THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Government Accounting Standards advisory board (GASAB) has come up with a Natural Resource Accounting (NRA) for tracking and maintaining the natural resources of India. It would also suggest recommendations for end-to-end mapping of supply and use of resources which would help the states in mopping up due revenues from the resources. In the following article attempts to explain the concept of Natural Resource Accounting (NRA) and its utility in present times.
NATURAL RESOURCE ACCOUNTING: KEY TENETS
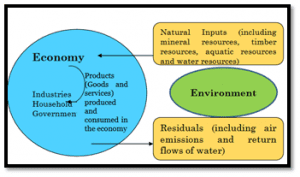
National Resource Accounting (NRA): Natural resource accounting is an accounting system that deals with stocks and stock changes of natural assets, comprising biota (produced or wild), subsoil assets (proved reserves), water and land with their aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. The concept of National Resource Accounting (NRA) has emerged to capture the intimate interplay between the various components of the natural environment and the economic progress of a country. It is based on the concept ‘measurement of a resource leads to its better management.
- The need: Mankind in its quest for rapid economic development has manipulated nature to serve its economic interests and, in the process, harmed nature. This has resulted in environmental degradation, leading to climate change, extreme weather conditions and frequent natural disasters. The importance of judicious use of resources, their controlled usage and sustainability for future generations led to the idea of Sustainable Development (SD).
- Inherent in Sustainable Development: Accounting of Natural Resources is one of the most crucial
 elements of SD is that it provides an outline of resource bases, and pace of usage with an eye on their sustainability and embeds environmental aspects into the economic indices.
elements of SD is that it provides an outline of resource bases, and pace of usage with an eye on their sustainability and embeds environmental aspects into the economic indices. - Measuring the downside of growth: The idea is to quantify the adverse impact of economic development on the environment and adjust/reduce it from GDP to arrive at Green GDP, essentially signifying the impact of economic development on the environment and sustainable growth.
- Quantifies the non-renewal damage to the environmental resources and assists in the determination of development in real terms.
- Aid to policy framing: A sound database of how a particular economy is utilizing the resources at hand is of significant help to policymakers to understand the potential impact of their decisions.
- Combating Climate Change: Asset and flow accounts have been recognized as a useful framework for monitoring, measuring and analyzing climate change.
- Interrelation between economy and environment: It helps to organise information on the status, use, and value of natural resources and environmental assets as well as expenditures on environmental protection and resource management. Natural resource accounting inter-alia refers to the interconnection and linkages in the economy and our environment or surrounding.
EVOLUTION OF NATURAL RESOURCE ACCOUNTING
- The need for NRA took its first step at the United Nations (UN) conference on Human Environment in 1970 when the relationship between economic development and environmental degradation was discussed for the first time.
- The Brundtland Commission, set up by the UN, articulated the idea of the close association between the environment and economic activities in 1987, which was followed up by environmental accounting and the Earth Summit at Rio de Janeiro in 1992.
- In line with these developments, the UN released the international standards for the compilation of national accounts in 1993 and revised it in 2009.
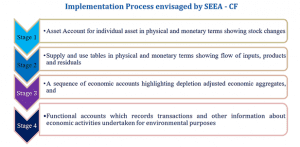
- Simultaneously, the UN also adopted the System of Economic and Environmental Accounting – Central Framework (SEEA – CF) in March 2012, which is the latest internationally accepted and adopted framework for resource accounting. The SEEA – CF prescribed a four-stage implementation process as mentioned below:
NATURAL RESOURCE ACCOUNTING IN INDIA

Working group on Environmental Auditing
(WGEA) (2010)
Formation of the Expert Group for framework related to Green National Accounts In India
To Assist the Government in developing the NRA
Identifying challenges in applying environmental accounting
Recommending strategies to overcoming challenges
Identifying best practices in NRA

Constitutional mandate under Article 150 to advice on forms of accounts
Section 23 of CAG’s DPC Act-Guidelines for general principles for Govt Accounting
Government Accounting Standards Advisory Board(GASAB)
• Mandated to formulate Government Accounting Standards and other pronouncements with a view to improve Governmental accounting and financial reporting
• To enhance the quality of decision- making and public accountability.
Comptroller and Auditor General of India (C&AG) constituted Government Accounting Standards Advisory Board (GASAB) with the support of the Government of India through a notification dated 12th August 2002. The decision to set up GASAB was taken in the backdrop of the new priorities emerging in Public Finance Management and to keep pace with international trends. The new priorities focus on good governance, fiscal prudence, efficiency & transparency in public spending.
The accounting systems, the world over, are being revisited with an emphasis on the transition from rule to principle-based standards and migration from cash to the accrual-based system of accounting. GASAB, as a nodal advisory body in India, is taking similar action to formulate and improve standards of government accounting and financial reporting and enhance accountability mechanisms. GASAB has suggested a well-laid-out implementation plan divided into three-term goals in consonance with the strategy envisaged by the SEEA – CF.
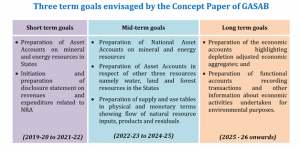
Out of seven resources listed by the SEEA framework, the Concept Paper has identified and suggested commencing with five major resources, namely Mineral & Non-Renewable Energy Resources, Water Resources, Forestry & Wildlife Resources and Land Resources, of which, Mineral & Non-Renewable Energy Resources has been considered mainly due to their finiteness and non-renewability and need for sustainability for future generations.
In way to progress further, the EnviStats (Environment Statistics) initiated in 2018 for the presentation of aggregate environment accounts for India with the asset accounts in physical terms of minerals, water, land and forest.
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has taken up several initiatives under the project Natural Capital Accounting and Valuation of the Ecosystem Services (CAVES) which aims to advance the theory and practice of ecosystem accounting in India
ASSESSMENT OF STATE-LEVEL IMPLEMENTATION
GOA
- Unable to compile major minerals physical flow account – mining ban
- Minor minerals stock position not ascertainable
- Break up of extraction not maintained
RAJASTHAN
- Variation between the revenue involvement and actual market value (roughly 10 times) clearly brought out
- Extensive coverage of minerals along with sub-minerals
MEGHALAYA
- Mapping of physical flows vis-à-vis revenue involved – a short collection of receipts ` 40 crores in one-year Sustainability of minerals in years brought out.
- Illegal extraction was detected, 4,284 MT of coal and more than 1 lakh tones of limestone illegally extracted.
- Recommendations made to State Government based on the study:
o Mines Department to reconcile figures with Land Customs Station to plug leakages.
o More close coordination is needed between the Mines & Geology Department and E&F Department to exchange data on the extraction of minerals from their respective jurisdiction.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- NRA has deep inter-linkage to sustainable development; and 10 of the 17 goals (Sustainable Development Goals or commonly known as the SDGs, 2030) are directly or indirectly related to the management of natural resources and their accounting. The government of India is a signatory to the UN General Assembly resolution on the adoption of SDGs titled, “transforming our world; the 2030 agenda for sustainable development”. Thus, it becomes an obligation for GOI to develop fine standards of resource accounting.
- NRA intends to capture the intimate interplay between various components of the natural environment and the economy. Also, it can connect to other datasets to provide invaluable information on the larger picture connecting the environment with the economy. Thus, even from an economic point of view, NRA is important for India.
- Further, NRA helps to quantify the adverse impact on the environment due to economic development and aid sustainable growth. This makes NRA more relevant in present times.
THE CONCLUSION: For a world that is riding on unprecedented development, it is imperative that we keep our historic relation of ours with nature in harmony. Accounting for natural resources will definitely aid both economical and ethical perspectives of life on earth. For example, accounting for forest wealth has a number of useful policy benefits, including the provision of a framework for analyzing and presenting detailed and diverse data in a manner which supports economically informed policy choices.
QUESTIONS TO PONDER
- What do you understand by Natural Resource Accounting (NRA)? Enumerate the basic tenets of NRA.
- Discuss the evolution and need of Natural Resource Accounting (NRA) in the Indian context.
Spread the Word




