THE GEOGRAPHY: CLIMATOLOGY
1. IDMC-ADB REPORT: SOUTHWEST MONSOON LASTING LONGER, DISPLACING MILLIONS IN SOUTH ASIA
THE CONTEXT: The recently released joint report of the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) raised concerns regarding long southwest monsoon causing large-scale displacement of masses in South Asia.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The report found that southwest monsoon is lasting longer than its season and overlapping with the northeast monsoon, causing more severe downpour, flooding and storms in South Asia.
• While the southwest monsoon reached the peninsular India on time, it had stayed beyond seasonal boundary of September.
• In 2021, it had lasted until October, overlapping with the northeast monsoon
• This report assessed the forced movement within a country boundary and displacement due to natural disasters during the period of 2010-21.
• It found that disasters displaced about 61.4 million people in south Asia during this period. of this, 58.6 million were displaced because of weather-related disasters.
• Floods and storms caused about 90 per cent of the total displacement.
• Floods caused the displacement of 37.4 million and storm, including major tropical cyclones, caused 21 million internal displacements.
• El Nino Southern Oscillation variation has played a major role in the increased instances of flooding and storms.
• Climate change is also causing prolonged and unpredictable monsoon seasons.
• In the overall Asia-Pacific region, about 225 million individuals were displaced during the 2010-2021 period.
• This means that nearly 19 million people were displaced because of disaster each year.
• This is more than 75 per cent of the total global figure on displacement.
• 95 per cent of all disaster displacements in Asia Pacific are caused by monsoon rains, floods and storms.
• The disaster displacement risks are mainly worsened by rapid urbanization, socioeconomic vulnerability and population growth in hazard-prone areas.
About IDMC
Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) is an international non-governmental organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It was established in 1998 by the Norwegian Refugee Council – a humanitarian NGO that works towards protecting rights of people who are displaced.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. 77th SESSION OF THE UNITED NATIONS GENERAL ASSEMBLY
THE CONTEXT: The 77th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA77) opened on September 13 and will include a high-level debate organized from September 20 to 26 this year.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The theme of the UNGA 77 is “A watershed moment: transformative solutions to interlocking challenges”.
• The theme recognizes the shared roots of global crisis like COVID-19, climate change and conflict and highlights the importance of building global sustainability and resilience.
• The event is being organized at the UN Headquarters in New York.
• Discussions will be held among the world leaders on crisis in Ukraine, climate change, food security, access to education and gender equality.
• All 193 UN members will be represented at this event.
• Brazil will be the first UN member state to speak at the annual general debate. It has remained the first speaker for nearly 7 decades since the 10th UNGA in 1955.
• The US, which will host the event, will be the second member state to speak.
• After the first two speeches, the speaking order is set based on the factors like level of representation, the rank of the representatives, preferences and geographical balance.
About UNGA
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) is the United Nations’ main policy-making and representative organ. It was set up in 1945. It meets every year between September and December and again between January and August. Each of the 193 UN member states has an equal vote at the General Assembly, where important decisions of the United Nations take place, like appointment of the UN Secretary General, approval of the UN Budget and electing non-permanent members to the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). It also adopts resolutions to make recommendations. However, these resolutions are not enforceable.
3. INDIA’S PRESIDENCY OF AIBD EXTENDED FOR ONE YEAR
THE CONTEXT: The Asia-pacific Institute of Broadcasting Development (AIBD) has unanimously extended India’s presidency for one more year.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The member countries of the AIBD have decided to extend India’s presidency at the two-day General Conference of the Institute that was held in New Delhi.
• The General Conference of the AIBD was inaugurated by the Union Minister of Information and Broadcasting, Youth Affairs and Sports.
• It was organized from September 19 to 20 this year.
• The conference focused on theme “Building a Stronger Future of Broadcasting in post pandemic era”.
• During the event, all participating countries and member broadcasters have committed to work together for creating sustainable broadcasting environment, promoting latest technology know-how, quality content creation and various cooperative activities.
• A five-year plan for cooperative activities and exchanges programmes were finalized during the conference.
About AIBD
• The Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development (AIBD) was set up in 1977 with the support from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It is a regional intergovernmental organization that brings together countries of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UN-ESCAP) to collaborate in the field of electronic media development.
• Its objective is to achieve a vibrant and cohesive electronic media environment in the Asia Pacific region through policy formulation and resource development. It currently has 26 countries that are full members. These countries are represented by 43 organizations and 52 affiliate members.
VALUE ADDITION:
UN-ESCAP
The UN-ESCAP is one of the five regional commissions of the UN Economic and Social Council. It was established in 1947 to boost economic relationship between countries in Asia and the Far East as well as other regions across the globe. It currently has 53 member states and 9 associate members, mostly from Asia and Pacific. It also includes countries such as France, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
4. RBI ASKS LARGE UCBS TO SET UP BOARD-APPROVED POLICY, COMPLIANCE FUNCTION
THE CONTEXT: The RBI has directed urban cooperative banks (UCBs) belonging to tier 3 and tier 4 categories to create a Board-approved policy and compliance function.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The central bank has asked the urban cooperative banks with more than Rs.10,000 crore deposits (tier 4 category) to create a board-approved compliance policy and a compliance function, including the appointment of a Chief Compliance Officer (CCO), by April 1, 2023.
• Tier 3 UCBs i.e., those having more than Rs.1,000 crore and up to Rs.10,000 crore deposits are given the deadline of October 1,2023.
• The board approved Compliance Policy should give clear outline on the implementation of compliance philosophy, expectations on compliance culture, structure and role of the Compliance Function, the role of the CCO and the processes for the identification, assessment, monitoring, management and reporting on the compliance risk.
• The framework requires the Senior Management of these UCBs to undertake Compliance Risk Assessment every year.
• It also mandates the setting up of the Compliance Function, which shall ensure strict observance of all statutory and regulatory requirements for the UCBs, including standards of conduct, management of conflict of interest, fair treatment of customers and providing suitable customer service.
• While the organizational structure of the Compliance Function can be chosen by the UCBs, it should be independent and well-resourced. Its operations must be regularly reviewed by an independent entity.
Who is CCO?
The Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) would head the Compliance Department. The tenure of the CCO should last for at least 3 years. He/she will directly report to the MD and CEO and/or Board or Board Committee. The CCO will have the authority to communicate with any staff member and access all records or files required to undertake the entrusted responsibilities with regards to compliance risks.
THE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
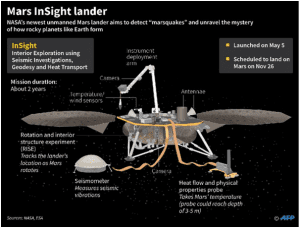
5. INSIGHT LANDER DETECTS SPACE ROCKS HITTING MARS
THE CONTEXT: NASA’s InSight lander has detected seismic and acoustic waves caused by the impact of four meteoroids and found the location of the craters left by these space rocks.
THE EXPLANATION:
• For the first time, scientists were able to calculate the locations of craters left by meteoroids on the Martian surface based on seismic and acoustic waves.
• The researchers confirmed the calculations made by InSight Lander using the NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
• The recent seismic measurements provide a new tool for the better investigation of the Mars and other planets where seismometer can be landed.
• One of the space rocks detected by the InSight Lander hit the Martian surface in 2020 and the rest landed in 2021. They have left craters of up to 7.2 meters wide.
• They landed between 85 km and 290 km from the InSight’s location.
• Mars is close to the solar system’s asteroid belt, which makes it highly vulnerable to impacts by space rocks.
• Its atmosphere is just 1 percent as thick as Earth’s. Hence, meteoroids pass through it without disintegrating unlike when they pass through the Earth’s atmosphere.
• However, this is the first time that InSight captured the sound of the space rock hitting the Red Planet.
• According to researchers, the past impacts may have been undetected because of the noise from wind or by seasonal changes in the atmosphere.
• It is possible that more such seismic and acoustic waves may be hidden within the lander’s nearly four years of data.
About InSight Mission
The Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission is a robotic lander that aims to study the deep interior of the Red Planet. This three-legged instrument landed on the Martian surface in 2018 on a vast and relatively plain surface north of the Martian equator called Elysium Planitia.
6. NASA’S PERSEVERANCE FINDS ORGANIC MATTER ON MARS
THE CONTEXT: The Perseverance Rover has collected samples having high concentration of organic matter from the Martian surface.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The Perseverance Rover has collected several organic rock samples from an ancient river delta on Mars.
• These samples are currently stored for collection by future Mars missions that would return them back to the Earth.
• These rock samples have large concentration of organic matter, the highest concentration since the start of the mission.
• With the latest collection, the rover has now collected a total of 12 samples.
• One of the rocks the Perseverance collected was nicknamed as Wildcat Ridge. This rock was likely formed when mud and sand settled in a saltwater lake as it evaporated billions of years ago.
• An instrument aboard the rover called SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) found that these samples contain a class of organic molecules that correlate with those of sulfate minerals.
• Sulfate minerals found in layers of sedimentary rock can provide insights into the watery environment on which the rock samples were discovered.
• The instrument’s analysis revealed that the organic materials may possibly be aromatics or stable molecules of carbon and hydrogen, which are connected to sulfates.
• This suggests that when the lake was evaporating, both sulfates and organic molecules deposited, preserved and concentrated in the region.
About Perseverance Rover
Perseverance Rover was launched as part of the NASA’s Mars Exploration Program. Its objective is to explore the Martian surface and detect the signs of past and present life on the planet. Its landing site is Jezero Crater.
VALUE ADDITION:
Jezero Crater
Jezero Crater spans across 45 km. it is a fan-shaped geological feature that is suspected to have hosted an ancient lake. It is believed that this site hosts evidences of Martian history in sedimentary rock, which formed when particles fused together in the previously water-filled environment.




