THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. KARNATAKA RIGHT TO FREEDOM OF RELIGION BILL
THE CONTEXT: The ‘Karnataka Protection of Right to Freedom of Religion Bill’ was recently passed by the state legislative council.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Karnataka’s anti-conversion bill was passed by the legislative assembly in December 2021.
- The bill bans forced religious conversions by direct or indirect means.
- It gives specific procedures for undertaking a religious conversion.
- This bill gives penalty to anyone who forcibly convert minor, woman, SC/ST, or a person of unsound mind with 3 to 10 years imprisonment and a fine of Rs.50,000.
- Mass conversion (two or more people) could result in 3 to 10 years of imprisonment and Rs.1 lakh fine.
- Under this legislation, any individual seeking to convert their religion must submit a declaration at least 30 days before the conversion to the District Magistrate.
- The religious convertor is also required to submit a form to the DM at least 30 days before the intended conversion.
- After these submissions, the DM would notify the proposed religious conversion on the notice board of the offices of DM and Tehsildar.
- Within 30 days of the public notice, anyone can file an objection to the conversion.
- If any such objection occurs, the DM is required to conduct an inquiry to investigate the intension, purpose and cause of the proposed conversion.
- Any conversion that occurs while not following the procedure will be considered illegal and void.
Anti-conversion bills
Besides Karnataka, other states have also passed similar legislations. Their purpose is to ban unlawful religious conversions, protect those who are forced to convert from one religion to another through misinterpretation, force, undue influence, coercion, allurement, promise of marriage or any other fraudulent means. Other states that introduced anti-conversion bills are Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jharkhand.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT: HUNGARY NO LONGER A FULL DEMOCRACY
THE CONTEXT: The European Parliament has adopted a report that declared Hungary to be no longer a democracy.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The European Parliament has recently adopted a parliamentary report that declared Hungary to be “a hybrid regime of electoral autocracy”.
- It concluded that the European values are currently under threat in Hungary and thus, it is no longer a
 democratic country.
democratic country. - The recent motion at the European Parliament is symbolic disapproval from the EU towards Hungary, that has witnessed years of opprobrium over the rule-of-law issues under the regime of the current populist Prime Minister Viktor Orban.
- However, this adoption may not lead to any specific punishment targeting Hungary.
- The recently adopted report listed a range of concerns about the country’s electoral system, judicial independence, academic and religious freedom and the overall rights of the vulnerable population.
- In 2018, the European Parliament had launched a procedure against the risk posed by Hungary to EU’s democratic values.
- In theory, this mechanism could result in Hungary losing its right to vote in the EU Council, where the critical decision-making takes place for the European bloc.
- However, it requires action from rest of the 26 EU members, who have shown little interest in antagonizing Hungary.
- The EU countries are wary of such a move since Hungary’s approval is critical for major decisions.
- Hungary is currently having close ties with Russia and it is involved in blocking further European sanctions on Moscow for its involvement in Ukraine crisis.
- The European parliament’s recognition of Hungary as electoral autocracy comes based reports from bodies belonging to the Council of Europe as well as case law from the EU’s court of justice and others.
- The verdict by the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) was also cited for this conclusion.
- In April 2022, the OSCE held that Hungary’s election that returned Orban to power for the fourth consecutive term was tainted by the lack of level playing field.
- It had sent a full-fledged mission to Hungary, an almost unprecedented step for an EU member state.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
3. INTERNATIONAL TREATY ON PLANT GENETIC RESOURCES FOR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: India to host 9th Session of Governing Body of the ITPGRFA in New Delhi.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The organization of 9th session of International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA) will provide a common platform for all the participating countries to deliberate upon the pivotal issues related to the development, conservation and protection of Plant Genetic Resources for the benefit of farming community.
- The scientific exchange of technological advancement among the countries will help mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change and food security globally.
- The plant genetic resources available with different countries will act as base material for development of new varieties to ensure better quality and higher productivity of crops.
- The GB9 is being held under the theme “Celebrating the Guardians of Crop Diversity: Towards an Inclusive Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework”.
- The theme aims to acknowledge the contribution of the world’s small-holder farmers to the effective management of PGRFA.
About ITPGRFA:
- ITPGRFA is a legally binding comprehensive agreement adopted in November, 2001 at Rome during the 31st session of Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- It entered into force on June 29, 2004 and currently has 149 Contracting Parties, including India.
- The treaty provides solutions to achieve food and nutritional security as well as climate resilient agriculture.
- Countries are inter-dependent for PGRFA and consequently a global order is essential to facilitate access and benefit sharing.
Relevance for India:
- India is endowed with rich crop genetic resources.
- It has successfully established legal, institutional and scholastic infrastructure to utilize the genetic diversity for breeding new varieties.
- With this unique status and as GB9 host, India is expected to play a crucial role in minimizing the dissonance between technology-rich developed and gene-rich developing countries to achieve functional resolutions on critical agenda items.
- The GB9 provides an excellent opportunity to convey the steadfast commitment of India to conservation and sustainable utilization of plant genetic diversity as well as farmers’ rights.
4. THE ANGAN 2022
THE CONTEXT: Recently a three-day international conference ANGAN 2022 is organized by Indo-Swiss Building Energy Efficiency Project (BEEP).
THE EXPLANATION:
- ANGAN 2022 (Augmenting Nature by Green Affordable New-habitat) is an international conference organized by Indo-Swiss Building Energy Efficiency Project (BEEP).
- It is organized based on the theme “Making the Zero-Carbon Transition in Buildings”.
- It is the second edition of the Augmenting Nature by Green Affordable New-habitat.
- Around 75 eminent speakers, representing more than 15 countries and international organizations, have come together to discuss ways to reduce carbon emission and improve energy efficiency in buildings.
- More than 500 delegates consisting of architects, engineers, builders, building material industries, teachers, students, researchers, central and state government officials are participating in this conference.
- Discussions were held on critical issues such as “Unlocking Finance for Low-Carbon Buildings and “Thermal Comfort and Climate Resilience in Residential buildings”.
- It had special session on “Women in the Resource Efficiency Conversation”.
- The purpose of this conference is to promote a healthy ecosystem as mentioned at the COP26 by Prime Minister on LiFE (Lifestyle And Environment) and Panchamrit, which aims to make India Net Zero by 2070.
- The conference promoted various low carbon products, technologies and innovations that can be used in the building sector.
- This conference-cum-exhibition event is expected to boost international and national strategic collaboration, partnership, network and information exchange for the creation of low carbon, energy efficient habitat.
BEEP
Indo-Swiss Building Energy Efficiency Project (BEEP) is a collaborative project between the Indian Government and the Swiss Government. The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), which comes under the Indian Government’s Ministry of Power, is providing the technical support for this project. It had helped formulate Eco-Niwas Samhita (energy conservation building code for residential buildings), designed around 50 buildings and trained more than 5,000 building sector professionals.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES/INITIATIVES IN NEWS
5. E-BAAL NIDAN PORTAL REVAMPED
THE CONTEXT: The NCPCR has revamped the E-Baal Nidan portal to include more features that would ease the tasks of complainants as well as NCPCR and SCPCRs in dealing with the complaints.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is E-Baal Nidan Portal?
- “E-Baal Nidan” is an online complaint mechanism launched in 2015 to enable individuals to report violations committed against a child and track the progress of the redressal of the complaint in the Commission.
- The portal eases the process of making a complaint to the NCPCR and ensures transparency in the redressal process.
- It ensures a timely disposal of cases by the NCPCR.
- Currently, the NCPCR is providing access to all State Commission for Protection of Child Rights.
- It will be providing user IDs and passwords for the State Commissions to enable them to view complaints registered on the portal and take necessary steps as mandated by the law.
- The portal also provides an option to transfer the registered complaints from the NCPCR to the concerned State Commission.
- It also gives option of joint inquiry if the State Commission wants the NCPCR to be involved.
- The portal segregates complaints based their subject matters like juvenile justice, PSCSO, child labour, education etc.
NCPCR
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) is a statutory body of the Indian Government set up under Section 3 of the Commission for the Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005. Its purpose is to protect the child rights and other related matters in India. It is also involved in the monitoring of the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012; Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 and Right to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009. It is also involved in examining and reviewing the safeguards provided by and under any law for the protection of child rights and recommend ways to improve their implementation.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
6. WORLD’S LARGEST MUSEUM OF HARAPPAN CULTURE IN RAKHIGARHI
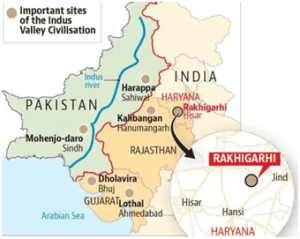
THE CONTEXT: The world’s largest museum on Harappan culture is currently being set up in Rakhigarhi, Haryana.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The museum on Harappan culture in Rakhigarhi would showcase some 5,000-year-old artefacts belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization.
- This world class museum would display photographs depicting Rakhigarhi’s history.
- The museum, which is currently under construction, would give recognition to Rakhigarhi at the international and national levels and increase job opportunities for the local communities.
- A special zone is being created in the museum for children to make them aware of the history in a recreational manner.
- The museum would also house an open-air theatre and a library.
About Rakhigarhi
- The village of Rakhigarhi was part of the Indus Valley Civilization from 2600 to 1900 BC. The two villages
 Rakhi Khas and Rakhi Shahpur currently host the archeological remains of the Indus Valley site. It was excavated for the first time in 1969. It is currently the largest settlement of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Rakhi Khas and Rakhi Shahpur currently host the archeological remains of the Indus Valley site. It was excavated for the first time in 1969. It is currently the largest settlement of the Indus Valley Civilization. - Since 1998, 56 skeletons have been discovered in the site. Among them, two women were found in mound number 7. They are estimated to be 7,000 years old.
- The presence of shell bangles in the site provides evidence of trade links to faraway places such as Afghanistan, Baluchistan, Gujarat and Rajasthan. Jewelry trade is among the most prominent in this site. People in this civilization are known to melt precious metals like copper, carnelian, agate and gold to make garlands of beads.
Development of 5 Iconic Sites
During the Union Budget 2020, the Central Government announced the development of five iconic sites – Rakhigarhi (Haryana), Hastinapur (Uttar Pradesh), Shiva sagar (Assam), Dholavira (Gujarat) and Adichanallur (Tamil Nadu). Museums will be developed in these sites with a total outlay of Rs.2,500 crore.
Spread the Word
 Rakhi Khas and Rakhi Shahpur currently host the archeological remains of the Indus Valley site. It was excavated for the first time in 1969. It is currently the largest settlement of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Rakhi Khas and Rakhi Shahpur currently host the archeological remains of the Indus Valley site. It was excavated for the first time in 1969. It is currently the largest settlement of the Indus Valley Civilization.


