have proteins that are harmful for American bollworm, spotted bollworm and tobacco caterpillar insect pests.
- The third gene – cp4-epsps – was obtained from another soil bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Its inclusion makes the cotton crop “tolerant” to the harmful herbicide glyphosate, which does not distinguish between the crops and weeds.
- The BG-II RRF cotton was developed by the American company Monsanto, which was acquired by Bayer in 2018.
- It underwent biosafety research and field trials in 2012-13. The results of the trials were submitted to the GEAC in 2013. However, the American company withdrew the application seeking environmental clearance for the crop due to regulatory uncertainties and lack of government decisions.
- Bayer had resubmitted the permission for environmental clearance to GEAC early this year.
What are genetically modified crops?
- Genetically modified crops are crops that had their DNAs altered to include certain desirable traits. The widely used GM soyabean, maize, cotton and canola are tolerant to herbicides and resistant to pest attacks.
- Other common traits included in genetically modified crops are resistance to virus, resistance to drought and improved fruit and tuber quality.
How are genetically modified crops regulated in India?
- Genetically modified crops pose threat to animal health, humans and biodiversity during the process of development, cultivation and transboundary movement.
- Hence, their production, cultivation and movement are highly regulated. Rules and Acts that ensure their regulation are Environmental Protection Act, 1986, Biological Diversity Act, 2002, Plant Quarantine Order, 2003, GM Policy under Foreign Trade Policy, Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 and Drugs and Cosmetics Rule (8th Amendment), 1988.
3. UTTAR PRADESH’S RANIPUR TIGER RESERVE BECOMES 53RD TIGER RESERVE INDIA
THE CONTEXT: Uttar Pradesh is set to have its fourth Tiger Reserve and 53rd tiger reserve in India. The tiger reserve is spread across over 529.36 sq km out of which the core area is 230.32 sq km and the buffer area is 299.05 sq km.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Apart from Ranipur, Uttar Pradesh has three tiger reserves, Dudhwa, Pilibhit, and Amangarh.
- Uttar Pradesh government approved the development of the first tiger reserve in the Bundelkhand region of the state on 28th September 2022.
- The UP government also approved the notification of the Ranipur Wildlife Protection Act 1973.
- UP Chief Minister has also decided to establish the Ranipur Tiger Conservation Foundation along with sanctioning of requisite posts.
- Ranipur Tiger Reserve is covered by northern tropical dry deciduous forests and is home to mammals like megafauna tiger, leopard, bear, spotted deer, sambhar, and chinkara among others.
- According to the state government, the establishment of the Tiger Reserve in Ranipur will lead to the opening up of eco-tourism in the area and create immense employment opportunities.
VALUE ADDITION:
Project Tiger
- Project Tiger is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched in 1973 to provide central assistance to the tiger States for tiger conservation in designated tiger reserves in India. The project is administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
National Tiger Conservation Authority
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
- It was established in 2005 following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It was constituted under enabling provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006, for strengthening tiger conservation, as per powers and functions assigned to it.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
4. RBI LAUNCHES FIRST PILOT FOR DIGITAL RUPEE
THE CONTEXT: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said the first pilot of the Central Bank Digital Currency — Digital Rupee (Wholesale segment) will be launched from 1st November 2022 for transactions in government securities.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to RBI, the use case for the pilot is settlement of secondary market transactions in government securities.
- Nine banks — State Bank of India (SBI), Bank of Baroda, Union Bank of India, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, Yes Bank, IDFC First Bank and HSBC — have been identified for participation in the pilot.
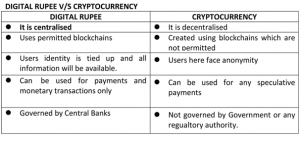
What is Digital Rupee?
- A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) or Digital Rupee is a digital form of currency notes issued by a central bank. Digital currency or rupee is an electronic form of money, that can be used in contactless transactions.
- Presenting Union Budget 2022, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) would be rolling out its digital currency soon.
CBDC can be classified into two types
1. Retail (CBDC-R): Retail CBDC would be potentially available for use by all
2. Wholesale (CBDC-W) is designed for restricted access to select financial institutions.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5. TIANGONG SPACE STATION’S FINAL MODULE LAUNCHED
THE CONTEXT: China successfully launched the final module of its Tiangong space station inching closer to its completion by the end of the year and a landmark moment in the country’s space ambitions.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is “Mengtian” module?
- “Mengtian” module was launched aboard a Long March-5B Y4 carrier rocket from Wenchang launch centre in China.
- It is the third and final module Tiangong space station and it is an important component of the Chinese space station, equipped with numerous cutting-edge scientific equipment.
- The module is expected to be operational for 10 years or more. The name “Mengtian” means “dreaming of the heavens”. It is the second of the two modules that will host science labs required for conducting research.
- This module, once docked on the core module Tianhe, will complete the T-shaped structure of the space station along with the other module Wentian, which was launched in July 2022.
- Mengtian will have workstations supporting experiments related to microgravity scientific studies and frontier scientific projects focusing on fluid physics, combustion and materials science and space technologies.
About Tiangong space station
- The Tiangong space station is currently being constructed by China and operated by the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) in the low Earth Orbit between 340 and 450 km above the surface.
- The mass of this space station is around one-fifth of the mass of the International Space Station. Its size is almost equivalent to the decommissioned Russian Mir Space Station. It has a core module named Tianhe (Harmony of the Heavens) and two laboratory cabin modules Wentian (Quest for the Heavens) and Mengtian.
- China was banned from the International Space Station since the year 2011 after the US refused to let NASA to work with China. Since then, Beijing has been heavily investing in its space programmes to compete with the US and Russia. It had even landed a rover to Mars and sent lunar probes during its early space missions.
6. DEMAND GROWS, BUT DNA TESTS FALL UNDER A GREY AREA
THE CONTEXT: Recently the Supreme Court has voiced concerns over the increasing use of DNA to prove cases.
THE EXPLANATION:
Current Challenges:
- More and more complainants are seeking DNA tests – such requests are increasing by around 20% each year.
- DNA Forensics Laboratory Private Limited says it tests around 300-400 samples each month that are both private requests and court-mandated.
- The numbers were only around 30-40 till five years ago.
- DNA Forensics Laboratory Private Limited is one of the biggest centres which is accredited with the National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL).
Justice vs privacy: The Supreme Court has recently held that compelling an unwilling person to undergo a DNA test would be a violation of his/her personal liberty and right to privacy.
The court is turning the spotlight on the spreading use of a technology that aids the cause of justice on the one hand but violates privacy on the other.
Global scenario: While the 3,000-odd DNA tests Indian labs perform annually is minuscule compared to the 70 other countries that rely on DNA technology.
VALUE ADDITION:
About DNA Testing:
- DNA is a very powerful tool for investigation because no two people can have the same DNA except in the case of identical twins.
- DNA/Genetic tests are performed on a sample of blood, hair, skin, amniotic fluid (the fluid that surrounds a fetus during pregnancy), or other tissue.
Where is it used?
Crime scenes:
- DNA tests are used in the criminal investigation by the police where they find the suspect by matching the DNA samples of the crime scene with the suspected person’s DNA.
Finding inheritance:
- DNA test is the only tool that can deliver justice in cases of abandonment of mothers and children.
- It is also a very powerful tool in civil cases where the court has to decide the matter relating to the maintenance and find the parents of the child.
Legislation on DNA testing:
- There is no legislation present in India which can provide specific guidelines to the investigating agencies or the court for dealing with DNA testing.
- Section 53 of the Code of Criminal Procedure,1973
- This section authorized a police officer for getting the assistance of a medical practitioner in good faith for the purpose of the investigation
- The section does not enable to collect blood semen etc. for bringing the charges against a person.
Courts’ stands:
Courts are also reluctant to use the DNA test technique because there are serious questions raised regarding the right of privacy which comes under Article 21 of the Constitution and the right against self-incrimination which comes under Article 20(3) of the Constitution.
VALUE ADDITION:
Autosomal DNA technique :
- It is a term used in genetic genealogy to describe DNA that is inherited from the autosomal chromosomes.
- An autosome is any of the numbered chromosomes, as opposed to the sex chromosomes.
- The autosomal DNA technique can be used even when very limited genetic data are available.
- Autosomal DNA tests can be used to confirm relationships with a high level of accuracy for parent/child relationships and all relationships up to the second cousin level.
o For all relationships additional contextual and genealogical information is required to confirm the nature of the relationship.




